MONURON
Synonym(s):Monuron
- CAS NO.:150-68-5
- Empirical Formula: C9H11ClN2O
- Molecular Weight: 198.65
- MDL number: MFCD00018556
- EINECS: 205-766-1
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-06-13 14:48:16
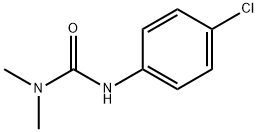
What is MONURON?
Chemical properties
White, crystalline solid; odorless. Very low solubility in water and hydrocarbonsolvents; slightly soluble in oils; partially soluble inalcohols; stable toward oxidation and moisture.
The Uses of MONURON
Monuron may be used as a reference standard in the determination of monuron in rice and corn using high performance liquid chromatography coupled with fluorescence detection combined with ultraviolet decomposition and post-column derivatization.
The Uses of MONURON
Herbicide, sugarcane-flowering suppressant.
Definition
ChEBI: A member of the class of ureas that is urea in which one of the nitrogens is substituted by a p-chlorophenyl group while the other is substituted by two methyl groups.
General Description
White crystalline solid or white powder with a slight odor. Melting point 175°C. Moderately toxic by ingestion. Used as an herbicide.
Air & Water Reactions
Insoluble in water. Is hydrolyzed slowly by acids and alkalis, and more rapidly on heating .
Reactivity Profile
MONURON is a chlorinated urea derivative. May react with azo and diazo compounds to generate toxic gases. May react with strong reducing agents to generate flammable gases. Reacts as a weak base. Combustion generates mixed oxides of nitrogen (NOx).
Hazard
Questionable carcinogen.
Health Hazard
Toxic properties are similar to Diuron; hydro-lyzes under acidic or alkaline conditions top-chloroaniline, which can cause anemia andmethemoglobinemia; LD50 data published inthe literature differ; acute and chronic tox-icity of this herbicide is probably of loworder; no reported case of human poisoning; showed clear evidence of carcinogenicity in male F344/N rats fed diets containing 750 ppm monuron for 2 years; causedcancers in the kidney and liver (NationalToxicology Program 1988); female rats andmale and female mice (B6C3F1) showed noevidence; induced cytomegaly of the renalepithelial cells in rats.
LD50 oral (rat): 3700 mg/kg (Bailey andWhite, 1965)
LD50 oral (rat): 1053 mg/kg (Lewis 1995).
Fire Hazard
Flash point data for MONURON are not available; however, MONURON is probably combustible.
Flammability and Explosibility
Not classified
Safety Profile
Moderately toxic by ingestion, intraperitoneal, and possibly other routes. Experimental teratogenic and reproductive effects. Questionable carcinogen with experimental carcinogenic data. Mutation data reported. An herbicide. When heated to decomposition it emits very toxic fumes of NOx and Cl-.
Environmental Fate
Biological. Monuron was mineralized in sewage samples obtained from a water treatment
plant in Ithica, NY. (4-Chlorophenyl)urea and 4-chloroaniline were tentatively identified
as metabolites (Wang et al., 1985).
Soil/Plant. In soils and plants, monuron is demethylated at the terminal nitrogen atom
coupled with ring hydroxylation forming 3-(2-hydroxy-4-chlorophenyl)urea and 3-(3-
hydroxy-4-chlorophenyl)urea (Hartley and Kidd, 1987). Walln?efer et al. (197
Photolytic. When an aqueous solution of monuron was exposed to sunlight or simulated
sunlight, the major degradative pathways observed were the photooxidation and demethylation
of the N-methyl groups (Crosby and Tang, 1969; Tanaka et al., 1982a),
Tanaka et al. (1981) studied the photolysis of monuron in dilute aqueous solutions in
order to fully characterize a substituted diphenylamine that was observed in an earlier
investigation (Tanaka et al., 1977). They identified this compound as an isomeric mixture
containing 92% 2-chloro-4¢,5-bis(N¢,N¢-dimethylureido)biphenyl and 8% 5-chloro-2,4¢-
bis(N¢,N¢-dimethylureido)biphenyl (Tanaka et al., 1981).
Tanaka et al. (1982) undertook a study to identify the several biphenyls formed in
earlier photolysis studies (Tanaka et al., 1979, 1981). They identified these compounds as
2,4¢-, 3,4¢- and 4,4¢-bis-(N¢,N¢-dimethylureido)biphenyls (fenuron biphenyls) (Ta
Purification Methods
Crystallise monuron from MeOH. [Beilstein 12 IV 1191.]
Properties of MONURON
| Melting point: | 173-174 °C (lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 301.31°C (rough estimate) |
| Density | 1,27 g/cm3 |
| vapor pressure | 0Pa at 20℃ |
| refractive index | 1.5330 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | 0-6°C |
| form | Crystalline Solid |
| pka | 14.22±0.70(Predicted) |
| color | White |
| Water Solubility | 262mg/L(25 ºC) |
| λmax | 244nm(H2O)(lit.) |
| Merck | 14,6261 |
| BRN | 2097922 |
| IARC | 3 (Vol. Sup 7, 53) 1991 |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Monuron (150-68-5) |
Safety information for MONURON
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07  Health Hazard GHS08  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral H351:Carcinogenicity H410:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P202:Do not handle until all safety precautions have been read and understood. P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P270:Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product. P273:Avoid release to the environment. P301+P312:IF SWALLOWED: call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician IF you feel unwell. P308+P313:IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/attention. |
Computed Descriptors for MONURON
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran



![N-(4-CHLOROPHENYL)-4-[1-METHYL-6-(METHYLAMINO)-3,5-DINITRO-1,4-DIHYDRO-2-PYRIDINYL]TETRAHYDRO-1(2H)-PYRAZINECARBOXAMIDE](https://img.chemicalbook.in/StructureFile/ChemBookStructure2/GIF/CB5349885.gif)


You may like
-
 Monuron 97.00% CAS 150-68-5View Details
Monuron 97.00% CAS 150-68-5View Details
150-68-5 -
 3-(4-Chlorophenyl)-1,1-dimethylurea CAS 150-68-5View Details
3-(4-Chlorophenyl)-1,1-dimethylurea CAS 150-68-5View Details
150-68-5 -
 3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 614-19-7 98%View Details
614-19-7 98%View Details
614-19-7 -
 20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 -
 3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 -
 4,6-dichloropyrimidine-5-carbaldehyde 98%View Details
4,6-dichloropyrimidine-5-carbaldehyde 98%View Details
5305-40-8
