Saccharin sodium
Synonym(s):Saccharin sodium;Saccharin sodium salt;Saccharin soluble;o-Sulfobenzimide sodium salt;2,3-Dihydro-3-oxobenzisosulfonazole sodium salt
- CAS NO.:128-44-9
- Empirical Formula: C7H5NNaO3S
- Molecular Weight: 206.17
- MDL number: MFCD00013092
- EINECS: 204-886-1
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-17 09:49:58
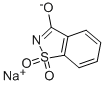
What is Saccharin sodium ?
Chemical properties
Saccharin sodium occurs as a white, odorless or faintly aromatic, efflorescent, crystalline powder. It has an intensely sweet taste, with a metallic or bitter aftertaste that at normal levels of use can be detected by approximately 25% of the population. The aftertaste can be masked by blending saccharin sodium with other sweeteners. Saccharin sodium can contain variable amounts of water.
The Uses of Saccharin sodium
Saccharin Sodium is a flavoring agent and non-nutritive sweetener. It is a salt of saccharin widely used as sweetener in food and beverage. As a high-intensity sweetener, Saccharin Sodium can be used in a wide variety of industries including: food production, beverage, cosmetics, agriculture/animal feed, and various other industries. Saccharin Sodium Salt Hydrate can be used for the purification of recombinant polypeptides, such as antibodies.
What are the applications of Application
Saccharin Sodium Salt is an inhibitor of the phosphotransferase and phosphohydrolase activities of glucose-6-phosphatase.
Production Methods
Saccharin is produced by the oxidation of o-toluene sulfonamide by potassium permanganate in a solution of sodium hydroxide. Acidification of the solution precipitates saccharin, which is then dissolved in water at 50℃ and neutralized by addition of sodium hydroxide. Rapid cooling of the solution initiates crystallization of saccharin sodium from the liquors.
Definition
ChEBI: Saccharin sodium is an organic molecular entity.
brand name
Sucaryl (Ross).
General Description
Saccharin sodium appears as odorless white crystals or crystalline powder. Aqueous solution is neutral or alkaline to litmus, but not alkaline to phenolphthalein. Effloresces in dry air. Intensely sweet taste. (NTP, 1992)
Air & Water Reactions
Water soluble.
Reactivity Profile
Saccharin sodium may react with oxidizing agents. . Very weak base in aqueous solution.
Hazard
The use of saccharin is being limited due to possible carcinogenicity.
Fire Hazard
Flash point data are not available for Saccharin sodium , but Saccharin sodium is probably combustible.
Pharmaceutical Applications
Saccharin sodium is an intense sweetening agent used in beverages,
food products, table-top sweeteners, and pharmaceutical formulations
such as tablets, powders, medicated confectionery, gels,
suspensions, liquids, and mouthwashes. It is also used
in vitamin preparations.
Saccharin sodium is considerably more soluble in water than
saccharin, and is more frequently used in pharmaceutical formulations.
Its sweetening power is approximately 300–600 times that of
sucrose. Saccharin sodium enhances flavor systems and may be used
to mask some unpleasant taste characteristics.
Injection of saccharin sodium has been used to measure the armto-
tongue circulation time.
Safety Profile
Confirmed carcinogen with experimental carcinogenic, neoplastigenic, tumorigenic, and teratogenic data. Moderately toxic by ingestion and intraperitoneal routes. A promoter. Experimental reproductive effects. Human mutation data reported. When heated to decomposition it emits very toxic fumes of SOx, Na2O, and NOx.
Safety
There has been considerable controversy concerning the safety of
saccharin and saccharin sodium in recent years; however, it is now generally regarded as a safe, intense sweetener. See Saccharin for
further information.
The WHO has set a temporary acceptable daily intake of up to
2.5 mg/kg body-weight for saccharin, including its salts.(3) In the
UK, the Committee on Toxicity of Chemicals in Food, Consumer
Products, and the Environment (COT) has set an acceptable daily
intake for saccharin and its salts (expressed as saccharin sodium) at
up to 5 mg/kg body-weight.
LD50 (mouse, oral): 17.5 g/kg
LD50 (rat, IP): 7.1 g/kg
LD50 (rat, oral): 14.2 g/kg
Potential Exposure
The information provided has to do, primarily, with the manufacturing of saccharin. Saccharin has been used as a nonnutritive sweetening agent. At one point the United States consumption pattern for all forms of saccharin has been estimated as 45% in soft drinks; 18% in tabletop sweeteners; 14% in fruits, juices, sweets, chew- ing gum, and jellies; 10% in cosmetics and oral hygiene products; 7% in drugs, such as coating on pills; 2% in tobacco; 2% in electroplating; and 2% for miscellaneous uses. Human exposure to saccharin occurs primarily through ingestion because of its use in many dietic foods and drinks and some personal hygiene products, including toothpastes and mouthwashes. The general public is exposed to saccharin, especially by persons required to reduce sugar intake.
Storage
Saccharin sodium is stable under the normal range of conditions
employed in formulations. Only when it is exposed to a high
temperature (125℃) at a low pH (pH 2) for over 1 hour does
significant decomposition occur. The 84% grade is the most stable
form of saccharin sodium since the 76% form will dry further under
ambient conditions. Solutions for injection can be sterilized by
autoclave.
Saccharin sodium should be stored in a well-closed container in a
dry place.
Shipping
UN3077 Environmentally hazardous substances, solid, n.o.s., Hazard class: 9; Labels: 9-Miscellaneous haz- ardous material, Technical Name Required.
Incompatibilities
Dust may form explosive mixture with air. Incompatible with strong oxidizers (chlorates, nitrates, peroxides, permanganates, perchlorates, chlorine, bromine, fluorine, etc.); contact may cause fires or explosions. Keep away from alkaline materials, strong bases, strong acids, oxoacids, and epoxides.
Incompatibilities
Saccharin sodium does not undergo Maillard browning.
Waste Disposal
Consult with environmental regulatory agencies for guidance on acceptable disposal practices. Generators of waste containing this contami- nant (≥100 kg/mo) must conform to EPA regulations governing storage, transportation, treatment, and waste disposal.
Regulatory Status
Accepted for use as a food additive in Europe; ‘E954’ is applied to both saccharin and saccharin salts. Included in the FDA Inactive Ingredients Database (buccal and dental preparations; IM and IV injections; oral and topical preparations). Included in nonparenteral medicines licensed in the UK. Included in the Canadian List of Acceptable Non-medicinal Ingredients.
Properties of Saccharin sodium
| Melting point: | >300°C |
| Density | 1.69[at 20℃] |
| vapor pressure | 0Pa at 25℃ |
| FEMA | 2997 | SACCHARINE, SODIUM SALT |
| storage temp. | 0-6°C |
| solubility | H2O: 1 M at 20 °C, clear, colorless; sparingly soluble in ethanol. |
| form | neat |
| pka | 0.003-0.003[at 20 ℃] |
| form | Solid |
| color | White crystals or a white, crystalline efflorescent powder |
| Odor | odourless or with a faint, aromatic odour |
| Water Solubility | >=10 g/100 mL at 20 ºC |
| Stability: | Stable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 128-44-9(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Saccharin sodium (128-44-9) |
Safety information for Saccharin sodium
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07  Health Hazard GHS08 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral H312:Acute toxicity,dermal H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H332:Acute toxicity,inhalation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation H350:Carcinogenicity |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Saccharin sodium
| InChIKey | WINXNKPZLFISPD-UHFFFAOYSA-M |
Saccharin sodium manufacturer
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran





You may like
-
 Sodium Saccharine 99%View Details
Sodium Saccharine 99%View Details -
 Sodium Saccharine 99%View Details
Sodium Saccharine 99%View Details -
 Saccharin sodium salt 99%View Details
Saccharin sodium salt 99%View Details -
 Saccharin Sodium Salt Hydrate 98%View Details
Saccharin Sodium Salt Hydrate 98%View Details -
 Saccharin sodium salt 98%View Details
Saccharin sodium salt 98%View Details
128-44-9 -
 Saccharin sodium salt 128-44-9 99%View Details
Saccharin sodium salt 128-44-9 99%View Details
128-44-9 -
 Saccharin Sodium 128-44-6 >98%View Details
Saccharin Sodium 128-44-6 >98%View Details
128-44-6 -
 Saccharin Sodium CASView Details
Saccharin Sodium CASView Details
