NAPHTHENIC ACID
- CAS NO.:1338-24-5
- Empirical Formula: C7H10O2
- Molecular Weight: 126.154
- MDL number: MFCD00147696
- EINECS: 215-662-8
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-09-25 17:15:13
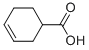
What is NAPHTHENIC ACID?
Chemical properties
CLEAR YELLOWISH TO BROWN VISCOUS LIQUID
Chemical properties
Naphthenic acid is a gold to black, odorless liquid.
The Uses of NAPHTHENIC ACID
The term naphthenic acid, as commonly used in the petroleum industry, refers collectively to all of the carboxylic acids present in crude oil.
The Uses of NAPHTHENIC ACID
Naphthenic acid is commonly used in the synthesis of useful metal naphthenates such as copper naphthenate, a wood preservative; titanium naphthenate, a precursor for the preparation of titanium oxide thin films and a rare earth naphthenate, a lubricant oil additive. It can also be in the synthesis of biodegradable naphthenic acid ionic liquids.
What are the applications of Application
Naphthenic acid is an unspecific mixture of several cyclopentyl and cyclohexyl carboxylic acids
General Description
NAPHTHENIC ACID is a dark colored liquid with an offensive odor. NAPHTHENIC ACID is insoluble in water. NAPHTHENIC ACID will burn though NAPHTHENIC ACID may take some effort to ignite. The primary hazard is the threat to the environment. Immediate steps should be taken to limit its spread to the environment. Since NAPHTHENIC ACID is a liquid NAPHTHENIC ACID can easily penetrate the soil and contaminate groundwater and nearby streams. NAPHTHENIC ACID is used to make paint dryers, detergents, and solvents.
Air & Water Reactions
Insoluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
NAPHTHENIC ACID is a carboxylic acid. Carboxylic acids donate hydrogen ions if a base is present to accept them. They react in this way with all bases, both organic (for example, the amines) and inorganic. Their reactions with bases, called "neutralizations", are accompanied by the evolution of substantial amounts of heat. Neutralization between an acid and a base produces water plus a salt. Carboxylic acids with six or fewer carbon atoms are freely or moderately soluble in water; those with more than six carbons are slightly soluble in water. Soluble carboxylic acid dissociate to an extent in water to yield hydrogen ions. The pH of solutions of carboxylic acids is therefore less than 7.0. Many insoluble carboxylic acids react rapidly with aqueous solutions containing a chemical base and dissolve as the neutralization generates a soluble salt. Carboxylic acids in aqueous solution and liquid or molten carboxylic acids can react with active metals to form gaseous hydrogen and a metal salt. Such reactions occur in principle for solid carboxylic acids as well, but are slow if the solid acid remains dry. Even "insoluble" carboxylic acids may absorb enough water from the air and dissolve sufficiently in NAPHTHENIC ACID to corrode or dissolve iron, steel, and aluminum parts and containers. Carboxylic acids, like other acids, react with cyanide salts to generate gaseous hydrogen cyanide. The reaction is slower for dry, solid carboxylic acids. Insoluble carboxylic acids react with solutions of cyanides to cause the release of gaseous hydrogen cyanide. Flammable and/or toxic gases and heat are generated by the reaction of carboxylic acids with diazo compounds, dithiocarbamates, isocyanates, mercaptans, nitrides, and sulfides. Carboxylic acids, especially in aqueous solution, also react with sulfites, nitrites, thiosulfates (to give H2S and SO3), dithionites (SO2), to generate flammable and/or toxic gases and heat. Their reaction with carbonates and bicarbonates generates a harmless gas (carbon dioxide) but still heat. Like other organic compounds, carboxylic acids can be oxidized by strong oxidizing agents and reduced by strong reducing agents. These reactions generate heat. A wide variety of products is possible. Like other acids, carboxylic acids may initiate polymerization reactions; like other acids, they often catalyze (increase the rate of) chemical reactions.
Health Hazard
Principal effect is that of mild primary irritation when encountered in high concentrations. Inhalation of vapor causes coughing. Liquid is moderately irritating to eyes and slightly to moderately irritating to skin; excessive exposure could result in dermatitis.
Flammability and Explosibility
Not classified
Safety Profile
Moderately toxic by ingestion and intraperitoneal routes. When heated to decomposition it emits acrid smoke and irritating fumes.
Potential Exposure
Used to make metallic naphthenates for paint dryers and cellulose preservatives. It is also used as a solvent; detergent, rubber reclaiming agent. Used in catalysts, cutting oils; drilling compounds; rust inhibitors; surfactants, emulsions, grease, and wood preservatives.
Shipping
UN3082 Environmentally hazardous substances, liquid, n.o.s., Hazard Class: 9; Labels: 9-Miscellaneous hazardous material, Technical Name Required.
Incompatibilities
Compounds of the carboxyl group react with all bases, both inorganic and organic (i.e., amines) releasing substantial heat, water, and a salt that may be harmful. Incompatible with arsenic compounds (releases hydrogen cyanide gas), diazo compounds, dithiocarbamates, isocyanates, mercaptans, nitrides, and sulfides (releasing heat, toxic, and possibly flammable gases), thiosulfates and dithionites (releasing hydrogen sulfate and oxides of sulfur). Incompatible with sulfuric acid, caustics, ammonia, aliphatic amines; alkanolamines, isocyanates, alkylene oxides; epichlorohydrin, strong oxidizers. Corrosive to metals.
Properties of NAPHTHENIC ACID
| Boiling point: | 160-198 °C (6 mmHg) |
| Density | 0.92 g/mL at 20 °C (lit.) |
| vapor pressure | 31.4Pa at 25℃ |
| refractive index | n |
| Flash point: | 149 °C |
| solubility | Practically insoluble in water |
| form | Liquid |
| pka | 5[at 20 ℃] |
| color | Clear colorless to yellow-brown |
| Water Solubility | 88.1mg/L at 20℃ |
| FreezingPoint | -30~-36℃ |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Naphthenic acids (1338-24-5) |
Safety information for NAPHTHENIC ACID
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H317:Sensitisation, Skin H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P302+P352:IF ON SKIN: wash with plenty of soap and water. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for NAPHTHENIC ACID
| InChIKey | VUSWCWPCANWBFG-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


You may like
-
 Naphthenic Acid CAS 1338-24-5View Details
Naphthenic Acid CAS 1338-24-5View Details
1338-24-5 -
 Naphthenic acid CAS 1338-24-5View Details
Naphthenic acid CAS 1338-24-5View Details
1338-24-5 -
 3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 614-19-7 98%View Details
614-19-7 98%View Details
614-19-7 -
 20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 -
 3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 -
 4,6-dichloropyrimidine-5-carbaldehyde 98%View Details
4,6-dichloropyrimidine-5-carbaldehyde 98%View Details
5305-40-8
