PAPAVERINE HYDROCHLORIDE
- CAS NO.:58-74-2
- Empirical Formula: C20H21NO4
- Molecular Weight: 339.39
- MDL number: MFCD00012745
- EINECS: 200-397-2
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2023-06-08 09:01:57
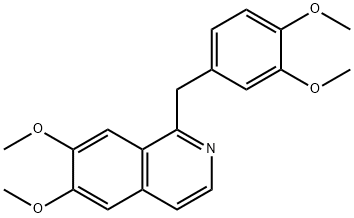
What is PAPAVERINE HYDROCHLORIDE?
Chemical properties
White crystalline powder; obtained asorthorhombic prisms from an alcohol–ethermixture; melts at 147°C (296.6°F); sublimesunder vacuum; insoluble in water; soluble inacetone, glacial acetic acid, and benzene.
Originator
Lempav Ty-Med ,Lemmon,US,1975
The Uses of PAPAVERINE HYDROCHLORIDE
folate metabolic inhibitor, coccidiostat
The Uses of PAPAVERINE HYDROCHLORIDE
muscle relaxant (smooth), cerebral vasodilator
The Uses of PAPAVERINE HYDROCHLORIDE
opium alkaloid
The Uses of PAPAVERINE HYDROCHLORIDE
Papaverine occurs in opium to the extent of0.8–1.0%, commonly associated with narcotine.It is used as a smooth muscle relaxantand in medicine for its vasodilator action onthe blood vessels in the brain. It is effectiveagainst asthma.
Background
An alkaloid found in opium but not closely related to the other opium alkaloids in its structure or pharmacological actions. It is a direct-acting smooth muscle relaxant used in the treatment of impotence and as a vasodilator, especially for cerebral vasodilation. The mechanism of its pharmacological actions is not clear, but it apparently can inhibit phosphodiesterases and it may have direct actions on calcium channels.
Indications
For the treatment of impotence and vasospasms.
What are the applications of Application
Papaverine is a phosphodiesterase inhibitor
Definition
ChEBI: A benzylisoquinoline alkaloid that is isoquinoline substituted by methoxy groups at positions 6 and 7 and a 3,4-dimethoxybenzyl group at position 1. It has been isolated from Papaver somniferum.
Indications
Papaverine (Pavabid) is a nonspecific phosphodiesterase inhibitor that increases cAMP and cGMP levels in penile erectile tissue. Papaverine is particularly known as a smooth muscle relaxant and vasodilator. Its principal pharmacological action is as a nonspecific vasodilator of smooth muscles of the arterioles and capillaries. Various vascular beds and smooth muscle respond differently to papaverine administration both in intensity and duration. Papaverine decreases the resistance to arterial inflow and increases the resistance to venous outflow.
Manufacturing Process
To 3.65 g (0.01 mol) of monohydrated adenosine-5'-monophosphoric acid, brought into suspension in a mixture of 45 ml of water and 5 ml of ethanol, are added 339 g (0.01 mol) of papaverine base (melting point, 147°C). The mixture is gently heated until a final temperature of 40°C is reached. The solution obtained is then filtered and the filtrate is concentrated under vacuum. The remaining product quickly crystallizes. After drying to 50°C to constant weight, there are obtained 6.68 g of desired product, in the monohydrated state, as a white crystalline powder, which melts at 140°C and is very soluble in water.
brand name
Pavabid (Hoechst Marion Roussel).
Therapeutic Function
Vasodilator, Platelet aggregation inhibitor
Health Hazard
Papaverine is an inhibitor of cyclic nucleotidephosphodiesterase, producing vasodilatoryeffect. The acute toxic effects relative tophenanthrene-type opium alkaloids (e.g.,morphine, heroin) are low and the symptomsare not the same. Papaverine is neither a narcoticnor an addictive substance. Excessivedoses may produce drowsiness, headache,facial flushing, constipation, nausea, vomiting,and liver toxicity.
The LD50 data reported in the literatureshow variation. An oral LD50 value in rats ison the order of 400 mg/kg.
Mechanism of action
When administered by intracavernosal injection, papaverine, a weak and nonspecific PDE inhibitor, is thought to cause relaxation of the cavernous smooth muscles and vasodilation of the penile arteries by inhibition of PDE. These effects result in increased arterial blood flow into the corpus cavernosa and in swelling and elongation of the penis. Venous outflow also is reduced, possibly as a result of increased venous resistance.
Pharmacokinetics
Papaverine is a nonxanthine phosphodiesterase inhibitor for the relief of cerebral and peripheral ischemia associated with arterial spasm and myocardial ischemia complicated by arrhythmias. The main actions of Papaverine are exerted on cardiac and smooth muscle. Like qathidine, Papaverine acts directly on the heart muscle to depress conduction and prolong the refractory period. Papaverine relaxes various smooth muscles. This relaxation may be prominent if spasm exists. The muscle cell is not paralyzed by Papaverine and still responds to drugs and other stimuli causing contraction. The antispasmodic effect is a direct one, and unrelated to muscle innervation. Papaverine is practically devoid of effects on the central nervous system. Papaverine relaxes the smooth musculature of the larger blood vessels, especially coronary, systemic peripheral, and pulmonary arteries.
Clinical Use
Papaverine is highly effective in men with psychogenic and neurogenic ED but less effective in men with vasculogenic ED. Papaverine–phentolamine combinations have been used in self-injection procedures. Papaverine doses may range from 15 to 60 mg. Papaverine treatment in patients with severe arterial or venous incompetence is usually unsuccessful, but autoinjections using low doses sufficient to achieve an erection are safe and efficient.
Side Effects
Major side effects associated with papaverine therapy include priapism, corporeal fibrosis, and occasional increases in serum aminotransferases. Intracorporeal scarring may be related to the low pH of the vehicle that is necessary to solubilize papaverine.Attempts to buffer papaverine to render it more suitable for intracavernosal injection have not been entirely satisfactory, and such delivery may still lead to intracorporeal scarring.
Safety Profile
Poison by ingestion, intramuscular, subcutaneous, intradermal, intraperitoneal, and intravenous routes. Human systemic effects: coma, somnolence. Its central nervous system action is about midway between those of morphme and codeine, and large doses do not produce the amount of excitement caused by codeine or the soporific action of morphine. Mutation data reported. A cerebral vasodilator and smooth muscle relaxant. Combustible when exposed to heat or flame. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of NOx. See also MORPHINE.
Synthesis
Papaverine, 1-veratryl-6,7-dimethoxyisoquinolin (19.4.7), is synthesized from veratrol. Veratrol undergoes chloromethylation, forming 3,4-dimethoxybenzylchloride (19.4.1). Reacting this with potassium cyanide gives 3,4-dimethoxybenzylcyanide (19.4.2). The resulting 3,4-dimethoxybenzylcyanide undergoes reduction by hydrogen over Raney nickel, forming homoveratrylamine (19.4.3). At the same time 3,4-dimethoxybenzylcyanide (19.4.2) undergoes acidic hydrolysis giving 3,4-dimethoxyphenylacetic acid (19.4.4). The interaction of the resulting compounds brings to corresponding amide (19.4.5). The cyclization of this by Bischler¨CNapieralski method, using phosphorous oxychloride, gives 3,4-dihydropapaverine (19.4.6), which is dehydrated into the desired papverine when heated in tetraline at high temperatures.

Metabolism
Not Available
Properties of PAPAVERINE HYDROCHLORIDE
| Melting point: | 226 °C |
| Boiling point: | 475.36°C (rough estimate) |
| Density | d420 1.337 |
| refractive index | 1.6250 (estimate) |
| solubility | H2O: 25 mg/mL |
| form | powder |
| pka | 6.4(at 25℃) |
| color | white |
| Water Solubility | 37.33mg/L(37.5 ºC) |
| Merck | 14,7019 |
| BRN | 312930 |
Safety information for PAPAVERINE HYDROCHLORIDE
Computed Descriptors for PAPAVERINE HYDROCHLORIDE
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid 1-Bromo-3,5-Di-Tert-Butylbenzene S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran







You may like
-
 2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 -
 42831-50-5 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID 98%View Details
42831-50-5 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID 98%View Details
42831-50-5 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1