RAYON
- CAS NO.:61788-77-0
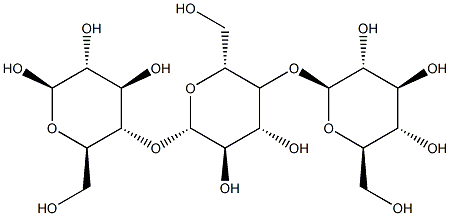
- Empirical Formula: C18H32O16
- Molecular Weight: 504.43708
- Update Date: 2025-12-17 09:49:49
What is RAYON?
The Uses of RAYON
Rayon, the first commercial manmade fiber, is composed of cellulose
in a quite pure form. It is produced by the treatment of wood pulp
with alkali and carbon disulfide to form a viscous solution of cellulose
xanthate. This viscous solution, called viscose, is extruded through spinnerets
into an aqueous acid bath that coagulates the cellulose xanthate,
decomposes it, and regenerates the cellulose.
Rayon fibers are easily wetted by water and provide easy access to dye
molecules. Dyeing may take place by absorption or by reaction with the
hydroxyl groups. Rayon fibers may also be dyed with mordant and vat
dyes.
The Uses of RAYON
Nonwoven fabrics, surgical dressings, mechan- ical rubber goods, coated fabrics, felts and blankets, blends with cotton for home furnishings, etc.
Definition
Generic name for a semisynthetic fiber composed of regenerated cellulose as well as man- ufactured fibers composed of regenerated cellulose in which substituents have replaced not more than 15% of the hydrogen of the hydroxyl groups. Rayon was first made
Definition
An artificial fiber formed from wood pulp (cellulose). There are two types. Viscose rayon is made by dissolving the cellulose in carbon disulfide and sodium hydroxide. The solution is forced through a fine nozzle into an acid bath, which regenerates the fibers. Acetate rayon is made by dissolving cellulose acetate in an organic solvent, and forcing the solution through a nozzle. The solvent is evaporated, and the cellulose acetate thus obtained as fibers.
Definition
rayon: textile made from cellulose.There are two types, both madefrom wood pulp. In the viscoseprocess, the pulp is dissolved in carbondisulphide and sodium hydroxideto give a thick brown liquidcontaining cellulose xanthate. Theliquid is then forced through finenozzles into acid, where the xanthateis decomposed and a cellulose filamentis produced. The product is viscoserayon. In the acetate process cellulose acetate is made and dissolvedin a solvent. The solution isforced through nozzles into air,where the solvent quickly evaporatesleaving a filament of acetate rayon.
Preparation
Viscose rayon is obtained by reacting the hydroxy groups of cellulose with car- bon disulfide in the presence of alkali to give xanthates. When this solution is poured (spun) into an acid medium, the reaction is reversed and the cellulose is regenerated (coagulated).
Hazard
Flammable, not self-extinguishing, moder- ate fire risk.
Industrial uses
Rayon is a general name for artificial-silk textile fibers or yarns made from cellulose nitrate, cellulose acetate, or cellulose derivatives. In general, the name rayon is limited to the viscose, cuprammonium, and acetate fibers, or to fibers having a cellulose base. Other synthetic-fiber groups have their own group names, such as azlon for the protein fibers and nylon for the polymeric amine fibers, in addition to individual trade names.
Viscose rayon is made by treating the cellulose with caustic soda and then with carbon disulfide to form cellulose xanthate, which is dissolved in a weak caustic solution to form the viscose.
Rayons manufactured by the different processes vary both chemically and physically.
Safety information for RAYON
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidYou may like
-
 Black Rayon Printed Top, 3/4 SleeveView Details
Black Rayon Printed Top, 3/4 SleeveView Details
61788-77-0 -
 Semi-Stitched Straight Heavy Rayon Printed Kurti, Age Group: 18 To 60View Details
Semi-Stitched Straight Heavy Rayon Printed Kurti, Age Group: 18 To 60View Details
61788-77-0 -
 Reyon Multicolor Rayon Gold Print 58 inch (704-B)View Details
Reyon Multicolor Rayon Gold Print 58 inch (704-B)View Details
61788-77-0 -
 Rayon Kurti Pant Dupatta SetView Details
Rayon Kurti Pant Dupatta SetView Details
61788-77-0 -
 14 kg Rayon Designer Kids Kurti CatalogueView Details
14 kg Rayon Designer Kids Kurti CatalogueView Details
61788-77-0 -
 Rayon Latest designer kurtiView Details
Rayon Latest designer kurtiView Details
61788-77-0 -
 Rayon chikan embroidery sequence work men's kurta fabricView Details
Rayon chikan embroidery sequence work men's kurta fabricView Details
61788-77-0 -
 RAYON 140GRM KURTI WITH PANTView Details
RAYON 140GRM KURTI WITH PANTView Details
61788-77-0
