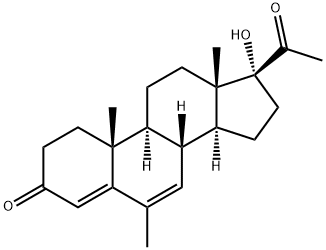
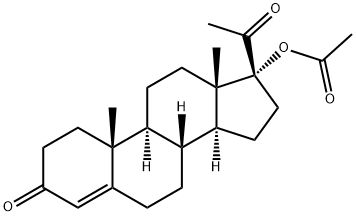
Medroxyprogesterone Acetate
Synonym(s):17α-Acetoxy-6α-methylprogesterone;17α-Hydroxy-6α-methyl-4-pregnene-3,20-dione 17-acetate;6α-Methyl-17α-acetoxyprogesterone;6α-Methyl-17α-hydroxyprogesterone acetate;Medroxyprogesterone 17-acetate
- CAS NO.:71-58-9
- Empirical Formula: C24H34O4
- Molecular Weight: 386.52
- MDL number: MFCD00010483
- EINECS: 200-757-9
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-03-05 15:30:44
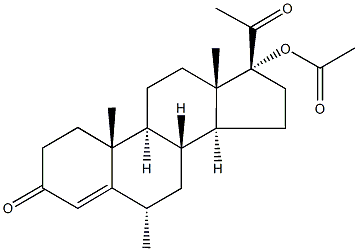
What is Medroxyprogesterone Acetate?
Absorption
Absorption of oral medroxyprogesterone acetate (MPA) varies considerably between formulations. A 1000mg oral dose reaches an average Cmax of 145-315nmol/L while a 500mg oral dose reaches an average Cmax of 33-178nmol/L with a Tmax of 1-3 hours and a lag time of half an hour. The AUC of a 500mg oral dose of MPA was 543.4-1981.1nmol*L/h depending on formulation.
Intramuscular MPA reaches a Cmax of 4.69±1.52nmol/L with a Tmax of 4.75±2.09 days and an AUC of 81.58±27.64days*nmol/L. Subcutaneous MPA reaches a Cmax of 3.83±1.56nmol/L with a T±max of 6.52±2.07 days and an AUC of 72.26±38.73days*nmol/L. However, the pharmacokinetics of MPA may also vary depending on injection site.
Toxicity
The oral LD50 in rats is >6400mg/kg and in mice is >16g/kg. The intraperitoneal LD50 in rats is >900mg/kg and in mice is >1500mg/kg. The subcutaneous LD50 in rats is >900mg/kg and in mice is>1500mg/kg.
Patients experiencing and overdose or oral medroxyprogesterone acetate (MPA) may present with nausea, vomiting, breast tenderness, dizziness, abdominal pain, drowsiness, fatigue, and withdrawal bleeding. Treat patients by stopping MPA and beginning symptomatic treatment. Patients who have been given too much of a MPA depo injection should contact a healthcare professional, hospital emergency department, or local poison control immediately.
Description
Medroxyprogesterone 17-acetate is a synthetic progestogen.,, It prevents fertilization and increases the rate of transport of eggs from the fallopian tubes to the uterus in female ferrets when administered prior to ovulation. Medroxyprogesterone 17-acetate reversibly blocks ovulation in rats when injected on the last day of diestrus. It also has anti-androgenic activity in rats, decreasing plasma testosterone (Item Nos. 15645 | ISO60154) levels via induction of hepatic testosterone reductase activity. Medroxyprogesterone 17-acetate exhibits immunosuppressive effects in vitro and in vivo, inhibiting the production of IFN-γ by CD2/CD3/CD28-stimulated peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) at concentrations ≥10 nM and extending the survival of rabbit skin allografts., Injectable formulations containing medroxyprogesterone 17-acetate have been used as contraceptives.
Chemical properties
White or almost white, crystalline powder.
Originator
Provera,Upjohn,US,1959
The Uses of Medroxyprogesterone Acetate
Medroxyprogesterone Acetate is a synthetic progesterone receptor agonist that is used to treat amenorrhea (unusual stopping of menstrual periods) and abnormal uterine bleeding.
Background
Medroxyprogesterone acetate (MPA) is a progesterone derivative that is more resistant to metabolism for improved pharmacokinetic properties. MPA can be use to treat secondary amenorrhea, endometrial hyperplasia, abnormal uterine bleeding, osteoporosis, vasomotor symptoms in menopause, vulvar and vaginal atrophy, prevent pregnancy, manage pain in endometriosis, prevent pregnancy, and is also used in palliative care for endometrial and renal carcinoma.
Medroxyprogesterone acetate was granted FDA approval on 18 June 1959.
Indications
Medroxyprogesterone acetate (MPA) oral tablets are indicated to treat secondary amenorrhea, reduce the incidence of endometrial hyperplasia in postmenopausal women, and to treat abnormal uterine bleeding due to hormonal imbalance, not organic pathology. Oral tablets containing MPA and conjugated estrogens are indicated to prevent postmenopausal osteoporosis and to treat moderate to severe menopausal symptoms such as vasomotor symptoms, vulvar atrophy, and vaginal atrophy. Subcutaneous MPA is indicated to prevent pregnancy and manage pain associated with endometriosis. Intramuscular MPA is indicated to prevent pregnancy, and at higher concentrations for palliative treatment of endometrial or renal carcinoma.
What are the applications of Application
Medroxyprogesterone 17-Acetate is a synthetic progesterone receptor agonist
Definition
ChEBI: Medroxyprogesterone acetate is an acetate ester resulting from the formal condensation of the 17alpha-hydroxy group of medroxyprogesterone with the carboxy group of acetic acid. A widely used progestin in menopausal hormone therapy and in progestogen-only birth control. It has a role as a progestin, an androgen, a female contraceptive drug, a synthetic oral contraceptive, an adjuvant, an inhibitor, an antioxidant and an antineoplastic agent. It is a steroid ester, an acetate ester, a 20-oxo steroid, a 3-oxo-Delta(4) steroid and a corticosteroid. It is functionally related to a medroxyprogesterone.
brand name
Amen (Amarin); Curretab (Solvay Pharmaceuticals); Cycrin (ESI); Provera (Pharmacia & Upjohn);Clinovie;Cliovir;Dep0-clinover;Dep0-map;Depcorlutin;Depo-prodasone;Depo-progevera;Depo-promone;Deporone;Dugen;Farlurin;Farlutale;Gesinal;Gestapuran;Gestapuron;G-farlutal;Hysron;Intex;Luteocrin orale;Luteodione;Luteos;Lutoporal;Metigestene;Nadigest;Nogest;Onco-provera;Perlutest;Petogen;Piermap;Povera;Promone-e;Pronone;Proverone;Provest;Sindomens;Sodelut "g";Supprestal;Verafen;Veramix plus v.
Therapeutic Function
Progestin
World Health Organization (WHO)
A depot preparation containing 150 mg medroxyprogesterone acetate was introduced over 20 years ago for use as a long-acting injectable contraceptive. Subsequently, positive results of carcinogenicity studies carried out in beagle bitches led to refusal of registration in the United States. These findings were later considered irrelevant to contraceptive use in women and the drug was approved by the Food and Drug Administration. Menstrual irregularities are the most common adverse effect associated with depot medroxyprogesterone acetate. Risk-benefit judgements differ significantly from country to country, having regard to differing national circumstances. The preparation is, however, widely available and is included in the WHO Model List of Essential Drugs. (Reference: (WHTAC4) The Use of Essential Drugs, 4th Report of the WHO Expert Committee, 796, , 1990)
General Description
Medroxyprogesterone acetate is an odorless white to off-white microcrystalline powder. It is a synthetic, acetate derivative of the sex hormone progesterone. (NTP, 1992)
Air & Water Reactions
Medroxyprogesterone 17-acetate is sensitive to prolonged exposure to air and light. Insoluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
Flammable and/or toxic gases are generated by the combination of alcohols with alkali metals, nitrides, and strong reducing agents. They react with oxoacids and carboxylic acids to form esters plus water. Oxidizing agents convert them to aldehydes or ketones. Alcohols exhibit both weak acid and weak base behavior. They may initiate the polymerization of isocyanates and epoxides.
Hazard
Possible carcinogen.
Fire Hazard
Flash point data for Medroxyprogesterone 17-acetate are not available; however, Medroxyprogesterone 17-acetate is probably combustible.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Medroxyprogesterone 17-acetate (MPA) is a synthetic progestin used as a contraceptive, in hormone replacement therapy and for the treatment of endometriosis. It is a more potent progestin that the nonacetylated form.
Pharmacokinetics
Medroxyprogesterone acetate (MPA) inhibits gonadotropin production, reduces nuclear estrogen receptors and DNA synthesis in epithelial cells of the endometrium, and induces p53 dependant apoptosis in cancer cell lines. MPA oral tablets have a half life of 40-60 hours and other formulations can have half lives that are considerably longer, so the duration of action is long. The therapeutic window is wide as patients may take doses ranging from 5mg orally daily to 1000mg as a depo injection weekly. Long term use of MPA is associated with a reduction in bone density and patients who taking MPA during adolescence may have lower peak bone mass than untreated patients, which can also increase the risk of osteoporosis and fractures in the future.
Clinical Use
Progestogen:
Cachexia (unlicensed), contraception, epilepsy, male
hypersexuality, malignant neoplasms, respiratory
disorders, sickle-cell disease, dysfunctional uterine
bleeding, endometriosis
Safety Profile
Suspected carcinogen with experimental carcinogenic, neoplastigenic, tumorigenic, and teratogenic data. Human systemic effects by intravenous route: increased intraocular pressure. Human teratogenic effects by an unspecified route: developmental abnormalities of the urogenital system. Human reproductive effects by multiple routes: spermatogenesis, menstrual cycle changes or dlsorders, postpartum effects, female fertility effects, abortion, newborn behavioral effects. Human mutation data reported. Experimental reproductive effects. A drug for the treatment of secondary amenorrhoea and dysfunctional uterine bleeding. When heated to decomposition it emits acrid smoke and irritating fumes.
Veterinary Drugs and Treatments
In cats, MPA has been used when either castration is ineffective or
undesirable to treat sexually dimorphic behavior problems such as
roaming, inter-male aggressive behaviors, spraying, mounting, etc.
MPA has also been used as a tranquilizing agent to treat syndromes
such as feline psychogenic dermatitis and alopecia, but treatment
with “true” tranquilizing agents may be preferable.
In humans, parenteral MPA has been used as a long-acting
contraceptive in females, to decrease sexually deviant behavior in
males, and as an antineoplastic agent for some carcinomas (see
Pharmacology section above). Oral MPA is used in human females
to treat secondary amenorrhea and to treat abnormal uterine bleeding
secondary to hormone imbalances.
Metabolism
Medroxyprogesterone acetate undergoes beta hydroxylation to form the metabolites 6-beta (M-2), 2-beta (M-4), and 1-beta-hydroxymedroxyprogesterone acetate (M-3). M-2 and M-4 are further metabolized to 2-beta,6-beta-dihydroxymedroxyprogesterone (M-1). M-3 is further metabolized to 1,2-dehydromedroxyprogesterone acetate (M-5).
Metabolism
Among the first of these substituted 17α-acetoxyprogesterone analogues to be utilized therapeutically was medroxyprogesterone acetate, a 6α-methyl progesterone analogue. This analogue is 25-fold more active than ethisterone. Following oral administration, medroxyprogesterone acetate is completely and rapidly deacetylated by first-pass metabolism to medroxyprogesterone. Medroxyprogesterone is extensively metabolized via pathways similar to those for progesterone, except for 6α-hydroxylation. Most medroxyprogesterone acetate metabolites are excreted in the urine, primarily as glucuronide conjugates. Plasma protein binding for medroxyprogesterone is approximately 86%, primarily to serum albumin, with no binding to SHBG.
References
1. Chang, M.C. Effects of medroxyprogesterone acetate and of ethinyl oestradiol on the fertilization and transportation of ferret eggs. J. Reprod. Fertil. 13(1), 173-174 (1967). DOI:10.1530/JRF.0.0130173
2. Dickmann, Z. Short-and long-term effects of a single injection of depo-medroxyprogesterone acetate (provera) on the vaginal smear, ovulation and mating in the rat. J. Reprod. Fertil. 32(3), 447-451 (1973). DOI:10.1530/JRF.0.0320447
3. Albin, J., Vittek, J., Gordon, G.G., et al. On the mechanism of the anti-androgenic effect of medroxyprogesterone acetate. Endocrinology 93(2), (1973). DOI:10.1210/ENDO-93-2-417
4. Huijbregts, R.P., Michel, K.G., and Hel, Z. Effect of progestins on immunity: Medroxyprogesterone but not norethisterone or levonorgestrel suppresses the function of T cells and pDCs. Contraception 90(2), 123-129 (2014). DOI:10.1016/j.contraception.2014.02.006
5. Turcotte, J.G., Haines, R.F., Brody, G.L., et al. Immunosuppression with medroxyprogesterone acetate. Transplantation 6(2), 248-260 (1968). DOI:10.1097/00007890-196803000-00010
6. Hofmeyr, G.J., Singata-Madliki, M., Lawrie, T.A., et al. Effects of the copper intrauterine device versus injectable progestin contraception on pregnancy rates and method discontinuation among women attending termination of pregnancy services in South Africa: A pragmatic randomized controlled trial. Reprod. Health 13, 42 (2016). DOI:10.1186/s12978-016-0153-9
7. Thomas CP, Liu KZ, Vats HS. Medroxyprogesterone acetate binds the glucocorticoid receptor to stimulate alpha-ENaC and sgk1 expression in renal collecting duct epithelia. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2006 Feb;290(2):F306-12. Epub 2005 Sep 27. DOI:10.1152/AJPRENAL.00062.2005
8. Braden BB, Talboom JS, Crain ID, Simard AR, Lukas RJ, Prokai L, Scheldrup MR, Bowman BL, Bimonte-Nelson HA. Medroxyprogesterone acetate impairs memory and alters the GABAergic system in aged surgically menopausal rats. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2010Mar;93(3):444-53. DOI:10.1016/j.nlm.2010.01.002
Properties of Medroxyprogesterone Acetate
| Melting point: | 206-207 °C(lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 432.7°C (rough estimate) |
| alpha | D +61° (in chloroform) |
| Density | 1.0346 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 48 ° (C=1, Dioxane) |
| storage temp. | Sealed in dry,2-8°C |
| solubility | Practically insoluble in water, freely soluble in methylene chloride, soluble in acetone, sparingly soluble in ethanol (96 per cent) |
| form | neat |
| form | Solid |
| color | White |
| Water Solubility | <0.1 g/100 mL at 23 ºC |
| Merck | 13,5817 |
| BRN | 2066112 |
| Stability: | Stable, but weakly air and light sensitive. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 71-58-9(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| IARC | 2B (Vol. 21, Sup 7) 1987 |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Medroxyprogesterone acetate (71-58-9) |
Safety information for Medroxyprogesterone Acetate
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Health Hazard GHS08 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H351:Carcinogenicity H413:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P201:Obtain special instructions before use. P202:Do not handle until all safety precautions have been read and understood. P273:Avoid release to the environment. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P308+P313:IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/attention. P405:Store locked up. |
Computed Descriptors for Medroxyprogesterone Acetate
Medroxyprogesterone Acetate manufacturer
Allmpus Laboratories Pvt Ltd
Add Biotec
New Products
Methyl (R)-1-Boc-4,4-difluoropyrrolidine-2-carboxylate 2,2-Difluoropropylamine hydrochloride tert-butyl 3-bromoazetidine-1-carboxylate (R)-1-Boc-3-hydroxypyrrolidine DIFLUOROACETIC ANHYDRIDE 2,2-Difluoropropionic acid Diallylamine, 99% Calcium hydroxide, 95% Aluminum oxide, basic 2-Bromophenylacetonitrile, 97% L-tert-Leucine,97% N-Hydroxy-2-methylpropanimidamide 4-(3,4-Dichlorophenyl)-3,4-Dihydro-N-Methyl-1-(2H)-Naphthalenimine (Schiff Base) 2-AMINO-3,5-DIBROMO BENZALDEHYDE [ADBA] L-Glutamic Acid Dimethyl Ester Hcl 10-Methoxy-5H-dibenz[b,f]azepine 5-Cyanophthalide N, N-Carbonyldiimidazole (CDI) Dibenzoyl Peroxide Titanium Dioxide 2-(Methylthio) Benzonitrile Sodium Acetate Anhydrous Allopurinol 1,5-DibromopentaneRelated products of tetrahydrofuran



You may like
-
 Medroxyprogesterone Acetate 98%View Details
Medroxyprogesterone Acetate 98%View Details -
 Medroxyprogesterone Acetate CAS 71-58-9View Details
Medroxyprogesterone Acetate CAS 71-58-9View Details
71-58-9 -
 Medroxyprogesterone 17-acetate 99% (HPLC) CAS 71-58-9View Details
Medroxyprogesterone 17-acetate 99% (HPLC) CAS 71-58-9View Details
71-58-9 -
 Medroxyprogesterone 17-acetate 98% (HPLC) CAS 71-58-9View Details
Medroxyprogesterone 17-acetate 98% (HPLC) CAS 71-58-9View Details
71-58-9 -
 Medroxyprogesterone Acetate CAS 71-58-9View Details
Medroxyprogesterone Acetate CAS 71-58-9View Details
71-58-9 -
 Medroxyprogesterone 17-acetate CAS 71-58-9View Details
Medroxyprogesterone 17-acetate CAS 71-58-9View Details
71-58-9 -
 Medroxyprogesterone acetate CAS 71-58-9View Details
Medroxyprogesterone acetate CAS 71-58-9View Details
71-58-9 -
 Medroxyprogesterone acetate CAS 71-58-9View Details
Medroxyprogesterone acetate CAS 71-58-9View Details
71-58-9
