Rezafungin
- CAS NO.:1396640-59-7
- Empirical Formula: C63H85N8O17
- Molecular Weight: 1226.41
- MDL number: MFCD34593622
- Update Date: 2024-11-19 20:33:22
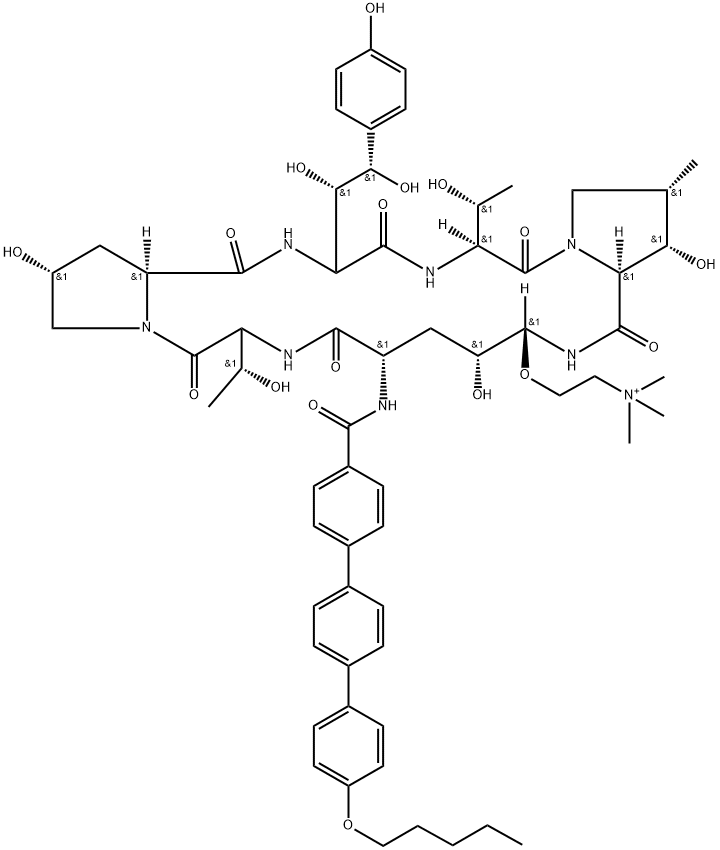
What is Rezafungin?
Absorption
Between 50 mg (0.125 times the approved maximum recommended loading dose) and 400 mg and with single or multiple doses, the Cmax and AUC of rezafungin increase in a dose-proportional manner. In patients with candidemia and invasive candidias given an initial 400 mg loading dose of rezafungin, followed by a 200 mg dose once weekly, the Cmax, AUC from time zero to 168 hours post-dose (AUC0-168) and Cmin on day 1 were 19.2 mcg/mL, 827 mcg?h/mL and 2.4 mcg/mL, respectively. In the same group of patients, the Cmax, AUC0-168 and Cmin on day 15 were 11.8 mcg/mL, 667 mcg?h/mL and 2.2 mcg/mL, respectively. Compared to healthy subjects, the AUC0-168 and Cmax were 30% and 19% lower in patients with candidemia. Age, sex, race, weight and hepatic impairment did not have a clinically significant effect on rezafungin pharmacokinetics.
Toxicity
During clinical studies, no cases of rezafungin overdose were reported. Since rezafungin is highly protein bound, it is not anticipated to be dialyzable. In non-clinical studies, rezafungin did not show evidence of mutagenicity in a standard battery of assays, and did not affect mating or fertility in male or female rats given up to 45 mg/kg of rezafungin intravenously (6 times the clinical exposure) every 3 days. At doses greater or equal than 30 mg/kg of rezafungin, male mice presented lower sperm motility, and at 45 mg/kg, they had mild/moderate hypospermia and no detectable motile sperm. In rats given 45 mg/kg of rezafungin intravenously every 3 days for 3 months, males showed minimal tubular degeneration/atrophy in the testes and cellular debris in the epididymides at the end of the study. The carcinogenicity of rezafungin has not been evaluated in non-clinical studies.
Description
Rezafungin is a novel, once-weekly antifungal being developed for the treatment and prevention of serious fungal infections.Rezafungin is a member of the echinocandin class of drugs. Echinocandins are considered the safest antifungal drugs available and are suggested by the Infectious Disease Society of America (IDSA) as first-line treatment for fungal infections.
The Uses of Rezafungin
Rezafungin (CD-101) is a second generation echinocandin with a similar spectrum and mechanism of action. Along with fosmanogepix, ibrexafungerp, olorofim, and opelconazole, rezafungin heralds a new era in the treatment of fungal infections.
Background
Rezafungin is an echinocandin antifungal drug. Unlike other echinocandins such as caspofungin and micafungin, rezafungin has long‐acting pharmacokinetics and a high stability that allows for it to have long dosing intervals maintaining high plasma exposure. Rezafungin has a half-life higher than 130 hours and can be administered once a week instead of daily. It can only be administered intravenously but does not reach therapeutic concentrations in the central nervous system, eye and urine. Rezafungin is active against Candida albicans, Candida glabrata, Candida parapsilosis and Candida tropicalis, as well as other Candida and Aspergillus spp.
Clinical studies have shown that rezafungin is non-inferior to caspofungin for the treatment of candidaemia and invasive candidiasis. In March 2023, the FDA approved rezafungin for injection for the treatment of candidemia and invasive candidiasis in adults with limited or no alternative treatment options.
Indications
Rezafungin is indicated in patients 18 years of age or older who have limited or no alternative options for the treatment of candidemia and invasive candidiasis.
Side Effects
Adverse effects associated with the use of Rezzayo may include, but are not limited to, the following: hypokalemia, pyrexia, diarrhea, anemia, vomiting, nausea, hypomagnesemia, abdominal pain, constipation, and hypophosphatemia.
Mechanism of action
Rezafungin is a semi-synthetic echinocandin. Rezafungin inhibits the 1,3-B-D-glucan synthase enzyme complex, which is present in fungal cell walls but not in mammalian cells. This results in the inhibition of the formation of 1,3-B-D-glucan, an essential component of the fungal cell wall of many fungi, including Candida species (spp.). Inhibition of 1,3-B-D-glucan synthesis results in concentration-dependent in vitro fungicidal activity against Candida spp., however, the clinical significance of this activity is unknown.
Pharmacokinetics
Clinical studies showed that with the recommended dosage regimen, rezafungin exposure is on the plateau of the exposure-efficacy response curve. At a dose 3.5 times the maximum approved recommended loading dose, rezafungin did not lead to a clinically relevant QTc interval prolongation. The use of rezafungin is associated with infusion-related reactions, photosensitivity and hepatic adverse reactions.
Metabolism
Rezafungin is metabolized by hydroxylation of the terphenyl, pentyl ether side chain, to form three hydroxylated metabolite isomers: 2’-, 3′-, or 4’-hydroxylpentyl rezafungin. Rezafungin can also be metabolized through a reaction that involves the loss of the pentyl group via O-dealkylation, forming despentyl-rezafungin. There is minimal subsequent conjugation (sulfation) of the hydroxyl metabolites. Rezafungin is not metabolized in the liver and is not expected to be a clinically relevant substrate of CYP450 enzymes.
References
[1] Syed, Yahiya Y. “Rezafungin: First Approval.” Drugs 83 9 (2023): 833–840.
[2] Desnos-Ollivier, Marie and Fanny Lanternier. “New antifungals development: rezafungin in candidiasis treatment.” Lancet Infectious Diseases 22 3 (2023).
Properties of Rezafungin
Safety information for Rezafungin
Computed Descriptors for Rezafungin
| InChIKey | LNFCWEXGZIEGJW-WIQSWMFQNA-O |
New Products
4-AMINO-TETRAHYDRO-PYRAN-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID HCL 4-(Dimethylamino)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-4-carbonitrile 4-Aminotetrahydropyran-4-carbonitrile Hydrochloride (R)-3-Aminobutanenitrile Hydrochloride 3-((Dimethylamino)methyl)-5-methylhexan-2-one oxalate 1,4-Dioxa-8-azaspiro[4.5]decane 5-Bromo-2-nitropyridine Nimesulide BP Aceclofenac IP/BP/EP Diclofenac Sodium IP/BP/EP/USP Mefenamic Acid IP/BP/EP/USP Ornidazole IP Diclofenac Potassium THOMAIND PAPER PH 2.0 TO 4.5 1 BOX BUFFER CAPSULE PH 9.2 - 10 CAP SODIUM CHLORIDE 0.1N CVS ALLOXAN MONOHYDRATE 98% PLATINUM 0.5% ON 3 MM ALUMINA PELLETS (TYPE 73) LITHIUM AAS SOLUTION 2-Bromo-1-(bromomethyl)-3-chloro-5-nitrobenzene 2-Bromo-3-nitroaniline N-(3-Hydroxypropyl)-N-methylacetamide 3-Bromo-6-chloropyridazine 4-ethyl-3-nitrobenzoic acidYou may like
-
 1-Methyl-6-oxo-1,6-dihydropyridazine-3-carbonitrile 98%View Details
1-Methyl-6-oxo-1,6-dihydropyridazine-3-carbonitrile 98%View Details
99903-60-3 -
 88491-46-7 98%View Details
88491-46-7 98%View Details
88491-46-7 -
 1823368-42-8 98%View Details
1823368-42-8 98%View Details
1823368-42-8 -
 2-(3-(tert-butyl)phenoxy)-2-methylpropanoic acid 1307449-08-6 98%View Details
2-(3-(tert-butyl)phenoxy)-2-methylpropanoic acid 1307449-08-6 98%View Details
1307449-08-6 -
 Ethyl 3-(furan-2-yl)-3-hydroxypropanoate 25408-95-1 98%View Details
Ethyl 3-(furan-2-yl)-3-hydroxypropanoate 25408-95-1 98%View Details
25408-95-1 -
 2-Chloro-5-fluoro-1-methoxy-3-methylbenzene 98%View Details
2-Chloro-5-fluoro-1-methoxy-3-methylbenzene 98%View Details
1805639-70-6 -
 1784294-80-9 98%View Details
1784294-80-9 98%View Details
1784294-80-9 -
 Lithium ClavulanateView Details
Lithium ClavulanateView Details
61177-44-4