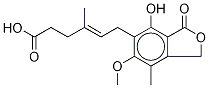
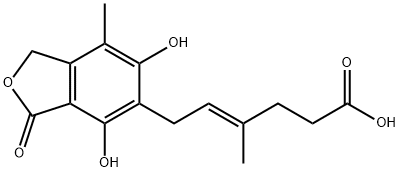
Mycophenolic acid
Synonym(s):6-(1,3-Dihydro-7-hydroxy-5-methoxy-4-methyl-1-oxoisobenzofuran-6-yl)-4-methyl-4-hexanoic acid;6-(4-Hydroxy-6-methoxy-7-methyl-3-oxo-5-phthalanyl)-4-methyl-4-hexenoic acid;6-(4-Hydroxy-6-methoxy-7-methyl-3-oxo-5-phthalanyl)-4-methyl-4-hexenoic Acid, MPA;Mycophenolic Acid - CAS 24280-93-1 - Calbiochem;NSC 129185
- CAS NO.:24280-93-1
- Empirical Formula: C17H20O6
- Molecular Weight: 320.34
- MDL number: MFCD00036814
- EINECS: 246-119-3
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-24 15:44:27

What is Mycophenolic acid ?
Absorption
Between 360 mg and 2,160 mg, mycophenolic acid follows a linear and dose-proportional pharmacokinetic profile. The enteric-coating of mycophenolic acid tablets prevents release under acidic conditions (stomach, pH < 5). However, enteric-coated mycophenolic acid tablets are highly soluble in neutral pH conditions such as those in the intestine. In renal transplant patients, the median delay (Tlag) in the rise of mycophenolic acid concentration ranged between 0.25 and 1.25 hours, and the Tmax ranged between 1.5 and 2.75 hours. Adult renal transplant patients on cyclosporine given mycophenolic acid had a Tmax of 2 h, a Cmax of 26.1 μg/mL, and an AUC0-12 of 66.5 μg?h/mL. Stable pediatric (5-16 years old) renal transplant patients had a Cmax and AUC 33% and 18% higher than the ones detected in adults.
In stable renal transplant patients treated with cyclosporine, the gastrointestinal absorption and absolute bioavailability of delayed-release tablets of mycophenolic acid were 93% and 72%, respectively. Following the administration of a high-fat meal (55 g fat, 1000 calories), the AUC of mycophenolic acid (enteric-coated tablets, 720 mg) was comparable to the one detected during fasting. However, a high-fat meal can lead to a 33% decrease of the Cmax, a 3.5-hour delay in the Tlag (range of -6 to 18 hours), and a 5.0-hour delay in the Tmax (range of -9 to 20 hours). To avoid variability in the absorption of mycophenolic acid, this drug should be taken on an empty stomach.
Toxicity
There are anecdotal reports of deliberate or accidental overdoses with mycophenolic acid; however, not all patients have experienced related adverse reactions. In those cases where adverse reactions have been reported, reactions fall within the safety profile of its class of drugs. A mycophenolic acid overdose could lead to the oversuppression of the immune system and increase the susceptibility to infection. It may be appropriate to interrupt or discontinue mycophenolic acid if blood dyscrasias occur. Some of the signs and symptoms associated with mycophenolic acid overdose are hematological abnormalities, such as leukopenia and neutropenia, and gastrointestinal symptoms, such as abdominal pain, diarrhea, nausea and vomiting, and dyspepsia.
Carcinogenicity studies of 104 weeks done in rats and mice, suggest that mycophenolate sodium does not induce the formation of tumours. Rats were given up to 9 mg/kg of mycophenolate sodium, which corresponded to 0.6-1.2 times the systemic exposure observed in renal transplant patients, while mice were given 180 mg/kg, an equivalent of 0.6 times the mycophenolate sodium therapeutic dose. The genotoxicity of mycophenolate sodium was confirmed by the mouse lymphoma/thymidine kinase assay, the micronucleus test in V79 Chinese hamster cells, and the in vivo mouse micronucleus assay. Mycophenolate mofetil, a prodrug of mycophenolic acid, had a similar genotoxic profile. At daily oral doses as high as 18 mg/kg and 20 mg/kg, mycophenolate sodium had no effect on male and female rat fertility, respectively. The oral LD50 of mycophenolic acid is 352 mg/kg in rats and 1000 mg/kg in mice.
Description
Mycophenolic acid is an immunosuppresive microbial metabolite that has been found in P. brevicompactum. It is also an active metabolite of mycophenolate mofetil that is formed via carboxylesterase 1 (CES1) and CES2. Mycophenolic acid is an inhibitor of IMP dehydrogenase (IMPDH) type I and type II (IC50s = 32 and 11 nM, respectively, in cell-free assays) and inhibits DNA synthesis in L strain mouse fibroblasts when used at concentrations ranging from 0.1 to 10 μg/ml. It is active against several strains of C. albicans, C. parakrusei, C. tropicalis, and C. neoformans (MICs = 3.9-31.25 μg/ml), as well as various strains of S. aureus (MICs = 31.25-125 μg/ml). Mycophenolic acid (150 mg/kg) reduces splenomegaly in a mouse model of Friend virus-induced leukemia. It decreases the number of hemolytic plaque forming cells isolated from the spleen of mice immunized with sheep red blood cells (RBCs) when administered at doses ranging from 60 to 240 mg/kg. Formulations containing mycophenolic acid have been used as immunosuppressive agents in the prevention of organ transplant rejection.
Chemical properties
White to Off-White Powder
The Uses of Mycophenolic acid
Mycophenolic acid is a common Penicillium metabolite first reported in the 1930s as a possible mycotoxin. Re-investigation showed mycophenolic acid to display broad antitumour, antiviral, antifungal and antiprotozoan activities. Its potent immunosuppressant activity led to its commercial development to prevent kidney transplant rejection. Mycophenolic acid acts by inhibiting inosine monophosphate dehydrogenase, controlling the rate of de novo purine synthesis in proliferating B and T lymphocytes.
The Uses of Mycophenolic acid
An antibiotic produced by Penicillium brevi-compactum, P. Stoloniferum and related spp. A selective inhibitor of lymphocyte proliferation by blocking inosine monophosphate dehydrogenase, an enzyme involved in the de novo synthesis of purine nucleotides.
The Uses of Mycophenolic acid
immune suppressant, antineoplastic, antiviral
The Uses of Mycophenolic acid
antineoplastic, progestin
What are the applications of Application
Mycophenolic acid is a small molecule IMPDH inhibitor
Background
Mycophenolic acid is a potent immunosuppressant agent that inhibits de novo purine biosynthesis. It was derived from Penicillium stoloniferum, and has also shown antibacterial, antifungal and antiviral properties.. Mycophenolic acid is used in immunosuppressive regimens as part of a triple therapy that includes a calcineurin inhibitor (ciclosporin or tacrolimus) and prednisolone. This regimen can be used in place of the older anti-proliferative azathioprine due to its stronger immunosuppressive potency. However, mycophenolic acid treatment is more expensive and requires therapeutic drug monitoring to optimize efficacy and minimize toxicity. Mycophenolic acid is available as enteric-coated tablets of delayed-release, in an effort to improve upper gastrointestinal adverse events by delaying mycophenolic acid release until it reaches the small intestine. Mycophenolate mofetil, a prodrug of mycophenolic acid, is also prescribed to transplant recipients to prevent organ rejection.
Indications
Mycophenolic acid is an antimetabolite immunosuppressant indicated for prophylaxis of organ rejection in adult patients receiving kidney transplants and in pediatric patients at least 5 years of age and older who are at least 6 months post kidney transplant. Mycophenolic acid is used in combination with cyclosporine and corticosteroids.
Definition
ChEBI: A member of the class of 2-benzofurans that is 2-benzofuran-1(3H)-one which is substituted at positions 4, 5, 6, and 7 by methyl, methoxy, (2E)-5-carboxy-3-methylpent-2-en-1-yl, and hydroxy groups, respectively. It is an antibiotic produced by Penicillium brevi-compactum, P. stoloniferum, P. echinulatum and related species. An immunosuppressant, it is widely used (partiularly as its sodium salt and as the 2-(morpholin-4-yl)ethyl ester prodrug, mycophenolate mo etil) to prevent tissue rejection following organ transplants and for the treatment of certain autoimmune diseases.
brand name
Myfortic (Novartis).
General Description
Assayed in therapeutic drug monitoring to ensure patients remain within the drug′s therapeutic range, mycophenolic acid is an immunosuppressant drug and the active metabolite of the prodrug mycophenolate mofetil. This analytical standard is suitable for LC-MS/MS applications including therapeutic drug monitoring and other clinical or diagnostic applications.
Biological Activity
Immunosuppressive agent with antiviral and antitumor effects in vitro and in vivo . Potently inhibits inosine monophosphate dehydrogenase, thus inhibiting de novo GTP synthesis leading to decreased RNA and DNA synthesis. Reversibly inhibits proliferation of T and B lymphocytes and antibody formation.
Mechanism of action
Mycophenolic acid (MPA) is a potent inhibitor of inosine monophosphate dehydrogenase (IMPDH) that prevents the ab initio biosynthesis of purine nucleotides. It predominantly affects lymphocytes, leading to inhibition of DNA synthesis in T cells and B cells, thereby suppressing cell-mediated immune responses and antibody formation.MPA also inhibits glycosylation and expression of adhesion molecules, as well as the recruitment of lymphocytes and monocytes to sites of inflammation.MPA depletes tetrahydrobiopterin and reduces nitric oxide production via inducible NO synthase without affecting the activity of constitutive NO synthase[1].
Pharmacokinetics
Mycophenolic acid is a potent inhibitor of inosine monophosphate dehydrogenase (IMPDH) that blocks de novo biosynthesis of purine nucleotides. This affects lymphocytes primarily and leads to the suppression of DNA synthesis in T- and B-cells. Mycophenolic acid arrests the T-lymphocyte cell cycle at the G1/S interface and inhibits the proliferation of lymphocytes. Also, it has been suggested that mycophenolic acid suppresses cytokine production by limiting the number of cytokine-producing cells. The enteric-coating of mycophenolic acid tablets prevents the development of upper gastrointestinal adverse events by delaying drug release until it reaches the small intestine.
Patients treated with mycophenolic acid have a higher risk of developing new or reactivated viral infections, serious infections, blood dyscrasias (including pure red cell aplasia), serious gastrointestinal tract complications, acute inflammatory syndrome associated with mycophenolate products, lymphoma, and other malignancies. The use of mycophenolic acid is also associated with an increased risk of first-trimester pregnancy loss and congenital malformations. Mycophenolic acid should be avoided in patients with rare hereditary deficiency of hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyl-transferase (HGPRT). Patients treated with mycophenolic acid should not receive live attenuated vaccines or donate blood or semen.
Metabolism
Mycophenolic acid is mainly metabolized by glucuronyl transferase to form glucuronidated metabolites. Mycophenolic acid glucuronide (MPAG), the major metabolite of mycophenolic acid, does not display pharmacological activity. However, the acyl glucuronide minor metabolite has a pharmacological activity similar to mycophenolic acid. The AUC ratio of mycophenolic acid:MPAG:acyl glucuronide is approximately 1:24:0.28 at a steady state.
Storage
Room temperature
Purification Methods
Purify the acid by dissolving it in the minimum volume of EtOAc, applying onto a silica gel column (0.05-0.2 mesh) and eluting with a mixture of EtOAc/CHCl3/AcOH (45:55:1) followed by recrystallisation from heptane/EtOAc, from aqueous EtOH or from hot H2O and drying in vacuo. It is a weak dibasic acid, moderately soluble in Et2O, CHCl3 and hot H2O but weakly soluble in *C6H6 and toluene. [Birch & Wright Aust J Chem 22 2635 1969, Canonica et al. J Chem Soc, Perkin Trans 1 2639 1972, Birkinshaw et al. Biochem J 50 630 1952, Beilstein 18 II 393, 18 III/IV 6513.]
References
References/Citations 1) Eugui et al. (1991), Lymphocyte-selective cyostatic and immunosuppressive effects of mycophenolic acid in vitro: role of deoxyguanosine nucleotide depletion; Scand. J. Immunol., 33 161 2) Jonsson et al. (2002), Mycophenolic acid inhibits inosine 5′-monophosphate dehydrogenase and suppresses production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, nitric oxide and LDH in macrophages; Cell. Immunol., 216 93 3) Allison et al. (1993), Mechanisms of action of mycophenolic acid; Ann. NY Acad. Sci., 696 63 4) Quemeneur et al. (2002), Mycophenolic acid inhibits IL-2-dependent T cell proliferation, but not IL-2-dependent survival and sensitization to apoptosis; J. Immunol., 169 2747
References
[1] ALLISON A. Mechanisms of action of mycophenolate mofetil[J]. Lupus, 2005, 14 1: 2-8. DOI:10.1177/096120330501400102.
Properties of Mycophenolic acid
| Melting point: | 141°C |
| Boiling point: | 419.24°C (rough estimate) |
| Density | 1.2300 (rough estimate) |
| vapor pressure | 0Pa at 22℃ |
| refractive index | 1.5200 (estimate) |
| Flash point: | 2℃ |
| storage temp. | Sealed in dry,Store in freezer, under -20°C |
| solubility | methanol: 50 mg/mL, clear, colorless to faintly yellow |
| form | powder |
| pka | 4.5(at 25℃) |
| color | white to white with yellow cast |
| Water Solubility | 13mg/L(25 ºC) |
| Merck | 14,6327 |
| BRN | 1295848 |
| Stability: | Stable for 2 years from date of purchase as supplied. Solutions in DMSO or ethanol may be stored at -20° for up to 3 months. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 24280-93-1(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | 4-Hexenoic acid, 6-(1,3-dihydro-4-hydroxy-6-methoxy-7-methyl-3-oxo-5-isobenzofuranyl)-4-methyl-, (4E)- (24280-93-1) |
Safety information for Mycophenolic acid
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07  Health Hazard GHS08  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral H341:Germ cell mutagenicity H372:Specific target organ toxicity, repeated exposure H410:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P201:Obtain special instructions before use. P202:Do not handle until all safety precautions have been read and understood. P260:Do not breathe dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P273:Avoid release to the environment. P301+P312:IF SWALLOWED: call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician IF you feel unwell. P308+P313:IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/attention. |
Computed Descriptors for Mycophenolic acid
Mycophenolic acid manufacturer
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran




You may like
-
 24280-93-1 99%View Details
24280-93-1 99%View Details
24280-93-1 -
 Mycophenolic Acid CAS 24280-93-1View Details
Mycophenolic Acid CAS 24280-93-1View Details
24280-93-1 -
 Mycophenolic acid 98% CAS 24280-93-1View Details
Mycophenolic acid 98% CAS 24280-93-1View Details
24280-93-1 -
 Mycophenolic acid 95.00% CAS 24280-93-1View Details
Mycophenolic acid 95.00% CAS 24280-93-1View Details
24280-93-1 -
 Mycophenolic acid 99% (HPLC) CAS 24280-93-1View Details
Mycophenolic acid 99% (HPLC) CAS 24280-93-1View Details
24280-93-1 -
 Mycophenolic acid 99% (HPLC) CAS 24280-93-1View Details
Mycophenolic acid 99% (HPLC) CAS 24280-93-1View Details
24280-93-1 -
 Mycophenolic acid solution CAS 24280-93-1View Details
Mycophenolic acid solution CAS 24280-93-1View Details
24280-93-1 -
 Mycophenolic Acid CAS 24280-93-1View Details
Mycophenolic Acid CAS 24280-93-1View Details
24280-93-1
