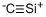MONOCRYSTALLINE POWDER
Synonym(s):Nanodiamond
- CAS NO.:7782-40-3
- Empirical Formula: C
- Molecular Weight: 12.0107
- MDL number: MFCD00211867
- EINECS: 231-953-2
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 14:08:52
What is MONOCRYSTALLINE POWDER?
Chemical properties
very hard crystals or light green powder
Chemical properties
Diamond is among the strongest Raman scatterers, and Raman spectroscopy is an important diagnostic tool for determining diamond film quality. Diamond has an intense Raman band at 1332 cm-1, the presence of which verifies a material contains diamond. The more regular the crystal lattice, the narrower the width of this band. Graphite has two first-order phonon Raman bands, a strong band at 1580 cm?1 and a weaker one at 1357 cm-1.
Physical properties
Exists in two major varieties: those bearing nitrogen as an impurity (Type I) and those without nitrogen (Type II). These two subgroups are further subdivided into Types Ia, Ib, IIa, and IIb. Type Ia diamonds are the most common type of naturally occurring diamond; they exhibit 0.1 to 0.2 wt.% nitrogen present in small aggregates, including platelets. By contrast, nitrogen in Type Ib diamonds is dispersed substitutionally. Of the two Type II diamond types, Type IIb is a semiconductor due to minute amounts of boron impurities and exhibits a blue color, whereas Type IIa diamonds are comparatively pure. Electric insulator (E = 7 eV.). Burns in oxygen.
The Uses of MONOCRYSTALLINE POWDER
Diamond powder is generally used as an abrasive to grind and polish hard surfaces.
The Uses of MONOCRYSTALLINE POWDER
Jewelry. Polishing, grinding, cutting glass, bearings for delicate instruments; manufacture of dies for tungsten wire and similar hard wires; making styli for recorder heads, long-lasting phonograph needles. In semiconductor research.
The Uses of MONOCRYSTALLINE POWDER
Monocrystalline diamond particles internalized in human endothelial cells have potential applications in drug delivery.
Definition
ChEBI: An allotropic form of the element carbon with cubic structure which is thermodynamically stable at pressures above 6 GPa at room temperature and metastable at atmospheric pressure. At low pressures diamond converts rapidly to graphite at temperatures above 1900 K in an inert atmosphere. The chemical bonding between the carbon atoms is covalent with sp3 hybridization.
General Description
Diamond nanopowder (DNPs) may be produced by multicathode direct current plasma chemical vapor deposition and high pressure high temperature (HPHT).
Potential uses of nano-diamond are in biosensor applications. Surface modification of nano-diamond may enhance its linking mechanism with specific biomolecules. DNPs can be subjected to functionalization post Fenton treatment. These functionalized DNPs may be used as gene delivery systems.
Structure and conformation
Diamond crystallographic structure consists to a face centered cubic crystal lattice where the carbon atoms occupy the eight corners, the centers of the six faces and half of the tetrahedral crystallographic sites (Z = 8). The most common crystal habits for euhedral crystals found in nature are the octahedron {111}, the cube {100}, and the dodecahedron {110} sometimes rounded due to etching. Diamond normally cleaves on the (111) plane but cleavage has been observed on the (110) plane and to a lesser extent some other crystallographic planes.

Properties of MONOCRYSTALLINE POWDER
| Melting point: | 4440°C |
| Boiling point: | 4827℃ [COT88] |
| Density | 3.5 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.) |
| refractive index | nD20 2.4173 |
| solubility | insoluble in H2O |
| form | synthetic polycrystalline powder |
| color | Clear, Impurities (i.e. Nitrogen) and irradiation can change color to yellow, green, blue, pink, or brown. |
| Crystal Structure | Cubic, Diamond - Space Group Fd3m |
| Merck | 14,2987 |
| Stability: | Stable. |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Diamond (7782-40-3) |
Safety information for MONOCRYSTALLINE POWDER
Computed Descriptors for MONOCRYSTALLINE POWDER
New Products
Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL N-octanoyl benzotriazole 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid DIETHYL AMINOMALONATE HYDROCHLORIDE 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5-BROMO-2CYANO PYRIDINE 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 Diamond powder CASView Details
Diamond powder CASView Details -
 Diamond powder CASView Details
Diamond powder CASView Details -
 Diamond powder CASView Details
Diamond powder CASView Details -
 Diamond powder CASView Details
Diamond powder CASView Details -
 Diamond powder CAS 7782-40-3View Details
Diamond powder CAS 7782-40-3View Details
7782-40-3 -
 Diamond powder CAS 7782-40-3View Details
Diamond powder CAS 7782-40-3View Details
7782-40-3 -
 Diamond Nanopowder CAS 7782-40-3View Details
Diamond Nanopowder CAS 7782-40-3View Details
7782-40-3 -
 Diamond powder, 0-1 μm CAS 7782-40-3View Details
Diamond powder, 0-1 μm CAS 7782-40-3View Details
7782-40-3