POLY(METHYL METHACRYLATE)
- CAS NO.:9010-88-2
- Empirical Formula: C10H16O4
- Molecular Weight: 200.23
- MDL number: MFCD00134349
- EINECS: 618-459-6
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-10-23 17:25:30
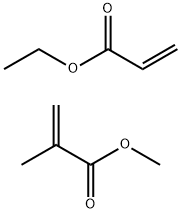
What is POLY(METHYL METHACRYLATE)?
The Uses of POLY(METHYL METHACRYLATE)
Poly(methyl methacrylate-co-ethyl acrylate) (PMMAEA) copolymers may be used to prepare single phase mixture with phenolic derivative. PMMAEA may be used to form latex interpenetrating polymer networks (LIPNs). Membranes of PMMAEA were reportedly used for separation of heavy metal ions from aqueous solutions.
Preparation
Acrylic acid is H2C=CH-COOH and methacrylic acid is H2C=C(CH3)COOH. These compounds and their methyl esters are both quite reactive and difficult to store and handle. The monomer used to form poly(methyl methacrylate), 2-hydroxy-2-methylpropanenitrile, is prepared by the following reaction:

2-Hydroxy-2-methylpropanenitrile is then reacted with methanol (or other alcohol) to yield methacrylate ester. Free-radical polymerization is initiated by peroxide or azo catalysts and produce poly(methyl methacrylate) resins having the following formula:

Key properties are good resistance to heat, light, and weathering. This polymer is unaffected by most detergents, cleaning agents, and solutions of inorganic acids, alkalies, and aliphatic hydrocarbons. Poly(methyl methacrylate) has light transmittance of 92% with a haze of 1–3% and its clarity is equal to glass.
Industrial uses
Poly(methyl methacrylate), the polymerizedmethyl ester of methacrylic acid, is thermoplastic.The method of polymerization may be variedto achieve specific physical properties, orthe monomer may be combined with other components.Sheet materials may be prepared bycasting the monomer in bulk. Suspension polymerizationof the monomeric ester may be usedto prepare molding powders.
Conventional poly(methyl methacrylate) isamorphous; however, reports have been publishedof methyl methacrylate polymers of regularconfiguration, which are susceptible tocrystallization. Both the amorphous and crystallineforms of such crystallization-susceptible polymers possess physical properties that aredifferent from those of the conventional polymer,and suggest new applications.
Industrial uses
Polymethyl methacrylate is a clear solid, hardbut easily scratched. Its dielectric properties areonly moderate, and its use is restricted to undemandingconditions at normal ambient temperatures,usually in a molded form, where appearanceis important.
Properties of POLY(METHYL METHACRYLATE)
| Melting point: | 150 °C |
| Density | 1.2 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) |
| refractive index | n |
| solubility | alcohols and aliphatic hydrocarbons: insoluble |
| form | powder |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Ethyl acrylate methyl methacrylate polymer (9010-88-2) |
Safety information for POLY(METHYL METHACRYLATE)
Computed Descriptors for POLY(METHYL METHACRYLATE)
New Products
Indole Methyl Resin tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Boc-His(Boc)-OH 2-CTC Resin 4-Chloro-7-tosy1-7Hpyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine 5,7-Dibromo-1H-indole 2,5-dichloro-N-hydroxy-4,6-dimethylpyridine-3-carboximidamide 2,2-Dimethoxy-7-azaspiro[3.5]nonane hydrochloride 4-chloromethyl-5-methyl-1,3-dioxol-2-one (DMDO-Cl) R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID 4-((2-hydroxyethyl)thio)benzoic acid 1-(TERT-BUTOXYCARBONYL)-2-PYRROLIDINONE Methyl 6-methylnicotinate 3-Pyridineacrylic acid tert-Butyl carbazate TETRAHYDRO-2H-PYRAN-3-OL 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 1,3-Diethyl-1,3-Diphenylurea Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


You may like
-
 Poly(methyl methacrylate-co-ethyl acrylate) CAS 9010-88-2View Details
Poly(methyl methacrylate-co-ethyl acrylate) CAS 9010-88-2View Details
9010-88-2 -
 Pyridine 99.5% HPLC /UV SpectroscopyView Details
Pyridine 99.5% HPLC /UV SpectroscopyView Details
110-86-1 -
 Guanine , 99%View Details
Guanine , 99%View Details
73-40-5 -
 Piperazine Spot supply, best priceView Details
Piperazine Spot supply, best priceView Details
110-85-0 -
 Dibutyl PhthalateView Details
Dibutyl PhthalateView Details
84-74-2 -
 Imidazole Spot supply, competitive priceView Details
Imidazole Spot supply, competitive priceView Details
288-32-4 -
 Octadecyl 3-(3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxyphenyl)propionate 98% (GC)View Details
Octadecyl 3-(3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxyphenyl)propionate 98% (GC)View Details
2082-79-3 -
 Thiourea 99% ARView Details
Thiourea 99% ARView Details
62-56-6
