NORBORMIDE
- CAS NO.:991-42-4
- Empirical Formula: C33H25N3O3
- Molecular Weight: 511.57
- MDL number: MFCD01632784
- EINECS: 213-589-6
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-10-28 16:00:23
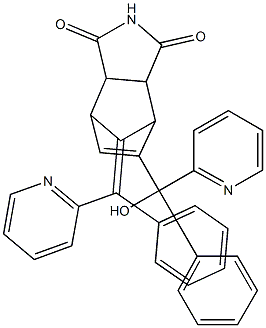
What is NORBORMIDE?
Description
Norbormide was first introduced on the market in 1964 as a selective raticide, but does not have a current registration for commercial use in the European Union or North America. Current use as a pesticide is minimal to nonexistent worldwide. This compound’s toxicity is highly specific for rats.
Chemical properties
White solid. Insoluble in water; soluble in dilute acids.
Chemical properties
Nonyl trichlorosilane is a clear fuming liquid. Irritating odor.
The Uses of NORBORMIDE
Norbormide is used as a rodenticide. It acts as a vasoconstrictor and calcium channel blocker, but is selectively toxic to rats and has relatively low toxicity to other species, due to a species specific action of opening the permeability transition pores in rat mitochondria.
The Uses of NORBORMIDE
The only commercial use was as a rodenticide specifically for Rattus species. However, there have been some reports of this compound or its derivatives being investigated as a calcium channel blocker for use as a potential drug to treat human cardiovascular disease.
Definition
A rodenticide specific for rats, supposedly nontoxic to other animals or to humans .
General Description
Colorless to off-white crystalline powder. Used as a selective rat poison.
Reactivity Profile
When heated to decomposition, NORBORMIDE emits toxic fumes of nitrogen oxides. Avoid alkalis. [EPA, 1998].
Hazard
Toxic by ingestion.
Health Hazard
Moderately to highly toxic to humans. Probable human lethal dose is 50 to 500 mg/kg, or 1 teaspoon to 1 pint for a 150 lb. person.
Fire Hazard
When heated to decomposition, NORBORMIDE emits toxic fumes of nitrogen oxides. Avoid alkalies.
Safety Profile
Poison by ingestion andintravenous routes. A rodenticide. When heated todecomposition it emits toxic fumes of NOx.
Potential Exposure
This material is used as a selective, fast acting rat poison.
Environmental Fate
Because of its use as a rodenticide, norbormide may have entered the environment, particularly as a soil contaminant. The vapor pressure for norbormide is estimated to be 4.3 ×10-22 mmHg at 25 ℃, while Henry’s constant is 2.7 × 10-23 atmm3 mol-1. Therefore, volatilization from wet or dry soil is not likely to occur. If present in contaminated soil, norbormide may be transported in the air and undergo wet or dry deposition. Also, with a Koc of 2000, there would be some minor soil mobility. The high Koc coupled with a bioconcentration factor (BCF) of 290 predicts that norbormide contaminating aquatic systems would adsorb to suspended solids or sediments and would bioconcentrate.
Shipping
UN2588 Pesticides, solid, toxic, Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials, Technical Name Required.
Toxicity evaluation
Norbormide causes an extreme and irreversible vasoconstriction in small arteries in rats following both systemic and local administration. However, large rat arteries (e.g., aorta), nonvascular rat smooth muscles (e.g., duodenum and trachea), and all smooth muscles from non-rat species do not constrict even at high concentrations/doses of norbormide. The massive peripheral vasoconstriction in small rat arteries subsequently reduces coronary blood flow rate, leading to cardiac arrhythmias and possible death. However, small artery vasoconstriction in vascular beds supplying other organs (e.g., brain, kidney, and liver) and subsequent severe ischemic damage are likely responsible for death in most cases. The norbormideinduced vasoconstriction is mediated by activation of phospholipase C/protein kinase C and calcium influx via L-type voltage-dependent calcium channels. In contrast, norbormideresistant arteries and smooth muscles exhibit inhibition of L-type voltage-dependent calcium channels and instead exhibit a mild relaxation response. A lethal dose of norbormide in rats (1 g kg-1) can also elevate the blood glucose level twofold with a decrease in both liver and muscle glycogen. Exposed animals became comatose within 30 min to 2 h after treatment. The hyperglycemic effect of this compound in rats is considered to be a secondary effect.
Incompatibilities
Compounds of the carboxyl group react with all bases, both inorganic and organic (i.e., amines) releasing substantial heat, water and a salt that may be harmful. Incompatible with arsenic compounds (releases hydrogen cyanide gas), diazo compounds, dithiocarbamates, isocyanates, mercaptans, nitrides, and sulfides (releasing heat, toxic and possibly flammable gases), thiosulfates and dithionites (releasing hydrogen sulfate and oxides of sulfur).
Waste Disposal
Small amounts may be treated with alkali, then landfilled. Large amounts should be incinerated . In accordance with 40CFR165, follow recommendations for the disposal of pesticides and pesticide containers. Must be disposed properly by following package label directions or by contacting your local or federal environmental control agency, or by contacting your regional EPA office.
Properties of NORBORMIDE
| Melting point: | 190-198° |
| Boiling point: | 598.31°C (rough estimate) |
| Density | 1.2065 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.7800 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | Amber Vial, -20°C Freezer, Under inert atmosphere |
| solubility | Chloroform (Slightly), Methanol (Slightly, Heated) |
| form | Solid |
| color | Crystals |
| Water Solubility | 60mg/L(room temperature) |
| Stability: | Light Sensitive |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Norbormide (991-42-4) |
Safety information for NORBORMIDE
Computed Descriptors for NORBORMIDE
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 1-methylindoline-2,3-dione 98%View Details
1-methylindoline-2,3-dione 98%View Details
2058-74-4 -
 614-19-7 98%View Details
614-19-7 98%View Details
614-19-7 -
 3112-85-4 Methyl phenyl sulfone 98%View Details
3112-85-4 Methyl phenyl sulfone 98%View Details
3112-85-4 -
 20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 -
 3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 -
 4,6-dichloropyrimidine-5-carbaldehyde 98%View Details
4,6-dichloropyrimidine-5-carbaldehyde 98%View Details
5305-40-8
