N-ISOVALERYLGLYCINE
Synonym(s):[(3-Methylbutanoyl)amino]acetic acid;N-(3-Methyl-1-oxobutyl)glycine;N-(3-Methylbutanoyl)glycine
- CAS NO.:16284-60-9
- Empirical Formula: C7H13NO3
- Molecular Weight: 159.18
- MDL number: MFCD00059629
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-11-13 21:11:14
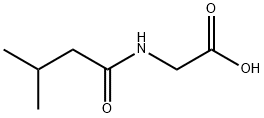
What is N-ISOVALERYLGLYCINE?
Description
Isovaleroylglycine is a compound found in the urine of patients with isovaleric acidemia, a disorder created by defective leucine metabolism due to a deficiency in the isovaleryl coenzyme A dehydrogenase. It has been used as a diagnostic tool in the diagnosis of various acidemias and mitochondrial fatty acid β-oxidation defects.
Chemical properties
White to Off-White Solid
The Uses of N-ISOVALERYLGLYCINE
N-Isovalerylglycine is a useful diagnostic tool in the diagnosis of many organic acidemias and mitochondrial fatty acid β-oxidation defects. N-Isovalerylglycine is found in the urine of patients with isovaleric acidemia, an inborn error of leucine metabolism.
Definition
ChEBI: An N-acylglycine in which the acyl group is specified as isovaleryl.
Properties of N-ISOVALERYLGLYCINE
| Melting point: | 105°C |
| Boiling point: | 371.8±25.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.097±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | Sealed in dry,Room Temperature |
| solubility | DMSO (Slightly), Methanol (Slightly) |
| form | Solid |
| pka | 3.58±0.10(Predicted) |
| color | White to Off-White |
| BRN | 1766622 |
Safety information for N-ISOVALERYLGLYCINE
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for N-ISOVALERYLGLYCINE
New Products
4-AMINO-TETRAHYDRO-PYRAN-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID HCL 4-(Dimethylamino)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-4-carbonitrile 4-Aminotetrahydropyran-4-carbonitrile Hydrochloride (R)-3-Aminobutanenitrile Hydrochloride 3-((Dimethylamino)methyl)-5-methylhexan-2-one oxalate 1,4-Dioxa-8-azaspiro[4.5]decane 5-Bromo-2-nitropyridine Diclofenac Potassium Ornidazole IP Diclofenac Sodium IP/BP/EP/USP Mefenamic Acid IP/BP/EP/USP Aceclofenac IP/BP/EP Nimesulide BP SODIUM AAS SOLUTION ZINC AAS SOLUTION BUFFER SOLUTION PH 10.0(BORATE) GOOCH CRUCIBLE SINTERED AQUANIL 5 BERYLLIUM AAS SOLUTION AMOXICILLIN (AMOXYCILLIN) TRIHYDRATE Methylcobalamin (vitamin B12) SODIUM VALPROATE SODIUM METHYL PARABEN LAMOTRIGINERelated products of tetrahydrofuran


You may like
-
 N-Isovalerylglycine CAS 16284-60-9View Details
N-Isovalerylglycine CAS 16284-60-9View Details
16284-60-9 -
 N-Isovaleroylglycine 95% CAS 16284-60-9View Details
N-Isovaleroylglycine 95% CAS 16284-60-9View Details
16284-60-9 -
 89796-99-6 Aceclofenac IP/BP/EP 98%View Details
89796-99-6 Aceclofenac IP/BP/EP 98%View Details
89796-99-6 -
 61-68-7 98%View Details
61-68-7 98%View Details
61-68-7 -
 Diclofenac Sodium IP/BP/EP/USP 98%View Details
Diclofenac Sodium IP/BP/EP/USP 98%View Details
15307-79-6 -
 Ornidazole IP 16773-42-5 98%View Details
Ornidazole IP 16773-42-5 98%View Details
16773-42-5 -
 51803-78-2 Nimesulide BP 98%View Details
51803-78-2 Nimesulide BP 98%View Details
51803-78-2 -
 15307-81-0 98%View Details
15307-81-0 98%View Details
15307-81-0
Statement: All products displayed on this website are only used for non medical purposes such as industrial applications or scientific research, and cannot be used for clinical diagnosis or treatment of humans or animals. They are not medicinal or edible.