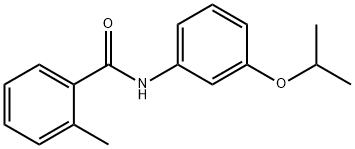
Mepronil
Synonym(s):3′-Isopropoxy-2-methylbenzanilide
- CAS NO.:55814-41-0
- Empirical Formula: C17H19NO2
- Molecular Weight: 269.34
- MDL number: MFCD00144739
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2023-04-23 13:52:06
What is Mepronil?
The Uses of Mepronil
Mepronil is an benzanilide based fungicide found in the raw materials of herbal medicine.
The Uses of Mepronil
Mepronil is used to control Basidiomycetes diseases in rice, cereals, potatoes, vegetables, sugar beet, fruit, vines, tobacco, turf grass and other crops.
What are the applications of Application
Mepronil is a benzanilide based fungicide
Definition
ChEBI: A member of the class of benzamides, obtained by formal condensation of the carboxy group of 2-methylbenzoic acid with the amino group of 3-(ispropyloxy)aniline. A fungicide used to control diseases caused by Basidomycetes including Rhizoctonia
Metabolic pathway
Mepronil is an analogue of flutolanil containing a 2-methyl group as opposed to the 2-trifluoromethyl group. The compounds have the same mode of action and are metabolised via similar routes except that the methyl group of mepronil provides an extra site for metabolic attack. The compound is metabolised by dealkylation and hydroxylation at both the methyl and isopropyl groups and by aryl hydroxylation. Some hydrolysis occurs in plants and animals.
Degradation
Mepronil is stable to light, heat and air and in solution over a pH range of 3-10. It is hydrolysed under strongly alkaline conditions (PM). Mepronil on a silica gel surface exposed to sunlight between September and December (Japan) was 66% degraded with an estimated half-life of 36 days. This could be shortened by the addition of the photosensitiser xanthone (Yumita and Yamamoto, 1982). Irradiation of an aqueous solution with UV light at 30 °C afforded 32% degradation in 80 hours. 14C-Aniline and 14C-carbonyl labelling was used in these experiments. Carbonyl label afforded marpally more metabolites, indicating that some amide bond cleavage occurred. Twelve photo-products were identified and four unknowns were detected. Aqueous photolysis afforded somewhat fewer products than the surface irradiation. Hydroxylation occurred initially at four positions in the molecule and these were followed by further oxidation, hydrolysis, cyclisation or cleavage. The products are shown in Scheme 1. The major products (5-10%) of surface photolysis were compounds 2, 3 and 4 and on aqueous photolysis were 6 and 13 with an unknown derived only from carbonyl labelling.
Properties of Mepronil
| Melting point: | 84-89°C |
| Boiling point: | 412.48°C (rough estimate) |
| Density | 1.0483 (rough estimate) |
| vapor pressure | 5.6 x 10-5 Pa (20 °C) |
| refractive index | 1.5400 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | 0-6°C |
| solubility | Chloroform (Slightly), DMSO (Slightly), Methanol (Very Slightly) |
| form | neat |
| Water Solubility | 12 mg l-1(20 °C) |
| pka | 13.10±0.70(Predicted) |
| color | White |
| BRN | 2381749 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 55814-41-0(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Mepronil(55814-41-0) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Mepronil (55814-41-0) |
Safety information for Mepronil
Computed Descriptors for Mepronil
New Products
4-AMINO-TETRAHYDRO-PYRAN-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID HCL 4-(Dimethylamino)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-4-carbonitrile 4-Aminotetrahydropyran-4-carbonitrile Hydrochloride (R)-3-Aminobutanenitrile Hydrochloride 3-((Dimethylamino)methyl)-5-methylhexan-2-one oxalate 1,4-Dioxa-8-azaspiro[4.5]decane 5-Bromo-2-nitropyridine Diclofenac Potassium Ornidazole IP Diclofenac Sodium IP/BP/EP/USP Mefenamic Acid IP/BP/EP/USP Aceclofenac IP/BP/EP Nimesulide BP SODIUM AAS SOLUTION ZINC AAS SOLUTION BUFFER SOLUTION PH 10.0(BORATE) GOOCH CRUCIBLE SINTERED AQUANIL 5 BERYLLIUM AAS SOLUTION AMOXICILLIN (AMOXYCILLIN) TRIHYDRATE Methylcobalamin (vitamin B12) SODIUM VALPROATE SODIUM METHYL PARABEN LAMOTRIGINERelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 Mepronil CAS 55814-41-0View Details
Mepronil CAS 55814-41-0View Details
55814-41-0 -
 Mepronil CAS 55814-41-0View Details
Mepronil CAS 55814-41-0View Details
55814-41-0 -
 89796-99-6 Aceclofenac IP/BP/EP 98%View Details
89796-99-6 Aceclofenac IP/BP/EP 98%View Details
89796-99-6 -
 61-68-7 98%View Details
61-68-7 98%View Details
61-68-7 -
 Diclofenac Sodium IP/BP/EP/USP 98%View Details
Diclofenac Sodium IP/BP/EP/USP 98%View Details
15307-79-6 -
 Ornidazole IP 16773-42-5 98%View Details
Ornidazole IP 16773-42-5 98%View Details
16773-42-5 -
 51803-78-2 Nimesulide BP 98%View Details
51803-78-2 Nimesulide BP 98%View Details
51803-78-2 -
 15307-81-0 98%View Details
15307-81-0 98%View Details
15307-81-0