Polycarbonate
Synonym(s):Poly(bisphenol A carbonate);Poly(dian carbonate);Poly[2,2-bis(4-hydroxyphenyl)propane carbonate];2,2-Bis(4-hydroxyphenyl)propane-carbonic acid copolymer;4,4′-Dihydroxydiphenyl-2,2-propane carbonate polymer
- CAS NO.:25037-45-0
- Empirical Formula: C16H18O5
- Molecular Weight: 290.32
- MDL number: MFCD00084476
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-11-18 17:49:23
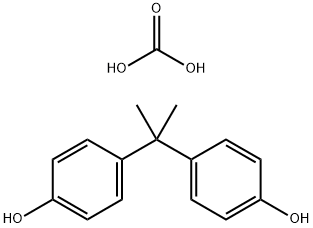
What is Polycarbonate?
Chemical properties
Polycarbonate is a polyester in which dihydric (or polyhydric) phenols are joined through carbonate linkages. The general-purpose type of polycarbonate is based on 2,2-bis(4'-hydroxybenzene)propane (bisphenol A) and has the general structure:

Polycarbonates are the toughest of all thermoplastics. They are window-clear, amazingly strong and rigid, autoclavable, and nontoxic. They have a brittleness temperature of 135℃.
Chemical properties
Bisphenol A polycarbonate has good oxidative stability, largely because of
the absence of secondary and tertiary carbon atoms. The polymer is stable in
air up to 150℃ over long periods; at higher temperatures some oxidation and
cross-linking occur. Ultraviolet light is strongly absorbed by the polycarbonate
and causes crazing and degradation. However, such effects are restricted
to the surface and in-depth deterioration does not occur. Thus, whilst film
may become brittle on weathering, moulded parts are not seriously affected.
Bisphenol A polycarbonate may be melt-processed by all of the standard
techniques although its melt-viscosity is rather high. Despite its fairly high
cost, the polymer has found a wide variety of uses. The largest application is
in the electronics/business machine field for such parts as connectors, terminals
and covers. An important new application is for compact discs. Other
uses include glazing, safety glasses, medical devices and domestic appliance
housing.
The Uses of Polycarbonate
Polycarbonates are plastics widely used in modern industry having good temperature and impact resistance. This plastic is particularly good to work with more conventional definition techniques (injection molding, extrusion into tubes or cylinders and thermoforming). It is also used when optical transparency is needed, having more than 80% transmission up to the 1560-nm range (short wave infrared range). It has moderated chemical resistance properties, being chemically resistant to diluted acids and alcohols. It is poorly resistant against ketones, halogens, and concentrated acids. The major disadvantage associated with polycarbonates is the low glass transition temperature (Tg> 40°C), but it is still largely used as low-cost material in microfluidic systems and also as a sacrificial layer.
The Uses of Polycarbonate
It was used to study the lipase degradation and monitored using gel permeation chromatography (GPC).
What are the applications of Application
Poly(Bisphenol A carbonate) is a polymer used as an analytical standard
Definition
A thermoplastic polymer consisting of polyesters of carbonic acid and dihydroxy compounds. They are tough and transparent, used for making soft-drink bottles and electrical connectors.
Preparation
To a solution of 2,2-bis-(4- hydroxyphenyl)propane 909 (0.68 g, 3 mmol) in dichloromethane (10 mL) was added triethylamine (0.60 g, 6 mmol), followed by a solution of triphosgene (0.30 g,1 mmol) in dichloromethane (10 mL). The mixture was stirred for 8 h at room temperature, washed with water (3×) and with aq. sodium hydrogen carbonate solution (3×), and dried over sodium sulfate. The solvent was removed in vacuo and the resulting colorless powder was dried under high vacuum; yield 0.74 g.
General Description
Service temperature, max.135°C
Properties of Polycarbonate
| Melting point: | 220~230℃ |
| Density | 1.2 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) |
| refractive index | n |
| solubility | chlorinated solvents: soluble |
| form | neat |
| Dielectric constant | 2.9(Ambient) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Carbonic acid, polymer with 4,4'-(1-methylethylidene)bis[phenol] (25037-45-0) |
Safety information for Polycarbonate
Computed Descriptors for Polycarbonate
Polycarbonate manufacturer
New Products
Indole Methyl Resin tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Boc-His(Boc)-OH 2-CTC Resin 4-Chloro-7-tosy1-7Hpyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine 5,7-Dibromo-1H-indole 2,5-dichloro-N-hydroxy-4,6-dimethylpyridine-3-carboximidamide 2,2-Dimethoxy-7-azaspiro[3.5]nonane hydrochloride 4-chloromethyl-5-methyl-1,3-dioxol-2-one (DMDO-Cl) R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID 4-((2-hydroxyethyl)thio)benzoic acid 1-(TERT-BUTOXYCARBONYL)-2-PYRROLIDINONE Methyl 6-methylnicotinate 3-Pyridineacrylic acid tert-Butyl carbazate TETRAHYDRO-2H-PYRAN-3-OL 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 1,3-Diethyl-1,3-Diphenylurea Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran






You may like
-
 Polycarbonate CASView Details
Polycarbonate CASView Details -
 Polycarbonate CASView Details
Polycarbonate CASView Details -
 Polycarbonate CASView Details
Polycarbonate CASView Details -
 Polycarbonate CASView Details
Polycarbonate CASView Details -
 Polycarbonate CASView Details
Polycarbonate CASView Details -
 Polycarbonate CASView Details
Polycarbonate CASView Details -
 Polycarbonate CASView Details
Polycarbonate CASView Details -
 Polycarbonate CASView Details
Polycarbonate CASView Details
