MEPHOBARBITAL
Synonym(s):Methylphenobarbital
- CAS NO.:115-38-8
- Empirical Formula: C13H14N2O3
- Molecular Weight: 246.26
- MDL number: MFCD00057563
- EINECS: 204-085-7
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 14:07:02
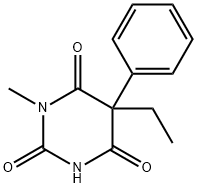
What is MEPHOBARBITAL?
Absorption
Approximately 50% of an oral dose of mephobarbital is absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract.
Chemical properties
White Crystalline Solid
Originator
Isonal, Roussel
The Uses of MEPHOBARBITAL
Controlled substance (depressant). Anticonvulsant; sedative; hypnotic
Background
A barbiturate that is metabolized to phenobarbital. It has been used for similar purposes, especially in epilepsy, but there is no evidence mephobarbital offers any advantage over phenobarbital.
Indications
For the relief of anxiety, tension, and apprehension, also used as an anticonvulsant for the treatment of epilepsy.
Definition
ChEBI: A member of the class of barbiturates, the structure of which is that of barbituric acid substituted at N-1 by a methyl group and at C-5 by ethyl and phenyl groups.
Manufacturing Process
46 parts metallic sodium was dissolved in 1000 parts absolute alcohol. The obtained solution was mixed with 264 parts of phenyl ethyl malonic acid diethyl ester and 80 parts of monomethyl urea and heated for 8 hours at reflux. Alcohol was distilled off, the residue was dissolved in water and neutralized with diluted sulfuric acid. N-Methylethylphenylbarbituric acid precipitated as a powder. It was filtered off, washed to neutral and dissolved in 50 parts of boiling alcohol. On cooling the obtained methylphenobarbital precipitated as the colorless prisms. MP: 176.5°C. This compound may be also prepared by condensation of equivalents of phenyl malonic ester and monomethyl urea, which was dissolved in above described solution of sodium ethylate.
brand name
Mebaral (Sterling Winthrop); Menta-Bal (Marion Merrell Dow).
Therapeutic Function
Anticonvulsant
General Description
Mephobarbital, 3-methyl-5-ethyl-5-phenylbarbituric acid (metharbital), is metabolicallyN-demethylated to phenobarbital, which many consider toaccount for almost all of the activity. Its principal use is asan anticonvulsant.
Pharmacokinetics
Methylphenobarbital, a barbiturate, is used in combination with acetaminophen or aspirin and caffeine for its sedative and relaxant effects in the treatment of tension headaches, migraines, and pain. Barbiturates act as nonselective depressants of the central nervous system (CNS), capable of producing all levels of CNS mood alteration from excitation to mild sedation, hypnosis, and deep coma. In sufficiently high therapeutic doses, barbiturates induce anesthesia.
Clinical Use
Mephobarbital is a barbiturate-derivative AED with a pKa of 7.7 (log P = 1.84 at pH 7.4). Approximately 50% of an oral dose of
mephobarbital is absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. The plasma concentrations required for its therapeutic effects are
unknown. The principal route of mephobarbital metabolism is N-demethylation by the liver to form phenobarbital, which may be
excreted in the urine unchanged and as its p-hydroxy metabolite and glucuronide or sulfate conjugates.
Conversion to the 4-hydroxy metabolite is stereoselective, being catalyzed by either CYP2C19 (R-enantiomer) or CYP2B6
(S-enantiomer); individuals who are CYP2C19 poor metabolizers show decreased clearance. Approximately 75% of a
single oral dose of mephobarbital is converted to phenobarbital. It has not been determined whether mephobarbital contributes
to the antiseizure effect or whether it results from its active metabolite, phenobarbital. Similarly, it is unclear whether
mephobarbital, like phenobarbital, is a potent inducer of the enzymes involved in the metabolism of other drugs, but because
the drug is chemically and pharmacologically similar to phenobarbital and is metabolized to phenobarbital, this possibility is
likely.
Mephobarbital is less commonly used in the treatment of generalized and partial seizures. Like phenobarbital, it is classified as
a long-acting barbiturate. No evidence exists that it is more effective than phenobarbital in equivalent doses; however, it may
be less sedating in children.
Safety Profile
Poison by ingestion and intraperitoneal routes. A human teratogen by an unspecified route with developmental abnormalities of the cardovascular (circulatory) system. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic NOx. See also BARBITURATES.
Metabolism
Hepatic, primarily by the hepatic microsomal enzyme system. About 75% of a single oral dose of mephobarbital is metabolized to phenobarbital in 24 hours.
Properties of MEPHOBARBITAL
| Melting point: | 1760C |
| Boiling point: | 389.26°C (rough estimate) |
| Density | 1.1855 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.6450 (estimate) |
| Flash point: | 11 °C |
| storage temp. | Controlled Substance, -20°C Freezer |
| solubility | Practically insoluble in water, very slightly soluble in ethanol (96 per cent). |
| pka | 7.99±0.10(Predicted) |
| form | Solid |
| color | White to Off-White |
| Water Solubility | 0.15g/L(20 ºC) |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 115-38-8 |
| EPA Substance Registry System | 2,4,6(1H,3H,5H)-Pyrimidinetrione, 5-ethyl-1-methyl-5-phenyl- (115-38-8) |
Safety information for MEPHOBARBITAL
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Flame Flammables GHS02  Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06  Health Hazard GHS08 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H225:Flammable liquids H370:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P210:Keep away from heat/sparks/open flames/hot surfaces. — No smoking. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. |
Computed Descriptors for MEPHOBARBITAL
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid 1-Bromo-3,5-Di-Tert-Butylbenzene S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


You may like
-
 2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 -
 42831-50-5 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID 98%View Details
42831-50-5 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID 98%View Details
42831-50-5 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1