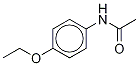
Phenacetin
Synonym(s):Phenacetin;Acetophenetidin;N-(4-Ethoxyphenyl)acetamide;p-Acetophenetidide;1-Acetyl-p-phenetidin
- CAS NO.:62-44-2
- Empirical Formula: C10H13NO2
- Molecular Weight: 179.22
- MDL number: MFCD00009094
- EINECS: 200-533-0
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-23 13:58:55
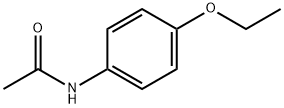
What is Phenacetin?
Description
Phenacetin, a painkiller, was the world’s first synthetic pharmaceutical drug. It was one of the first painkillers that was not derived from opium while at the same time being absent of antiinflammatory qualities. Phenacetinwas developed in 1878 by an American chemist, Harmon Northrop Morse. It was introduced into the pharmaceutical market in 1887. However, it was withdrawn in 1983 in the United States due to unacceptable levels of interstitial nephritis in patients and potential risks of tumorigenicity. Like in the United States, most Western countries did not ban phenacetin from marketing until 1983. Phenacetin is a component of APC (aspirin-phenacetin-caffeine).
Chemical properties
Acetophenetidin is a fine, white, crystalline powder or solid. Odorless with a slightly bitter taste
Originator
Phenacetin ,Environmental Health
The Uses of Phenacetin
Analgesic, antipyretic. Component of APC tablets, analgesic mixture also containing aspirin and caffeine. Phenacetin is reasonably anticipated to be a human carcinogen; analgesic mixtures containing Phenacetin are listed as known human carcinogens.
The Uses of Phenacetin
glycosylation inhibitor
The Uses of Phenacetin
Phenacetin was used as an analgesic and fever-reducing drug in both human and veterinary medicine for many years until it was implicated in kidney disease (nephropathy) due to abuse of analgesics and was withdrawn from the market. Phenacetin also was previously used as a stabilizer for hydrogen peroxide in hair-bleaching preparations.
What are the applications of Application
Phenacetin is a Cox-3 inhibitor
Definition
ChEBI: Phenacetin is a member of the class of acetamides that is acetamide in which one of the hydrogens attached to the nitrogen is substituted by a 4-ethoxyphenyl group. It has a role as a non-narcotic analgesic, a peripheral nervous system drug and a cyclooxygenase 3 inhibitor. It is a member of acetamides and an aromatic ether. It is functionally related to a N-phenylacetamide, a 4-ethoxyaniline and a paracetamol.
Manufacturing Process
A mixture of 10 g of 4-ethoxyaniline and 8.6 g of acetic anhydride in 28 g of dry benzene was refluxed for 4 hours. To the reaction mixture was added a small amount of Na2S2O4. After cooling the phenacetin was crystallized; yield 12.5 g (96%), M.P. 136°C.
brand name
[Names previously used: Acetophenetidin; Acetphenetidin.];292-comprimes 369, pulvules 3p bugesic;Acetylosal;Acifein;Acromas;Acropac;Algocratine;Alumidyne;Amypron;Amypylo-n;Angifebrine;Anodin;Antiflu des;Apadine;Apidin;Apracur;Arcin;Asceine;Ascophen;Ascthimindon;Asfeen;Ban-o-pain;Bexophene;Bromo quinina;Butal compound;Butorinal;Calmante muri;Capacetyl;Capramin;Caps dr knapp;Capsula dr. knapp;Ceachin;Cefinal;Cequinyl fort;Chloracet;Citramol;Codopyrin;Codral;Conta-schmerz;Coricidin f;Cotradol;Darvocomp-n;Darvon compuesto 65;Darvon n compuesto;Dentocaps;Dolafort;Dolomo;Doloxene comp forte, capsules;Dolviron;Doregrippin;Doscafis;Doviron;Drinacet;Estrifen;Femcaps;Fenascor;Fenbutal;Flexalgit;Florital;Fonal;Fridol;Friocellin;Funapann;Gripanidan;Harbureta;Hemagene taylor;Icn 65;Influenza tabs;Isollyl;Isomidon;Katagrip;Lekasin;Linarol;Manasul;Mardon;Migesic;Mironal;Monacet;Myolate;Neopyrine;Nevral vit b1 b6;Novacetol;Novosephalgin;Olfano;Omniadol;Papnin;Para-grip;Parametten;Pargesic compound;Pasadex;Pedigel;Phenacetine powder;Phenorial;Polypyrine;Poxy;Procomp-65;Prodigestan;Prodolor;Protension;Quadrochin;Rectoral;Refagan;Repro;Respritin;Rhinazol;Rinurel;Rinutan;Robaxisan-pm;Ron-drive;Rumicine;S antineuralgic;S fc;Sacadol;Sadaspir;Sedalmerck;Sk 65 compound caps.;Soma compound;Soma compuesto;Sonalgin;Spacin;Spasmindon;Spasmo-compralgyl;Synalogos-dc;T h;Tetrex-apc;Tetrracydin;Tiiomapirina;Tomapiena;Triplex;Uga-no;Vandar-65;Vasogesic;Vicks action 500;Zactirin compound-100.
Therapeutic Function
Analgesic
World Health Organization (WHO)
Phenacetin, an aniline derivative, was introduced into medicine as an antipyretic over a century ago. It subsequently gained recognition as an analgesic and was available in many proprietary analgesic preparations. However, in the 1940s its habitual use was first implicated as the cause of methaemoglobinaemia and chronic haemolysis. Since 1950 there have been many reports published indicating that abusive use is associated with cumulative renal damage. Evidence also exists to suggest that it may have a carcinogenic potential. The drug has been withdrawn in many countries but may remain available in others. (Reference: (WHODI) WHO Drug Information, 1, 5, 1980)
Synthesis Reference(s)
Synthesis, p. 168, 1995 DOI: 10.1055/s-1995-3868
General Description
Phenacetin is an odorless fine white crystalline solid with a lightly bitter taste. Used as an analgesic medicine.
Air & Water Reactions
Insoluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
Phenacetin react with oxidizing agents, iodine and nitrating agents.
Fire Hazard
Flash point data for Phenacetin are not available but Phenacetin is probably combustible.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Substrate of CYP1A2 and CYP2D6.
Clinical Use
Phenidine is a weak analgesic, antipyretic compound without antiinflammatory action. It has been used in combination with other compounds like aspirin, caffeine, or codeine, but due to hematological and nephrotoxic side effects has been withdrawn from the market and substituted by the less toxic paracetamol.
Safety Profile
Confirmed carcinogen producing tumors of the lildney and bladder. A human poison by an unspecified route. Poison by intravenous and possibly other routes. Moderately toxic by several routes. Human systemic effects by ingestion: cyanosis, liver damage, and methemoglobinemiacarboxyhemo-globinemia. Experimental teratogenic data. Other experimental reproductive effects. Mutation data reported. Chronic effects consist of weight loss, insomnia, shortness of breath, weakness, and often aplastic anemia. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of NOx,.
Potential Exposure
Phenacetin is used as an analgesic and antipyretic drug. It is used alone or in combination with aspirin and caffeine for mild to moderate muscle pain relief. Phenacetin has also been used as a stabilizer for hydrogen peroxide in hair bleaching preparations. A laboratory reagent. In veterinary medicine; it is used as an analgesic and antipyretic.
Carcinogenicity
Phenacetin is reasonably anticipated to be a human carcinogen based on sufficient evidence of carcinogenicity from studies in experimental animals.
Environmental Fate
Phenacetin occurs at room temperature as white, odorless
monoclinic prisms. It is soluble in water, alcohol, glycerol, and
acetone and is slightly soluble in benzene. It is unstable to oxidizing agents, iodine, and nitrating agents. Phenacetin has
a melting point of 134–135 °C; log Kow of 1.58; water solubility
of 30 mg l-1 at 25 °C; and vapor pressure of 0.00316mmHg at
25 °C.
Phenacetin’s former use and production as an analgesic may
have allowed release into the environment through various
waste streams. Phenacetin exists both as vapor and as particulate
if released to air. The vapor phase is expected to be readily
degraded by reaction with photochemically produced hydroxyl
radicals with a half-life reaction of 22 h. The particular phase,
however, is removed by wet and dry deposition reactions.
Phenacetin can enter the environment through leaching into
groundwater when released into the soil with moderate
mobility. When released into the water, it does not adsorb to
suspended solids and sediment, but is expected to be inert to
reaction with naturally occurring oxidants found in water with
a half-life of more than 30 days. Phenacetin has an estimated
bioconcentration factor of less than 100, and is not expected to
significantly bioaccumulate. Volatilization is insignificant.
Shipping
UN2811 Toxic solids, organic, n.o.s., Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials, Technical Name Required.
Purification Methods
Crystallise it from H2O or EtOH, and its solubility in H2O is 0.08% (at ~10o) and 1.2% (at ~100o), and in EtOH it is 6.7% (at ~10o) and 36% (at ~100o). Alternatively it can be purified by solution in cold dilute alkali and re-precipitating by addition of acid to neutralisation point. Dry it in air. [Beilstein 13 H 461, 13 IV 1092.]
Toxicity evaluation
It is unclear how phenacetin induces nephropathy. Studies proposed that phenacetin’s metabolite, acetaminophen (paracetamol), leads to lipid peroxidation that damages kidney cells through cyclooxygenases reaction that catalyzes the conversion of paracetamol into N-acetyl-p-benzoquinoneimine (NAPQI). NAPQI, in turn, depletes glutathione via nonenzymatic conjugation to glutathione, a naturally occurring antioxidant.With the depletion of glutathione, kidney cells are more susceptible to oxidative damage.
Incompatibilities
Oxidizing agents, iodine and nitrating agents.
Waste Disposal
It is inappropriate and possibly dangerous to the environment to dispose of expired or waste pharmaceuticals by flushing them down the toilet or discarding them to the trash. Household quantities of expired or waste pharmaceuticals may be mixed with wet cat litter or coffee grounds, double-bagged in plastic, discard in trash. Larger quantities shall carefully take into consideration applicable DEA, EPA, and FDA regulations. If possible, return the pharmaceutical to the manufacturer for proper disposal being careful to properly label and securely package the material. Alternatively, the waste pharmaceutical shall be labeled, securely packaged, and transported by a state licensed medical waste contractor to dispose by burial in a licensed hazardous or toxic waste landfill or incinerator. Consult with environmental regulatory agencies for guidance on acceptable disposal practices. Generators of waste containing this contaminant (≥100 kg/mo) must conform with EPA regulations governing storage, transportation, treatment, and waste disposal. Permanganate oxidation, microwave plasma treatment, alkaline hydrolysis or incineration.
Properties of Phenacetin
| Melting point: | 133-136 °C (lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 132 °C / 4mmHg |
| Density | 1.1248 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.5710 |
| Flash point: | 2℃ |
| storage temp. | Sealed in dry,Room Temperature |
| solubility | Chloroform (Slightly), Methanol (Slightly) |
| form | powder |
| pka | pKa 2.2(H2O) (Uncertain);3.5(aqueous acetone) (Uncertain) |
| color | White |
| Water Solubility | 0.076 g/100 mL |
| Sensitive | Hygroscopic |
| Merck | 14,7204 |
| BRN | 1869238 |
| Stability: | Stable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents, strong acids. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 62-44-2(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| IARC | 1 (Vol. 24, Sup 7, 100A) 2012 |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Acetamide, N-(4-ethoxyphenyl)-(62-44-2) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Phenacetin (62-44-2) |
Safety information for Phenacetin
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07  Health Hazard GHS08 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral H350:Carcinogenicity |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P201:Obtain special instructions before use. P202:Do not handle until all safety precautions have been read and understood. P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P270:Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product. P301+P312:IF SWALLOWED: call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician IF you feel unwell. P308+P313:IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/attention. |
Computed Descriptors for Phenacetin
| InChIKey | CPJSUEIXXCENMM-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 Phenacetin CAS 62-44-2View Details
Phenacetin CAS 62-44-2View Details
62-44-2 -
 Phenacetin 95% CAS 62-44-2View Details
Phenacetin 95% CAS 62-44-2View Details
62-44-2 -
 Phenacetin CAS 62-44-2View Details
Phenacetin CAS 62-44-2View Details
62-44-2 -
 Phenacetin melting point standard CAS 62-44-2View Details
Phenacetin melting point standard CAS 62-44-2View Details
62-44-2 -
 Phenacetin Melting Point Standard CAS 62-44-2View Details
Phenacetin Melting Point Standard CAS 62-44-2View Details
62-44-2 -
 Phenacetin CAS 62-44-2View Details
Phenacetin CAS 62-44-2View Details
62-44-2 -
 Phenacetin CAS 62-44-2View Details
Phenacetin CAS 62-44-2View Details
62-44-2 -
 20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0
