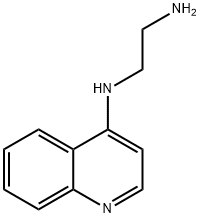
Piperaquinoline
- CAS NO.:4085-31-8
- Empirical Formula: C29H32Cl2N6
- Molecular Weight: 535.51
- MDL number: MFCD01237079
- EINECS: 202-303-5
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-10-28 16:48:35
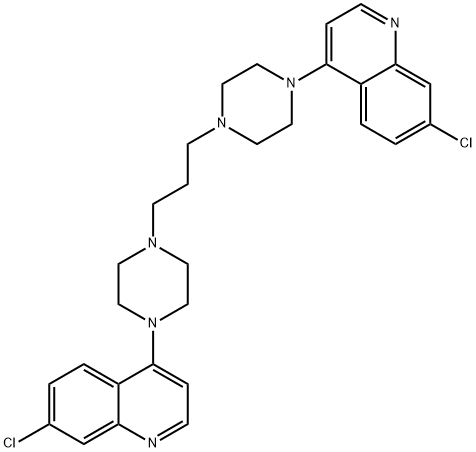
What is Piperaquinoline?
Absorption
Piperaquine is slowly absorbed and exhibits multiple peaks in its plasma concentration curve suggestive of enterohepatic recycling occurring alongside the absorption process . Due to this complication there is no discreet value for bioavailability but piperaquine is highly absorbed into systemic circulation. When taken with food, Cmax increases by 217% and mean exposure increases by 177%. Tmax is not affected by food and remains around 5 h . Piperaquine has been observed to accumulate more in females to a degree of 30-50% more than males . It also collects in red blood cells similar to Artenimol.
Toxicity
Studies of piperaquine in monkeys and dogs have shown some hepatotoxicity and reversible depression in white blood cells and neutrophils . Additional observations include infiltration of macrophages with intracytoplasmic basophilic granular material consistent with phospholipidosis and degenerative lesions in numerous organs and tissues. These effects were seen at exposure levels similar to clinical dosing in humans. At high doses, piperaquine can interfere with cardiac conduction and produce effects on blood pressure. Mild phototoxicity has been observed with piperaquine in rats exposed to UV light.
Chemical properties
To class white crystalline powder
Background
Piperaquine is an antimalarial agent first synthesized in the 1960's and used throughout China . Its use declined in the 1980's as piperaquine resistant strains of Plasmodium falciparum appeared and artemisinin derivatives became available. It has come back into use in combination with the artemisinin derivative Artenimol as part of the combination product Eurartesim . Eurartesim was first authorized for market by the European Medicines Agency in October 2011.
Indications
For the treatment of uncomplicated Plasmodium falciparum infection in adults, children, and infants aged 6 months and up weighing over 5 kg . Used in combination with Artenimol.
Definition
ChEBI: An aminoquinoline that is 1,3-di(piperazin-1-yl)propane in which the nitrogen at position 4 of each of the piperazine moieties is replaced by a 7-chloroquinolin-4-yl group.
Biological Activity
piperaquine, an antimalarial drug, is first synthesised in the 1960s and extensively used as prophylaxis and treatment during the next 20 years.
Pharmacokinetics
Piperaquine inhibits the P. Falciparum parasite's haem detoxification pathway .
in vitro
in 280 p. falciparum isolates, the ic50 for piperaquine ranged from 9.8 nm to 217.3 nm and a significant but low correlation was observed between the ic50 values for piperaquine and chloroquine. however, the coefficient of determination indicated that only 2.1% of the variation in the response to piperaquine was explained by the variation in the response to chloroquine. moreover, the mean value for piperaquine was 74.0 nm in the pfcrt k76 wild-type group and 87.7 nm in the 76t mutant group and such difference was not significant [1].
in vivo
male sd rats were orally administered piperaquine or as a short-term i.v. infusion. results showed that piperaquine disposition was best described by a 3-compartment model with a rapid initial distribution phase after i.v. administration. the pk of piperaquine was characterized by a low clearance, a large volume of distribution and a long terminal half-life [2].
Metabolism
Piperaquine undergoes N-dealkylation, separating its aliphatic bridge from one of the nitrogen-containing rings . The resulting aldehyde is then oxidized to a carboxylic acid to form metabolite 1 (M1). The same nitrogen-containing rings can also undergo hydroxylation at one of two sites to form M3 or M4. M2 is formed via N-oxidation of one of the nitrogens in the quinoline groups at either side of the molecule. M5 results when both of these nitrogens are oxidized. M1 and M2 are the major metabolism products . Each of these metabolites were observed in the urine.
References
[1] pascual a et al. in vitro piperaquine susceptibility is not associated with the plasmodium falciparum chloroquine resistance transporter gene. malar j. 2013 nov 25;12:431.
[2] tarning j, lindegardh n, sandberg s, day nj, white nj, ashton m. pharmacokinetics and metabolism of the antimalarial piperaquine after intravenous and oral single doses to the rat. j pharm sci. 2008 aug;97(8):3400-10.
[3] denis mb, davis tm, hewitt s, incardona s, nimol k, fandeur t, poravuth y, lim c, socheat d. efficacy and safety of dihydroartemisinin-piperaquine (artekin) in cambodian children and adults with uncomplicated falciparum malaria. clin infect dis. 2002 dec 15;35(12):1469-76.
Properties of Piperaquinoline
| Melting point: | 198-200 °C |
| Boiling point: | 721.1±60.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.292±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | Store at -20°C |
| solubility | ≤0.2mg/ml in DMSO |
| form | crystalline solid |
| pka | 8.92±0.50(Predicted) |
Safety information for Piperaquinoline
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Piperaquinoline
Piperaquinoline manufacturer
New Products
Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate (S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL N-octanoyl benzotriazole 4-Hydrazinobenzoic acid 3,4-Dibenzyloxybenzaldehyde 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) 4-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5-BROMO-2CYANO PYRIDINE 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
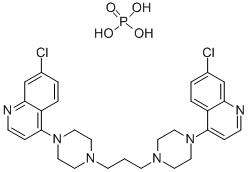
You may like
-
 4085-31-8 Piperaquine phosphate 98%View Details
4085-31-8 Piperaquine phosphate 98%View Details
4085-31-8 -
 4085-31-8 98%View Details
4085-31-8 98%View Details
4085-31-8 -
 Piperaquine 98%View Details
Piperaquine 98%View Details
4085-31-8 -
 Piperaquine 4085-31-8 98%View Details
Piperaquine 4085-31-8 98%View Details
4085-31-8 -
 Piperaquine tetraphosphate tetrahydrate 98% (HPLC) CAS 4085-31-8View Details
Piperaquine tetraphosphate tetrahydrate 98% (HPLC) CAS 4085-31-8View Details
4085-31-8 -
 N-Vinylformamide 99%View Details
N-Vinylformamide 99%View Details
13162-05-5 -
 2-ethyl-6-methyl-3-hydroxypyridine succinate 99%View Details
2-ethyl-6-methyl-3-hydroxypyridine succinate 99%View Details
127464-43-1 -
 2-ETHYLPYRIDINE 100-71-0 99%View Details
2-ETHYLPYRIDINE 100-71-0 99%View Details
100-71-0