Phytic acid
Synonym(s):myo-Inositol hexakis(dihydrogen phosphate)
- CAS NO.:83-86-3
- Empirical Formula: C6H18O24P6
- Molecular Weight: 660.04
- MDL number: MFCD00082309
- EINECS: 201-506-6
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-25 11:31:46
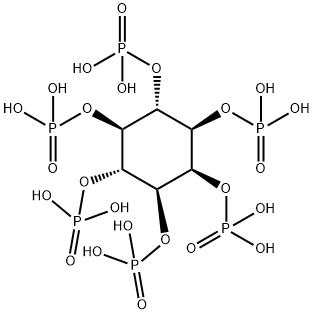
What is Phytic acid?
Chemical properties
colourless to pale yellow liquid
Originator
Rencal, Squibb, US ,1962
The Uses of Phytic acid
The principal storage form of phosphorus in many plant tissues, especially bran and seeds. It has antioxidant effect as well as neuroprotective effect by chelating iron. Inositol hexakisphosphate kina se type 2 (InsP6K2), which converts phytic acid to inositol pyrophosphate diphosphoinositol pentakisphosphate, is believed to induce pathogenesis of Huntington disease (HD).
The Uses of Phytic acid
A compound which inhibits cell differentiation and cell proliferation.
The Uses of Phytic acid
phytic acid is used to help maintain product stability. Its therapeutic activities are said to include skin-lightening, anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidant properties. It is naturally occurring in grains, seeds, and beans.
What are the applications of Application
Phytic acid solution is a compound which inhibits cell differentiation and cell proliferation
Definition
ChEBI: A myo-inositol hexakisphosphate in which each hydroxy group of myo-inositol is monophosphorylated.
Manufacturing Process
Cereal grains are particularly rich in phytates; corn steep water produced in the wet milling of corn, is one of the best sources of such material. To recover the phytate from corn steep water it is customary to neutralize the same withan alkaline material, suitably lime, causing the phytate to precipitate as a crude salt which can be removed readily by filtration. This material contains substantial amounts of magnesium, even though lime may have been employed as precipitant, and traces of other metallic ions, as well as some proteinaceous materials and other contaminants from the steep water. It may be partially purified by dissolving in acid and reprecipitating but, nevertheless, such commercial phytates do not represent pure salts. They always contain some magnesium, appreciable amounts of iron and nitrogenous materials, and traces of heavy metals, such as copper.
Heretofore, no economical method for preparing pure phytic acid was known. The classical method was to dissolve calcium phytate in an acid such as hydrochloric acid, and then add a solution of a copper salt, such as copper sulfate to precipitate copper phytate. The latter was suspended in water and treated with hydrogen sulfide, which formed insoluble copper sulfide and released phytic acid to the solution. After removing the copper sulfide by filtration, the filtrate was concentrated to yield phytic acid as a syrup.
The phytic acid in the form of a calcium phytate press cake may however be contacted with a cation exchange resin to replace the calcium with sodium to yield phytate sodium.
Therapeutic Function
Hypocalcemic
General Description
Phytic acid is a mineral chelator that can bind to minerals to form mineral-phytate complex.It can also complex with metal ions bound to the surface of magnesium alloy to form a conversion coating, which can improve the resistance of magnesium alloy towards corrosion.
Agricultural Uses
Phytic acid is inositol hexaphosphoric acid which exists in several stereoisomers. It is a source of phosphorus compounds for seeds and young plants.
Safety Profile
Poison by intravenous route. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of POx.
Properties of Phytic acid
| Melting point: | <25℃ |
| Boiling point: | 105 °C |
| Density | 1.432 g/mL at 25 °C |
| vapor pressure | 0.039Pa at 60℃ |
| refractive index | n |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | Acetone (Slightly), Methanol (Slightly), Water (Soluble) |
| form | Colourless to Light Brown Solution |
| pka | 1.13±0.10(Predicted) |
| Specific Gravity | 1.282 |
| color | Colorless to light yellow |
| Odor | odorless |
| Water Solubility | MISCIBLE |
| Merck | 14,7387 |
| BRN | 2201952 |
| Stability: | Stable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 83-86-3(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | myo-Inositol, hexakis(dihydrogen phosphate) (83-86-3) |
Safety information for Phytic acid
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Corrosion Corrosives GHS05  Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H290:Corrosive to Metals H302:Acute toxicity,oral H314:Skin corrosion/irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P234:Keep only in original container. P270:Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P301+P312:IF SWALLOWED: call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician IF you feel unwell. P303+P361+P353:IF ON SKIN (or hair): Remove/Take off Immediately all contaminated clothing. Rinse SKIN with water/shower. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Phytic acid
| InChIKey | IMQLKJBTEOYOSI-GPIVLXJGSA-N |
Phytic acid manufacturer
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


You may like
-
 83-86-3 Phytic acid 99%View Details
83-86-3 Phytic acid 99%View Details
83-86-3 -
 Phytic acid solution, 60% (w/w) in H2O CAS 83-86-3View Details
Phytic acid solution, 60% (w/w) in H2O CAS 83-86-3View Details
83-86-3 -
 Phytic Acid (ca. 50% in Water, ca. 1.1mol/L) CAS 83-86-3View Details
Phytic Acid (ca. 50% in Water, ca. 1.1mol/L) CAS 83-86-3View Details
83-86-3 -
 Phytic acid ca. 50% in water CAS 83-86-3View Details
Phytic acid ca. 50% in water CAS 83-86-3View Details
83-86-3 -
 Phytic acid solution CAS 83-86-3View Details
Phytic acid solution CAS 83-86-3View Details
83-86-3 -
 Phytic acid solution CAS 83-86-3View Details
Phytic acid solution CAS 83-86-3View Details
83-86-3 -
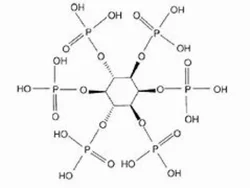 Inositol HexaphosphateView Details
Inositol HexaphosphateView Details
87-89-8 -
 20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0
