Lurbinectedin
- CAS NO.:497871-47-3
- Empirical Formula: C41H44N4O10S
- Molecular Weight: 784.88
- MDL number: MFCD22665743
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-11-19 23:02:33
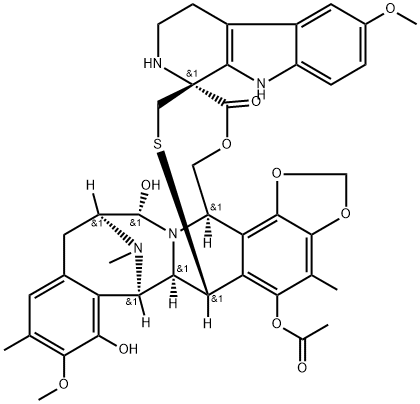
What is Lurbinectedin?
Absorption
Following intravenous administration, the Cmax and AUC0-inf were 107 μg/L and 551 μg*h/L, respectively. No accumulation between dosing intervals (every 3 weeks) has been observed. No significant differences in absorption were found between special populations (e.g. based on age, sex, ethnicity, etc.), but lurbinectedin has not been studied in the setting of severe renal impairment or moderate/severe hepatic impairment.
Toxicity
Data regarding overdosage with lurbinectedin are not available. Symptoms of overdose are likely to be consistent with lurbinectedin's adverse effect profile.
Description
Lurbinectedin is a synthetic tetrahydropyrrolo [4, 3, 2-de]quinolin-8(1H)-one alkaloid analogue with potential antineoplastic activity. Lurbinectedin covalently binds to residues lying in the minor groove of DNA, which may result in delayed progression through S phase, cell cycle arrest in the G2/M phase and cell death. Lurbinectedin was approved for medical use in the United States in June 2020.
The Uses of Lurbinectedin
Lurbinectedin is being developed for the treatment of various cancers. It has been granted approval for treatment of metastatic small cell lung cancer.
Background
Lurbinectedin is a DNA alkylating agent that has been investigated in the treatment of a variety of cancers, including mesothelioma, chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), breast cancer, and small-cell lung cancer (SCLC). It is a derivative of the marine-derived agent ecteinascidin (trabectedin), an anticancer agent found in extracts of the tunicate Ecteinascidia turbinata, with the primary difference being the substitution of the tetrahydroisoquinoline with a tetrahydro β‐carboline that results in increased antitumour activity of lurbinectedin as compared to its predecessor.
On June 15, 2020, the FDA granted accelerated approval and orphan drug designation to lurbinectedin for the treatment of adult patients with metastatic SCLC who have experienced disease progression despite therapy with platinum-based agents. This accelerated approval is based on the rate and duration of therapeutic response observed in ongoing clinical trials and is contingent on the verification of these results in confirmatory trials.
Indications
Lurbinectedin is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with metastatic small-cell lung cancer (SCLC) with disease progression on or after platinum-based chemotherapy.
What are the applications of Application
Lurbinectedin is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with metastatic small cell lung cancer (SCLC) with disease progression on or after platinum-based chemotherapy.
Biological Activity
Lurbinectedin (PM01183, PM-1183, LY-01017, Tryptamicidin, Zepsyre, ZEPZELCA), a DNA minor groove covalent binder with potent in vitro and in vivo anti-tumour activity. Lurbinectedin inhibits RMG1 and RMG2 cell growth with IC50 of 1.25 nM and 1.16 nM, respectively.
Mechanism of action
Lurbinectedin is a next-generation DNA minor groove binder that exerts potent antitumor activity in a low nanomolar range. Furthermore, it inhibits RNA-polymerase-II activity and promotes its specific degradation by the ubiquitin/proteasome machinery. In several human cancer cell lines, lurbinectedin blocks the transcription process through binding to CG-rich sequences near the promoters of protein-coding genes. This drug triggers both the degradation of phosphorylated RNA polymerase II (Pol II) on the DNA template and the generation of SSBs and DSBs that drive tumor cells to apoptosis. By attenuating the activity of the nucleotide excision repair (NER) mechanism, lurbinectedin was able to overcome cisplatin resistance in NER hyperactive cell lines. Lurbinectedin was also shown to inactivate Ewing Sarcoma Oncoprotein (EWS-FLI1) by nuclear redistribution leading to promotor inactivity and decreased mRNA and protein levels[1-2].
Pharmacokinetics
Lurbinectedin exerts its chemotherapeutic activity by covalently binding to DNA, resulting in double-strand DNA breaks and subsequent cell death. Lurbinectedin has been associated with myelosuppression, and patients receiving therapy with this agent should be closely monitored for evidence of cytopenias. Prior to beginning therapy, ensure baseline neutrophil counts are >1,500 cells/mm3 and platelet counts are >100,000/mm3. The supplementary use of granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF) should be considered if the neutrophil count falls below 500 cells/mm3. Lurbinectedin has also been associated with hepatotoxicity. Monitor liver function tests at baseline and regular intervals throughout therapy, and consider holding, reducing, or permanently discontinuing therapy based on the severity of observed hepatotoxicity.
Side Effects
The most common side effects include leukopenia, lymphopenia, fatigue, anemia, neutropenia, increased creatinine, increased alanine aminotransferase, increased glucose, thrombocytopenia, nausea, decreased appetite, musculoskeletal pain, decreased albumin, constipation, dyspnea, decreased sodium, increased aspartate aminotransferase, vomiting, cough, decreased magnesium and diarrhea.
in vitro
Lurbinectedin exhibits significant antitumor activity toward chemosensitive and chemoresistant CCC cells in vitro. Lurbinectedin plus SN-38 combination has strong synergistic effects on both the cisplatin-resistant and paclitaxel-resistant CCC cell lines.
in vivo
An examination of mouse CCC cell xenografts reveals that lurbinectedin significantly inhibits tumor growth. Lurbinectedin plus SN-38 combination results in a significant synergistic effect. Everolimus significantly enhances the antitumor activity of lurbinectedin-based chemotherapies.
Metabolism
Lurbinectedin is metabolized primarily by CYP3A4 in vitro, though specific data regarding its biotransformation are lacking. An N-desmethylated metabolite has been identified in canine subjects.
Mode of action
Lurbinectedin is an Alkylating Drug. The mechanism of action of lurbinectedin is as an Alkylating Activity.
References
[1] Kauffmann-Guerrero D, et al. Orphan Drugs in Development for the Treatment of Small-Cell Lung Cancer: Emerging Data on Lurbinectedin. Lung Cancer: Targets and Therapy, 2020; 11: 27–31.
[2] Gadducci A, et al. Trabectedin and lurbinectedin: Mechanisms of action, clinical impact, and future perspectives in uterine and soft tissue sarcoma, ovarian carcinoma, and endometrial carcinoma. Frontiers in Oncology, 2022; 12: 914342.
Properties of Lurbinectedin
| Density | 1.55±0.1 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | Store at -20°C |
| solubility | Soluble in DMSO |
| form | Solid |
| pka | 9.79±0.40(Predicted) |
| color | White to light yellow |
Safety information for Lurbinectedin
Computed Descriptors for Lurbinectedin
Lurbinectedin manufacturer
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateYou may like
-
 497871-47-3 Lurbinectedin 98%View Details
497871-47-3 Lurbinectedin 98%View Details
497871-47-3 -
 497871-47-3 98%View Details
497871-47-3 98%View Details
497871-47-3 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1