Sesame Oil
Synonym(s):Sesami oleum
- CAS NO.:8008-74-0
- Molecular Weight: 0
- MDL number: MFCD00132243
- EINECS: 232-370-6
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 14:08:57
What is Sesame Oil?
Chemical properties
clear yellow viscous liquid
Chemical properties
Refined sesame oil is a clear, pale-yellow colored liquid with a slight, pleasant odor and a bland taste. It solidifies to a soft mass at about -4℃.
Chemical properties
S. indicum is a genus of tropical African and Indian herbs. It is a rough, hairy, gummy, annual plant, about 70 to 80 cm high, having petiolate, ovate-lanceolate leaves, slightly toothed and mucilaginous. The pale or rose-colored flowers are solitary in the axils. The plant is cultivated for its black or white seeds. The seeds are tiny, oval shaped, sweet and oleaginous. Sesame seeds have a rich, nut-like flavor when roasted. Sesame oil is second only to coconut oil for culinary purposes, food and medicine; it is also used as a substitute for olive oil. The part used is the seed (oil).
The Uses of Sesame Oil
sesame oil is a commonly used carrier oil for cosmetic products, it has the same emollient properties as other nut and vegetable oils. Sesame oil is useful in suntan lotions as it blocks 30 percent of the sun’s burning uV rays. It is derived from sesame seeds.
The Uses of Sesame Oil
Pharmaceutic aid (solvent); pharmaceutic aid (vehicle, oleaginous).
The Uses of Sesame Oil
Sesame Oil is the oil obtained from sesame seeds. it consists princi- pally of oleic and linoleic fatty acids. it has resistance to oxidation. it is used in vegetable shortenings, salad oil, and cooking oil, and is found in frozen chicken chow mein.
What are the applications of Application
Sesame oil is a mixture of saturated, unsaturated, and polyunsaturated fatty acids derived from sesame seeds
Definition
A bland, yellowish, vegetable oil.
Production Methods
Sesame oil is obtained from the ripe seeds of one or more cultivated varieties of Sesamum indicum Linne′ (Fam. Pedaliaceae) by expression in a hydraulic press or by solvent extraction. The crude oil thus obtained is refined to obtain an oil suitable for food or pharmaceutical use. Improved color and odor may be obtained by further refining.
Composition
The seeds by expression yield a fixed oil consisting essentially of the glycerides of oleic and linoleic acids with small amounts of stearin, palmitin and myristin. Liquid fatty acids are present to about 70%, solid fatty acids 12 to 14%.
Aroma threshold values
Aroma characteristics at 100%: roasted nutty,sesame, peanut, hazelnut-like with some ashy coffee nuances.
Taste threshold values
Taste characteristics of extract at 650 ppm: nutty, roasted, pyrazine, cocoa and coffee, with a slightly smoky, savory nuance. Taste characteristics at 0.1%: roasted nutty, ashy coffee, sesame with a fatty, oily peanut-like note.
Pharmaceutical Applications
The major use of sesame oil in pharmaceutical formulations is as a
solvent in the preparation of sustained-release intramuscular
injections of steroids, such as estradiol valerate, hydroxyprogesterone
caproate, testosterone enanthate, and nandrolone decanoate, or other oil-soluble drug substances, such as the decanoates or
enanthate esters of fluphenazine. The disappearance of sesame oil
from the injection site, following subcutaneous or intramuscular
administration to pigs, has been reported to have a half-life of about
23 days. The in vitro drug release rates from oily depot
formulations containing sesame oil intended for intra-articular
administration have been reported.
Sesame oil may be used as a solvent in the preparation of
subcutaneous injections, oral capsules, rectal suppositories,
and ophthalmic preparations; it may also be used in the
formulation of suspensions and emulsions. Multipleemulsion
formulations, in which sesame oil was one of the oil
phases incorporated, have been investigated as a prolonged-release
system for rifampicin; microemulsions containing sesame oil
have been prepared for the transdermal delivery of ketoprofen.
Sesame oil has also been included in self-microemulsifying drug
delivery systems, and fast-disintegrating lyophilized dry emulsion
tablets for oral administration. It has also been used in the
preparation of liniments, pastes, ointments, and soaps. A sesame
paste (tahini), composed of crushed sesame seeds in sesame oil, has
been investigated as a novel suspending agent.
Sesame oil is additionally used as an edible oil and in the
preparation of oleomargarine.
Safety
Sesame oil is mainly used in intramuscular and subcutaneous
injections; it should not be administered intravenously. It is also
used in topical pharmaceutical formulations and consumed as an
edible oil.
Although it is generally regarded as an essentially nontoxic and
nonirritant material, there have been rare reports of hypersensitivity
to sesame oil, with sesamin suspected as being the primary
allergen. Anaphylactic reactions to sesame seeds have also
been reported. However, it is thought that the allergens in the seeds
may be inactivated or destroyed by heating as heat-extracted sesame
seed oil or baked sesame seeds do not cause anaphylactic reactions
in sesame seed-allergic individuals.
LD50 (rabbit, IV): 678 mg/kg
storage
Sesame oil is more stable than most other fixed oils and does not
readily become rancid; this has been attributed to the antioxidant
effect of some of its characteristic constituents. The PhEur 6.3
permits the addition of a suitable antioxidant to sesame oil.
Sesame oil may be sterilized by aseptic filtration or dry heat. It
has been reported that suitable conditions for the sterilization of
injections containing sesame oil are a temperature of 170℃ for 2
hours; it has been suggested that 150℃ for 1 hour is inadequate.
However, it has been demonstrated that dry heat sterilization of
sesame oil at 150℃ for 1 hour was sufficient to kill all added
Bacillus subtilis spores.
Sesame oil should be stored in a well-filled, airtight, lightresistant
container, at a temperature not exceeding 40℃. Sesame oil intended for use in the manufacture of parenteral dosage forms
should be stored under an inert gas in an airtight glass container.
Incompatibilities
Sesame oil may be saponified by alkali hydroxides.
Regulatory Status
Included in the FDA Inactive Ingredients Database (IM and SC injections; oral capsules, emulsions, and tablets; also topical preparations). Included in parenteral (IM injections) and nonparenteral (oral capsules) medicines licensed in the UK. Included in the Canadian List of Acceptable Non-medicinal Ingredients.
Properties of Sesame Oil
| Melting point: | -5 °C |
| Density | 0.919 |
| refractive index | 1.47-1.476 |
| Flash point: | 255 °C |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | chloroform: 0.1 mg/mL, clear, very faintly yellow |
| form | Liquid |
| color | Colorless to light yellow |
| Odor | at 100.00 %. sesame nutty roasted peanut coffee gourmand woody balsamic |
| Dielectric constant | 1.8(Ambient) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Sesame oil (8008-74-0) |
Safety information for Sesame Oil
Computed Descriptors for Sesame Oil
Sesame Oil manufacturer
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid 1-Bromo-3,5-Di-Tert-Butylbenzene S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
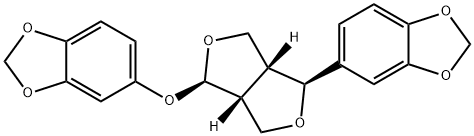
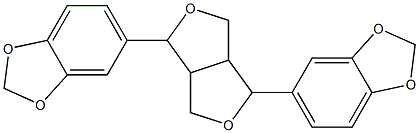





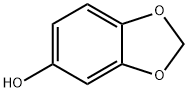
You may like
-
 Sesame oil, delivery vehicle for fat-soluble compounds CAS 8008-74-0View Details
Sesame oil, delivery vehicle for fat-soluble compounds CAS 8008-74-0View Details
8008-74-0 -
 Sesame oil, from sesamum indicum CAS 8008-74-0View Details
Sesame oil, from sesamum indicum CAS 8008-74-0View Details
8008-74-0 -
 Sesame Oil CAS 8008-74-0View Details
Sesame Oil CAS 8008-74-0View Details
8008-74-0 -
 Sesame oil CAS 8008-74-0View Details
Sesame oil CAS 8008-74-0View Details
8008-74-0 -
 Sesame oil from Sesamum indicum CAS 8008-74-0View Details
Sesame oil from Sesamum indicum CAS 8008-74-0View Details
8008-74-0 -
 Sesame oil CAS 8008-74-0View Details
Sesame oil CAS 8008-74-0View Details
8008-74-0 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1