Olmesartan
Synonym(s):4-(1-Hydroxy-1-methylethyl)-2-propyl-1-[[2′-(2H-tetrazol-5-yl)[1,1′-biphenyl]-4-yl]methyl]-1H-imidazole-5-carboxylic acid;Olmesartan acid
- CAS NO.:144689-24-7
- Empirical Formula: C24H26N6O3
- Molecular Weight: 446.5
- MDL number: MFCD00914967
- EINECS: 646-413-5
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-08-08 17:45:00
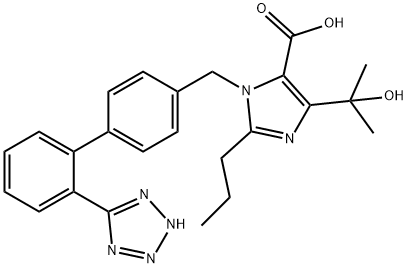
What is Olmesartan?
Absorption
When taken orally, the prodrug olmesartan medoxomil is rapidly absorbed in the gastrointestinal tract and metabolized to olmesartan. The esterification with medoxomil was created with the intention of increasing olmesartan bioavailability from 4.5% to 28.6%.
Oral administration of 10-160 mg of olmesartan has been shown to reach peak plasma concentration of 0.22-2.1 mg/L after 1-3 hours with an AUC of 1.6-19.9mgh/L. The pharmacokinetic profile of olmesartan has been observed to be nearly linear and dose-dependent under the therapeutic range. The steady-state level of olmesartan is achieved after once a day dosing during 3 to 5 days.
Toxicity
The reported LD50 of olmesartan in dogs was reported to be greater of 1500 mg/kg. Overdose is expressed as hypotension, tachycardia, and bradycardia when there is parasympathetic stimulation. In case of overdose, supportive treatment is recommended.
Olmesartan was shown to be safe on carcinogenic and fertility studies. However, in in vitro mutagenic studies showed a potential to induce chromosomal aberrations in cells and it tested positive for thymidine kinase mutations in the mouse lymphoma assay.
Chemical properties
White Solid
The Uses of Olmesartan
Olmesartan Acid (Olmesartan EP Impurity A) is an angiotensin II receptor antagonist. Used as an anti-hypertensive.
The Uses of Olmesartan
An labelled angiotensin II receptor antagonist. Used as an anti-hypertensive
The Uses of Olmesartan
Angiotensin II inhibitor, antihypertensive
The Uses of Olmesartan
An angiotensin II (AT1) receptor antagonist
Background
Olmesartan belongs to the angiotensin II receptor blocker (ARB) family of drugs, which also includes telmisartan, candesartan, losartan, valsartan, and irbesartan. ARBs selectively bind to angiotensin receptor 1 (AT1) and prevent the protein angiotensin II from binding and exerting its hypertensive effects, which include vasoconstriction, stimulation and synthesis of aldosterone and ADH, cardiac stimulation, and renal reabsorption of sodium, among others. Overall, olmesartan's physiologic effects lead to reduced blood pressure, lower aldosterone levels, reduced cardiac activity, and increased excretion of sodium.
Olmesartan also affects the renin-angiotensin aldosterone system (RAAS), which plays an important role in hemostasis and regulation of kidney, vascular, and cardiac functions. Pharmacological blockade of RAAS via AT1 receptor blockade inhibits negative regulatory feedback within RAAS, which is a contributing factor to the pathogenesis and progression of cardiovascular disease, heart failure, and renal disease. In particular, heart failure is associated with chronic activation of RAAS, leading to inappropriate fluid retention, vasoconstriction, and ultimately a further decline in left ventricular function. ARBs have been shown to have a protective effect on the heart by improving cardiac function, reducing afterload, increasing cardiac output and preventing ventricular hypertrophy and remodelling.
By comparison, the angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor (ACEi) class of medications (which includes drugs such as ramipril, lisinopril, and perindopril) inhibit the conversion of angiotensin I to angiotensin II through inhibition of the ACE enzyme. However, this does not prevent the formation of all angiotensin II within the body. The angiotensin II receptor blocker (ARB) family of drugs unique in that it blocks all angiotensin II activity, regardless of where or how it was synthesized.
Olmesartan is commonly used for the management of hypertension and Type 2 Diabetes-associated nephropathy, particularly in patients who are unable to tolerate ACE inhibitors. ARBs such as olmesartan have been shown in a number of large-scale clinical outcomes trials to improve cardiovascular outcomes including reducing risk of myocardial infarction, stroke, the progression of heart failure, and hospitalization. Like other ARBs, olmesartan blockade of RAAS slows the progression of diabetic nephropathy due to its renoprotective effects.
Orally available olmesartan is produced as the prodrug olmesartan medoxomil which is rapidly converted in vivo to the pharmacologically active olmesartan. It was developed by Daiichi Sankyo Pharmaceuticals and approved in 2002.
What are the applications of Application
Olmesartan acid is an angiotensin II (AT1) receptor antagonist
Indications
Olmesartan is indicated for the treatment of hypertension either alone or in combination with other antihypertensive agents.
Olmesartan is also used off-label for the management Type 2 Diabetes-associated nephropathy, heart failure, and post-myocardial infarction, particularly in patients who are unable to tolerate ACE inhibitors. ARBs such as olmesartan have been shown in a number of large-scale clinical outcomes trials to improve cardiovascular outcomes including reducing risk of myocardial infarction, stroke, the progression of heart failure, and hospitalization. Like other ARBs, olmesartan blockade of RAAS slows the progression of diabetic nephropathy due to its renoprotective effects.
Definition
ChEBI: Olmesartan is a biphenylyltetrazole. It has a role as an antihypertensive agent and an angiotensin receptor antagonist.
General Description
Olmesartan medoxomil, (5-methyl-2-oxo-1,3-dioxol-4-yl)methyl-5-(2-hydroxypropan-2-yl)-2-propyl-3-[[4-[2-(2H-tetrazol-5-yl)phenyl]phenyl]methyl]imidazole-4-carboxylate (Benicar, Olmetec) uses the tetrazolering system as its acidic system, which participates inreceptor binding.When administered to a patient, the drugis rapidly and completely bioactivated by ester hydrolysis ofthe medoxomil during absorption from the gastrointestinaltract. Once the prodrug is converted to the active form, virtuallyno further metabolism occurs. In September 2007, theFood and Drug Administration (FDA) approved its use as acombination product with the calcium channel blocker amlodipinefor the management of hypertension. This combinationproduct is sold under the tradename of Azor.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Olmesartan possesses anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidative stress properties. It protects neuronal cells against oligomerized amyloid β (Aβ)-induced cellular senescence.
Pharmacokinetics
Overall, olmesartan's physiologic effects lead to reduced blood pressure, lower aldosterone levels, reduced cardiac activity, and increased excretion of sodium.
Hypotension in Volume- or Salt-Depleted Patients
In patients with an activated renin-angiotensin aldosterone system, such as volume-and/or salt-depleted patients (e.g., those being treated with high doses of diuretics), symptomatic hypotension may be anticipated after initiation of treatment with olmesartan. Initiate treatment under close medical supervision. If hypotension does occur, place the patient in the supine position and, if necessary, give an intravenous infusion of normal saline. A transient hypotensive response is not a contraindication to further treatment, which usually can be continued without difficulty once the blood pressure has stabilized.
Valvular Stenosis: there is concern on theoretical grounds that patients with aortic stenosis might be at a particular risk of decreased coronary perfusion, because they do not develop as much afterload reduction.
Impaired Renal Function
As a consequence of inhibiting the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system, changes in renal function may be anticipated in susceptible individuals treated with olmesartan. In patients whose renal function may depend upon the activity of the renin-angiotensin- aldosterone system (e.g., patients with severe congestive heart failure), treatment with angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors and angiotensin receptor antagonists has been associated with oliguria and/or progressive azotemia and rarely with acute renal failure and/or death. Similar results may be anticipated in patients treated with olmesartan.
In studies of ACE inhibitors in patients with unilateral or bilateral renal artery stenosis, increases in serum creatinine or blood urea nitrogen (BUN) have been reported. There has been no long-term use of olmesartan medoxomil in patients with unilateral or bilateral renal artery stenosis, but similar results may be expected.
Sprue-like Enteropathy
Severe, chronic diarrhea with substantial weight loss has been reported in patients taking olmesartan months to years after drug initiation. Intestinal biopsies of patients often demonstrated villous atrophy. If a patient develops these symptoms during treatment with olmesartan, exclude other etiologies. Consider discontinuation of olmesartan medoxomil in cases where no other etiology is identified.
Electrolyte Imbalances
Olmesartan medoxomil contains olmesartan, a drug that inhibits the renin-angiotensin system (RAS). Drugs that inhibit the RAS can cause hyperkalemia. Monitor serum electrolytes periodically.
Metabolism
Olmesartan medoxomil is rapidly and completely bioactivated by ester hydrolysis to olmesartan during absorption from the gastrointestinal tract. This rapid first-pass metabolism was confirmed by the lack of measurable amounts of olmesartan medoxomil in plasma or excreta. This first-pass metabolism is not driven by cytochrome enzymes and hence it is not expected to interact with other drugs via this mechanism.
The pharmacologically active moiety does not appear to undergo further metabolism.
Storage
Store at +4°C
Properties of Olmesartan
| Melting point: | 186-188°C |
| Boiling point: | 738.3±70.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.33 |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | DMSO (Slightly), Methanol (Slightly, Heated) |
| pka | 2.39±0.50(Predicted) |
| form | powder |
| color | white to beige |
| Stability: | Hygroscopic |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 144689-24-7(CAS DataBase Reference) |
Safety information for Olmesartan
Computed Descriptors for Olmesartan
Olmesartan manufacturer
Clickchem Research LLP
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran




You may like
-
 144689-24-7 Olmesartan EP imp A 98%View Details
144689-24-7 Olmesartan EP imp A 98%View Details
144689-24-7 -
 Olmesartan EP Impurity A 144689-24-7 98%View Details
Olmesartan EP Impurity A 144689-24-7 98%View Details
144689-24-7 -
 144689-24-7 98%View Details
144689-24-7 98%View Details
144689-24-7 -
 144689-24-7 98%View Details
144689-24-7 98%View Details
144689-24-7 -
 Olmesartan 144689-24-7 98%View Details
Olmesartan 144689-24-7 98%View Details
144689-24-7 -
 144689-24-7 99%View Details
144689-24-7 99%View Details
144689-24-7 -
 Olmesartan CAS 144689-24-7View Details
Olmesartan CAS 144689-24-7View Details
144689-24-7 -
 Olmesartan CAS 144689-24-7View Details
Olmesartan CAS 144689-24-7View Details
144689-24-7
