Nicorandil
Synonym(s):2-(Pyridine-3-carbonylamino)ethyl nitrate;2-Nicotinamidoethyl nitrate;Ikorel;N-[2-(Nitrooxy)ethyl]-3-pyridinecarboxamide;SG-75
- CAS NO.:65141-46-0
- Empirical Formula: C8H9N3O4
- Molecular Weight: 211.17
- MDL number: MFCD00186520
- EINECS: 265-514-1
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-23 21:30:31
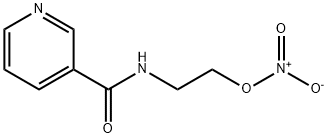
What is Nicorandil?
Absorption
Following oral administration, nicorandil is well absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract with the oral bioavailability of 75% with the maximum peak plasma concentration (Cmax) reached within 30-60 minutes. The mean Cmax is Cmax then is approximately 300 ng/ml . Steady-state plasma concentrations of nicorandil usually are reached within approximately 96-120 h after twice daily dosing (10 or 20mg) .
Toxicity
Common adverse effects include lethargy, back pain, chest pain, infection, feeling of weakness. In the cardiovascular system, hypotension, increased heart rate in higher doses, palpitations, worsened angina pectoris and vasodilation/flush may be observed. Dyspepsia, nausea, and vomiting may occur as gastrointestinal disorders. Headaches may arise from vasodilation. Other common side effects include myalgia, bronchitis, dyspnoea, and respiratory disorder . Nicorandil does not affect fertility of male or female rats, and shows no potential in carcinogenic, mutagenic or genotoxic studies . Oral LD50 values in mouse, rat and dog are 626 mg/kg, 1220 mg/kg and 62.5 mg/kg, respectively .
Chemical properties
Nicorandil is N-(2-hydroxyethyl)-nicotinamide nitrate (ester). It is a white crystalline powder or white needles with a faint, characteristic odour. It is freely soluble in methanol, ethanol, acetone or glacial acetic acid, slightly soluble in chloroform or water, almost insoluble in ether or benzene. Melting point 88.5-93.5 ℃. Acute toxicity LD50 rat (mg/kg): 1200-1300 orally, 800-1000 intravenously.
Originator
Chugai (Japan)
The Uses of Nicorandil
Nicorandil is a vasodilator used for the prophylaxis and treatment of angina. This medication widens blood vessels thus increasing the blood and oxygen flow to the heart. It is not currently available in the US.
Nicorandil is a nitric oxide donor and ATP-sensitive potassium channel opener. A study showed that Nicorandil is able to protect against stress-induced cell death in dystrophin-deficient cardiomyocytes and also preserve cardiac function in the mdx mouse heart subjected to ischemia and reperfusion injury.
Indications
Indicated for the prevention and treatment of chronic stable angina pectoris and reduction in the risk of acute coronary syndromes.
Background
Nicorandil is an orally efficacious vasodilatory drug and antianginal agent marketed in the UK, Australia, most of Europe, India, Philippines, Japan, South Korea, and Taiwan. It is not an approved drug by FDA. It is a niacinamide derivative that induces vasodilation of arterioles and large coronary arteries by activating potassium channels. It is often used for patients with angina who remain symptomatic despite optimal treatment with other antianginal drugs . Nicorandil is a dual-action potassium channel opener that relaxes vascular smooth muscle through membrane hyperpolarization via increased transmembrane potassium conductance and increased intracellular concentration of cyclic GMP. It is shown to dilate normal and stenotic coronary arteries and reduces both ventricular preload and afterload .
What are the applications of Application
Nicorandil is a small molecule KATP (Kir6) channel opener and NO donor
Definition
ChEBI: Nicorandil is a pyrimidinecarboxamide that is nicotinamide in which one of the hydrogens attached to the carboxamide nitrogen is replaced by a 2-(nitrooxy)ethyl group. It has both nitrate-like and ATP-sensitive potassium channel activator properties, and is used for the prevention and treatment of angina pectoris. It has a role as a vasodilator agent and a potassium channel opener. It is a pyridinecarboxamide and a nitrate ester. It derives from a nicotinamide.
Preparation
Nicorandil is obtained by treating nicotinic acid chloride hydrochloride with nitro-oxy-ethyl-amine nitrate in an organic solvent.
Nicorandil was synthesized from 2-aminoethanol by a four step process. In order to protect the amino group during nitration, 2-aminoethanol was first treated with phthalic anhydride. The amide formed was then nitrated using a nitrating mixture and was subsequently deprotected by reacting with hydrazine hydrate. The 2- nitroxyethylamine obtained was condensed with nicotinoyl chloride in pyridine. Treatment with aqueous sodium bicarbonate solution gave nicorandil as free base.
synthesis of Nicorandil
brand name
SIGMART; PERISALOL
Biochem/physiol Actions
Nicorandil is a hybrid ATP-sensitive K+ (KATP) channel opener and nicotinamide nitrate NO donor. Nicorandil selectively activates SUR2B- versus SUR2A-containing KATP channels. It enhances endothelial NO synthase expression and protects against ischemic ventricular arrhythmias. By activating potassium channels, and donating nitric oxide to activate the enzyme guanylate cyclase, Nicorandil causes activation of GMP leading to both arterial and venous vasodilatation. Nicorandil is selective for vascular potassium channels, but has no significant action on cardiac contractility and conduction.
Pharmacokinetics
Nicorandil is a potassium channel opener with nitrovasodilator (NO donor) actions, making it both an arterial and a venous dilator . It causes sustained dilation of both the arterial resistance and conductive vessels that increases coronary blood flow, however the effect of the drug on coronary arteries does not involve the coronary steal phenomenon . Activation of potassium channels lead to hyperpolarization of the smooth muscle cells, followed by arterial dilation and afterload reduction. Nicorandil is shown to increase pooling in the capacitance vessels with a decrease in preload through relaxing the venous vascular system. Overall, improved blood flow and reduced infarct size are achieved through reduction of end-diastolix pressure and decreased extravascular component of vascular resistance . Open studies showed the effectiveness of nicorandil treatment on various types of angina pectoris .
Clinical Use
Nicorandil is used for the prevention and treatment of chronic stable angina. It is usually used when angina becomes difficult to control by other drugs and is given as an additional treatment.
Drug interactions
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs
Avanafil, sildenafil, tadalafil and vardenafil: enhanced
hypotensive effect - avoid.
Riociguat: possible enhanced hypotensive effect -
avoid.
Metabolism
Nicorandil undergoes extensive hepatic metabolism . The main biotransformation pathways of nicorandil are denitration, followed by subsequent nicotinamide metabolism. The main pharmacologically inactive denitrated metabolite 2-nicotinamidoethanol can be detected in the urine. The derivatives formed from the nicotinamide metabolism of denitrated products are nicotinuric acid, nicotinamide, N-methylnicotinamide and nicotinic acid .
Metabolism
Metabolism of nicorandil is mainly by denitration of the molecule into the nicotinamide pathway. About 20% of a dose is excreted in the urine mainly as metabolites
Mode of action
The coronary vasodilating activity of nicorandil is considered to be the consequence of the increasing cyclic GMP production by stimulating guanylyl cyclase in the coronary vascular smooth muscle, similar to other nitrates/nitrites (in vitro). In addition, other mechanisms such as hyperpolarization of the cell membrane were investigated concerning its coronary blood flowincreasing and coronary vasospasmolytic effects.
The vasorelaxant effect of nicorandil in isolated blood vessels is suppressed by an ATP-sensitive K channel blocker or a guanylate cyclase inhibitor. Moreover, in a canine model of acute heart failure, the cardiac haemodynamics-improving effect of the drug (e.g. effect of increasing the aortic blood flow) was suppressed by an ATP-sensitive K channel blocker. Furthermore, the drug caused an increase in the cGMP content in isolated blood vessels. These facts suggest that the vasodilating effect of the drug is related to the effect of opening the ATP-sensitive K channel, as well as to the effect of increasing production of cGMP.
Properties of Nicorandil
| Melting point: | 92°C |
| Boiling point: | 350.85°C (rough estimate) |
| Density | 1.4271 (rough estimate) |
| RTECS | US4667600 |
| refractive index | 1.7400 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | DMSO: >10mg/mL |
| form | powder |
| pka | 12.70±0.46(Predicted) |
| color | white to off-white |
| Merck | 14,6521 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 65141-46-0 |
Safety information for Nicorandil
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Flame Flammables GHS02  Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H242:Self-reactive substances and mixtures; and Organic peroxides H302:Acute toxicity,oral |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P210:Keep away from heat/sparks/open flames/hot surfaces. — No smoking. P235:Keep cool. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P301+P312:IF SWALLOWED: call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician IF you feel unwell. P370+P378:In case of fire: Use … for extinction. P410:Protect from sunlight. |
Computed Descriptors for Nicorandil
Nicorandil manufacturer
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
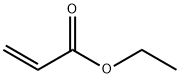
You may like
-
 Nicorandil 98%View Details
Nicorandil 98%View Details
65141-46-0 -
 65141-46-0 98%View Details
65141-46-0 98%View Details
65141-46-0 -
 Nicorandil 95% CAS 65141-46-0View Details
Nicorandil 95% CAS 65141-46-0View Details
65141-46-0 -
 Nicorandil, ≥98% (HPLC) CAS 65141-46-0View Details
Nicorandil, ≥98% (HPLC) CAS 65141-46-0View Details
65141-46-0 -
 Nicorandil CAS 65141-46-0View Details
Nicorandil CAS 65141-46-0View Details
65141-46-0 -
 Nicorandil DrugView Details
Nicorandil DrugView Details
65141-46-0 -
 Nicorandil Powder APIView Details
Nicorandil Powder APIView Details
65141-46-0 -
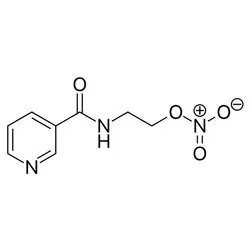 NicorandilView Details
NicorandilView Details
65141-46-0
