Levofloxacin
Synonym(s):(−)-Ofloxacin;Levofloxacin hemihydrate
- CAS NO.:100986-85-4
- Empirical Formula: C18H20FN3O4
- Molecular Weight: 361.37
- MDL number: MFCD00865049
- EINECS: 600-146-0
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-02-21 21:32:25
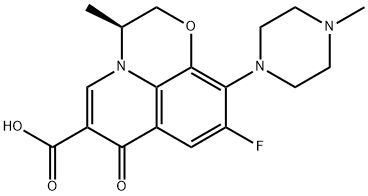
What is Levofloxacin?
Absorption
Absorption of levofloxacin following oral administration is rapid and essentially complete, with an oral bioavailability of approximately 99%. Due to its nearly complete absorption, the intravenous and oral formulations of levofloxacin may be interchangeable. The Tmax is generally attained 1-2 hours following administration and the Cmax is proportional to the given dose - an intravenous dose of 500mg infused over 60 minutes resulted in a Cmax of 6.2 ± 1.0 μg/mL whereas a 750mg dose infused over 90 minutes resulted in a Cmax of 11.5 ± 4.0 μg/mL. Oral administration with food prolongs the Tmax by approximately 1 hour and slightly decreases the Cmax, but these changes are not likely to be clinically significant.
Systemic absorption following oral inhalation is approximately 50% lower than that observed following oral administration.
Toxicity
The LD50 following oral administration in mice and rats is 1803 mg/kg and 1478 mg/kg, respectively.
Levofloxacin exhibits low potential for acute toxicity - following a single high dose of levofloxacin in several different test animals (e.g. mice, rats, monkeys) observed symptoms included ataxia, ptosis, decreased motor activity, dyspnea, tremors, and convulsions. Treatment of acute overdosage should involve stomach emptying (e.g. with activated charcoal) and general supportive measures. Consider monitoring of the patient's ECG to ensure QTc values remain within range. Levofloxacin is not efficiently removed by dialysis (peritoneal or hemodialysis) and is therefore of little benefit in cases of overdose.
Description
Levofloxacin, the optically active S-isomer of the fluoroquinolone antibiotic ofloxacin, is two to four times more potent than ofloxacin with reportedly less side effects in treating infections of the lower respiratory and urinary tract, prostate infections and sexually transmitted diseases. It has broad and potent antibacterial activity over common Grampositive and -negative aerobic pathogens and obligate anaerobes. Different from the cephem antibiotics, levofloxacin is unique in its marked selectivity against members of the family Enterobacteriaceae and its negligible effect on predominant anaerobes. Levofloxacin also exhibits satisfactory antimicrobial effects in surgical infections and it may be used for treatment of gastrointestinal infections such as traveler’s diarrhea associated with the pathogenic Enterobacteriaceae.
Chemical properties
Slight yellow powder
Originator
Daiichi (Japan)
The Uses of Levofloxacin
Antibacterial.
The Uses of Levofloxacin
Levofloxacin is a broad-spectrum antibiotic used in pharmacokinetic?, antibiotic resistance?, and resistance prevention?studies. Levofloxacin is active against Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. It inhibits DNA gyrase (type II topoisomerase) and topoisomerase IV, thereby inhibiting cell division.
Background
Levofloxacin is a fluoroquinolone antibiotic and the optical S-(-) isomer of racemic ofloxacin. It reportedly carries 8 to 128-fold more activity against both gram-negative and gram-positive bacteria compared to R-(+)-ofloxacin and remains stereochemically stable following administration (i.e. it does not invert to the inactive isomer). Levofloxacin, along with other quinolones such as gatifloxacin and moxifloxacin, is a member of the third generation of fluoroquinolones, colloquially referred to as the "respiratory quinolones" due to improved activity against gram-positive bacteria commonly implicated in respiratory infections.
Levofloxacin was first approved by the FDA in 1996, and was approved in Canada and several South American countries soon after.
Indications
In oral and intravenous formulations, levofloxacin is indicated in adults for the treatment of various infections caused by susceptible bacteria, including infections of the upper respiratory tract, lower respiratory tract, skin, skin structures, urinary tract, and prostate. The oral formulation is also indicated in both adults and children 6 months of age and older for the post-exposure management of inhalational anthrax caused by Bacillus anthracis and for the treatment and/or prophylaxis of plague caused by Yersinia pestis.
In its ophthalmic formulation, levofloxacin is indicated for the treatment of bacterial conjunctivitis caused by susceptible organisms. An inhalational solution available in Canada is indicated for the management of cystic fibrosis patients aged 18 years or older with chronic pulmonary Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections.
What are the applications of Application
Levofloxacin is an antibiotic compound
Definition
ChEBI: Levofloxacin is an optically active form of ofloxacin having (S)-configuration; an inhibitor of bacterial topoisomerase IV and DNA gyrase. It has a role as a DNA synthesis inhibitor, an antibacterial drug, a topoisomerase IV inhibitor and an EC 5.99.1.3 [DNA topoisomerase (ATP-hydrolysing)] inhibitor. It is a quinolone antibiotic, a fluoroquinolone antibiotic and a 9-fluoro-3-methyl-10-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)-7-oxo-2,3-dihydro-7H-[1,4]oxazino[2,3,4-ij]quinoline-6-carboxylic acid. It is an enantiomer of a dextrofloxacin.
Manufacturing Process
()-3-Acetoxymethyl-7,8-difluoro-2,3-dihydro-4H-[1,4]benzoxazine (m.p. 73-
74°C) was synthesized by hydrogenation of a compound prepared from 2,3-
difluoro-6-nitrophenol, 1-acetoxy-3-chloro-2-propane and potassium iodide.
The hydrogenation was carried out on Raney nickel. The resulting compound
was dissolved in THF, and 3,5-dinitrobenzoyl chloride and pyridine were added
thereto, followed by heating at 60°C for 3 hours. The mixture was
concentrated, and the concentrate was dissolved in ethyl acetate, washed
successively with diluted hydrochloric acid, an aqueous solution of sodium
bicarbonate and water, dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate and concentrated.
Addition of n-hexane to the concentrate caused precipitation of yellow crystals
of a racemate. The yield of 3,5-dinitrobenzoyl derivative of the ()-3-
acetoxymethyl-7,8-difluoro-2,3-dihydro-4H-[1,4]benzoxazine 3.93 g.
To 2.0 ml of Amberlite XAD 7 was added 2.0 ml of a 0.05 M phosphoric acid
buffer (pH 7.0) having dissolved therein 20 mg of lipoprotein lipase, and the
system was allowed to stand at room temperature for 18 hours to thereby
adsorb the enzyme onto the resin. The resin was filtered. A solution of 250
mg of 3,5-dinitrobenzoyl derivative of ()-3-acetoxymethyl-7,8-difluoro-2,3-
dihydro-4H-[1,4]benzoxazine as a substrate in 25 ml of a mixed solvent of
benzene and n-hexane (4:1 by volume) was added to the resin, followed byallowing to react at 37°C for 4 hours. It was obtained 117 mg of a 3,5-
dinitrobenzoyl derivative of the (-)-3-acetoxymethyl-7,8-difluoro-2,3-dihydro-
4H-[1,4]benzoxazine and 65 mg of a derivative of the (-)-3-acetoxymethyl-
7,8-difluoro-2,3-dihydro-4H-[1,4]benzoxazine.
In 135 ml THF was dissolved 3.03 g of a 3,5-dinitrobenzoyl derivative of (-)-
3-acetoxymethyl-7,8-difluoro-2,3-dihydro-4H-[1,4]benzoxazine, and 135 ml of
ethanol and 30 ml of 1.0 N potassium hydroxide were added to the solution.
After 30 min 3 ml of acetic acid was added thereto for neutralization. The
mixture was concentrated. The solid was subjected to column chromatography
using 40 g of silica gel and eluted with chloroform/methanol to obtain 1.17 g
of (-)-7,8-difluoro-2,3-dihydro-3-hydroxymethyl-4H-[1,4]benzoxazine; [α]D22
= -14.1° (c = 1.80, CHCl3).
To 1.17 g of (-)-7,8-difluoro-2,3-dihydro-3-hydroxymethyl-4H-[1,4]
benzoxazine was added 2.77 g of thionyl chloride in pyridine. The reaction
mixture was concentrated and the concentrate was subjected to column
chromatography using 40 g of silica gel and eluted with chloroform to obtain
1.18 g of the reaction product as a colorless oily product. This product was
dissolved in 30 ml of dimethyl sulfoxide, and 0.41 g of sodium borohydride
was added thereto, followed by heating at 80-90°C for 1 hour. The reaction
mixture was dissolved in 500 ml of benzene, washed with water to remove
the dimethyl sulfoxide, dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate and concentrated
under reduced pressure. The concentrate was subjected to column
chromatography using 40 g of silica gel and eluted with benzene to obtain
0.80 g of (-)-7,8-difluoro-2,3-dihydro-3-methyl-4H-[1,4]benzoxazine as a
colorless oily product; [α]D25 = -9.6° (c = 2.17, CHCl3). Optical Purity: >99%
e.e.
To 1.13 g of (-)-7,8-difluoro-2,3-dihydro-3-methyl-4H-[1,4]benzoxazine was
added 1.58 g of diethyl ethoxymethylenemalonate, and the mixture was
stirred at 130-140°C for 70 min. The reaction mixture was subjected to
column chromatography using 50 g of silica gel and eluted with chloroform to
obtain 2.47 g of diethyl [(-)-7,8-difluoro-3-methyl-2,3-dihydro-4H-[1,4]
benzoxazin-4-yl]methylenemalonate. This product was dissolved in 5 ml of
acetic anhydride, and 10 ml of a mixture of acetic anhydride and concentrated
sulfuric acid (2/1 by volume) with stirring under ice-cooling, followed by
stirring at 50-60°C for 40 min. To the reaction mixture were added ice and an
aqueous solution of sodium bicarbonate, and the product was extracted three
times with 150 ml portions of chloroform. The combined extract was washed
with water, dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate and concentrated. The
precipitate was washed with a small amount of diethyl ether to yield 1.32 g of
(-)-ethyl 9,10-difluoro-3-methyl-7-oxo-2,3-dihydro-7H-pyrido[1,2,3-de][1,4]
benzoxazine-6-carboxylate.
In 12 ml of acetic acid was dissolved 1.20 g of the resulting compound, and
25 ml of concentrated hydrochloric acid was added, followed by refluxing at
120-130°C for 90 min. Upon allowing the reaction mixture to stand at room
temperature, colorless crystals were precipitated, which were collected by
filtration and washed successively with a small amount of water, ethanol and
diethyl ether to obtain 0.96 g of (-)-9,10-difluoro-3-methyl-7-oxo-2,3-dihydro-
7H-pyrido[1,2,3-de][1,4]benzoxazine-6-carboxylic acid.
In 30 ml of diethyl ether was suspended 324 mg of the resulting compound,and a large excess of boron trifluoride ethyl etherate was added thereto,
followed by stirring at room temperature for 30 min to form a chelate
compound. The product was collected by filtration and washed with a small
amount of diethyl ether to obtain 373 mg of a powder. The powder was
dissolved in 7 ml of dimethyl sulfoxide, and 136 mg of N-methylpiperazine
and 228 mg of triethylamine were added thereto, followed by stirring at room
temperature for 17 hours. The reaction mixture was concentrated to dryness
under reduced pressure, and to the solid were added 15 ml of 95% methanol
and 0.31 ml of triethylamine. The resulting mixture was refluxed for 3 hours.
The reaction mixture was concentrated under reduced pressure, and the
residue was filtered and washed successively with a small amount of ethanol
and diethyl ether to obtain 350 mg of a white powder. Recrystallization from a
mixed solvent of ethanol and thick aqueous ammonia gave 230 mg of S-(-)-
ofloxacin (Levofloxacin).
Melting Point: 225-227°C (with decomposition); [α]D23 = -76.9° (c = 0.39,
0.05 N NaOH).
brand name
Iquix (Sanofi Winthrop); Levaquin (Ortho-McNeil); Quixin (Sanofi Winthrop);Cravit.
Therapeutic Function
Antibacterial
Antimicrobial activity
Levofloxacin is the active component of ofloxacin; d-ofloxacin is without significant antibacterial activity. It exhibits good activity in vitro against Gram-positive cocci (including Str. pneumoniae), Enterobacteriaceae, some fastidious Gram-negative bacilli and Ps. aeruginosa as well as chlamydiae, Mycoplasma pneumoniae, L. pneumophila and M. tuberculosis. MICs for Acinetobacter spp. and Sten. maltophilia are 0.06–0.25 and 0.5–2.0 mg/L, respectively. Activity against anaerobes is moderate to low.
General Description
Chemical structure: quinolone
Pharmaceutical Applications
For molecular weight and structure, see ofloxacin . Levofloxacin is the l-isomer of ofloxacin.
Pharmacokinetics
Levofloxacin is bactericidal and exerts its antimicrobial effects via inhibition of bacterial DNA replication. It has a relatively long duration of action in comparison with other antibiotics that allows for once or twice daily dosing. Levofloxacin is associated with QTc-interval prolongation and should be used with caution in patients with other risk factors for prolongation (e.g. hypokalemia, concomitant medications).
Levofloxacin has demonstrated in vitro activity against a number of aerobic gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria and may carry some activity against certain species of anaerobic bacteria and other pathogens such as Chlamydia and Legionella. Resistance to levofloxacin may develop, and is generally due to mutations in DNA gyrase or topoisomerase IV, or via alterations to drug efflux. Cross-resistance may occur between levofloxacin and other fluoroquinolones, but is unlikely to develop between levofloxacin and other antibiotic classes (e.g. macrolides) due to significant differences in chemical structure and mechanism of action.
As antimicrobial susceptibility patterns are geographically distinct, local antibiograms should be consulted to ensure adequate coverage of relevant pathogens prior to use.
Pharmacokinetics
Oral absorption: >95%
Cmax 500 mg oral: c. 5 mg/L after 1.5–2 h
750 mg oral: c. 8 mg/L after 1.5–2 h
500 mg intravenous (90-min infusion): c. 6 mg/L end infusion
750 mg intravenous (90-min infusion) :c. 12 mg/L end infusion
Plasma half-life :6–8 h
Volume of distribution:0.6–0.8 L/kg
Plasma protein binding: <25%
Co-administration with antacids, calcium, sucralfate and heavy metals decreases bioavailability and AUC. No interactions with warfarin or theophylline have been observed. Co-administration of a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug may increase the risk of convulsions. It undergoes limited metabolism and is primarily eliminated unchanged in urine by both glomerular filtration and tubular secretion. The free AUC:MIC ratio for Str. pneumoniae increases from about 55 to 70 when the daily dosage is raised from 500 mg to 750 mg.
It is stable in plasma and does not revert to d-ofloxacin. It undergoes limited metabolism and is primarily eliminated unchanged in the urine. Renal clearance in excess of the glomerular filtration rate suggests that tubular secretion also occurs. Concomitant administration of either cimetidine or probenecid reduces renal clearance by approximately onethird. Clearance is reduced and half-life is prolonged in patients with impaired renal function (creatinine clearance <50 mL/min) requiring dosage adjustment in such patients.
Clinical Use
Acute bacterial sinusitis
Acute bacterial exacerbations of chronic bronchitis, community-acquired pneumonia
Uncomplicated and complicated skin and skin structure infections
Uncomplicated and complicated urinary infections including acute pyelonephritis
Chronic bacterial prostatitis
Side Effects
Side effects have been reported in 6–7% of patients and include fever, rash and other events common to the group. Elderly patients are at increased risk of developing severe tendon disorders including rupture, a risk increased by concomitant corticosteroid therapy.
Metabolism
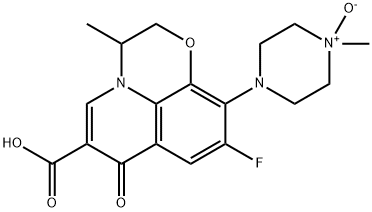
Only 2 metabolites, desmethyl-levofloxacin and levofloxacin-N-oxide, have been identified in humans, neither of which appears to carry any relevant pharmacological activity. Following oral administration, less than 5% of the administered dose was recovered in the urine as these metabolites, indicating very little metabolism of levofloxacin in humans. The specific enzymes responsible for the demethylation and oxidation of levofloxacin have yet to be ascertained.
Properties of Levofloxacin
| Melting point: | 218°C |
| Boiling point: | 572℃ |
| Density | 1.48±0.1 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| Flash point: | >110°(230°F) |
| storage temp. | Keep in dark place,Sealed in dry,2-8°C |
| solubility | chloroform: soluble10mg/mL |
| form | powder |
| pka | 5.19±0.40(Predicted) |
| color | white to faint yellow |
| optical activity | [α]20/D -104±4° in chloroform |
| Water Solubility | Slightly soluble in water or methanol. Soluble in glacial acetic acid or dichloromethane |
| Sensitive | Light Sensitive |
| Merck | 14,6771 |
| BRN | 7327015 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 100986-85-4(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | 7H-Pyrido[1,2,3-de]-1,4-benzoxazine-6-carboxylic acid, 9-fluoro-2,3-dihydro-3-methyl-10-(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)-7-oxo-, (3S)- (100986-85-4) |
Safety information for Levofloxacin
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07  Health Hazard GHS08 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral H317:Sensitisation, Skin H334:Sensitisation, respiratory |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P270:Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P301+P312:IF SWALLOWED: call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician IF you feel unwell. P302+P352:IF ON SKIN: wash with plenty of soap and water. |
Computed Descriptors for Levofloxacin
| InChIKey | GSDSWSVVBLHKDQ-JTQLQIEISA-N |
Levofloxacin manufacturer
New Products
Methyl (R)-1-Boc-4,4-difluoropyrrolidine-2-carboxylate 2,2-Difluoropropylamine hydrochloride tert-butyl 3-bromoazetidine-1-carboxylate (R)-1-Boc-3-hydroxypyrrolidine DIFLUOROACETIC ANHYDRIDE 2,2-Difluoropropionic acid Diallylamine, 99% Calcium hydroxide, 95% Aluminum oxide, basic 2-Bromophenylacetonitrile, 97% L-tert-Leucine,97% N-Hydroxy-2-methylpropanimidamide 4-(3,4-Dichlorophenyl)-3,4-Dihydro-N-Methyl-1-(2H)-Naphthalenimine (Schiff Base) 2-AMINO-3,5-DIBROMO BENZALDEHYDE [ADBA] L-Glutamic Acid Dimethyl Ester Hcl 10-Methoxy-5H-dibenz[b,f]azepine 5-Cyanophthalide N, N-Carbonyldiimidazole (CDI) Dibenzoyl Peroxide Titanium Dioxide 2-(Methylthio) Benzonitrile Sodium Acetate Anhydrous Allopurinol 1,5-DibromopentaneRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

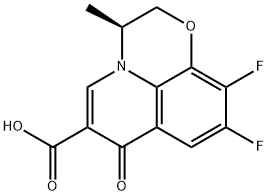
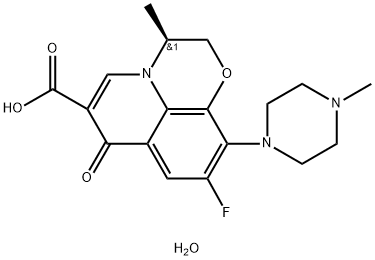
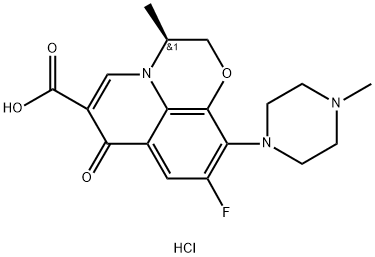
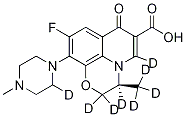
You may like
-
 Levofloxacin 98%View Details
Levofloxacin 98%View Details
100986-85-4 -
 Levofloxacin 100986-85-4 98%View Details
Levofloxacin 100986-85-4 98%View Details
100986-85-4 -
 Levofloxacin 99% (HPLC) CAS 100986-85-4View Details
Levofloxacin 99% (HPLC) CAS 100986-85-4View Details
100986-85-4 -
 Levofloxacin 98% CAS 100986-85-4View Details
Levofloxacin 98% CAS 100986-85-4View Details
100986-85-4 -
 Levofloxacin, ≥98%(HPLC) CAS 100986-85-4View Details
Levofloxacin, ≥98%(HPLC) CAS 100986-85-4View Details
100986-85-4 -
 Levofloxacin CAS 100986-85-4View Details
Levofloxacin CAS 100986-85-4View Details
100986-85-4 -
 Levofloxacin CAS 100986-85-4View Details
Levofloxacin CAS 100986-85-4View Details
100986-85-4 -
 Levofloxacin CAS 100986-85-4View Details
Levofloxacin CAS 100986-85-4View Details
100986-85-4
