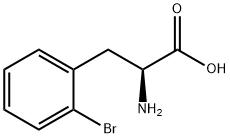
L-Penicillamine
Synonym(s):L- (+)-2-Amino-3-mercapto-3-methylbutanoic acid β,β-Dimethyl-L -cysteine;3,3-Dimethyl-L -cysteine;3-Mercapto-L -valine
- CAS NO.:1113-41-3
- Empirical Formula: C5H11NO2S
- Molecular Weight: 149.21
- MDL number: MFCD00064303
- EINECS: 214-203-9
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-03-04 13:31:24
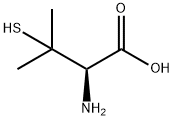
What is L-Penicillamine?
Chemical properties
white to almost white crystalline powder
The Uses of L-Penicillamine
As a Penicillin metabolite, L-Penicillamine can be used in the treatment of Wilson’s disease, Cystinuria, Scleroderma and arsenic poisoning.
The Uses of L-Penicillamine
L-Penicillamine is a metabolite of penicillin. L-Penicillamine is used in the treatment of Wilson’s disease, Cystinuria, Scleroderma and arsenic poisoning.
The Uses of L-Penicillamine
Metal-chelating agent
Definition
ChEBI: The L-enantiomer of penicillamine.
Indications
Penicillamine (Cuprimine) can be used to treat acute, severe rheumatoid arthritis, producing reductions in joint pain, edema, and stiffness.The response to penicillamine is usually delayed (4–12 weeks), and remissions can last several months after withdrawal of treatment. Radiographic evidence of this drug’s efficacy is limited; thus, penicillamine is seldom used to treat rheumatoid arthritis.
Mechanism of action
The mechanism of action of penicillamine is unknown, but some evidence suggests that it may involve the inhibition of angiogenesis, synovial fibroblast proliferation, or transcriptional activation. Because penicillamine can chelate copper and promote its excretion, it is used to treat Wilson’s disease (hepatolenticular degeneration) and has also been used in mercury and lead intoxication.
Pharmacology
Penicillamine is readily absorbed from the GI tract and is rapidly excreted in the urine, largely as the intact molecule. Gradually increasing its dose minimizes side effects, which necessitate discontinuance of penicillamine therapy in perhaps one-third of patients. The most common side effects are maculopapular pruritic dermatitis, GI upset, loss of taste sensation, mild to occasionally severe thrombocytopenia and leukopenia,and mild proteinuria, which at times may progress to the nephritic syndrome. Discontinuance of therapy usually results in a rapid disappearance of side effects.
Safety Profile
A poison by intraperitoneal route. Mutation data reported. Whenheated to decomposition it emits toxic vapors of NOx and SOx.
Purification Methods
Same as preceding entry for its enantiomer. [Beilstein 4 IV 3228.]
Properties of L-Penicillamine
| Melting point: | 206 °C (dec.)(lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 251.8±35.0 °C(Predicted) |
| alpha | 61.9 º (C=0.5 IN 1 M NAOH) |
| Density | 1.113 (estimate) |
| refractive index | 63 ° (C=1, 1mol/L NaOH) |
| storage temp. | Keep in dark place,Inert atmosphere,Room temperature |
| solubility | Aqueous Base (Sparingly), DMSO (Slightly, Heated), Water (Slightly) |
| pka | 2.13±0.12(Predicted) |
| form | Crystalline Powder |
| color | White to almost white |
| optical activity | [α]24/D +61.9°, c = 0.5 in 1 M NaOH |
| Merck | 14,7088 |
| BRN | 1722374 |
| Stability: | Hygroscopic |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 1113-41-3(CAS DataBase Reference) |
Safety information for L-Penicillamine
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for L-Penicillamine
| InChIKey | VVNCNSJFMMFHPL-GSVOUGTGSA-N |
L-Penicillamine manufacturer
GRK RESEARCH LABORATORIES PVT LTD
New Products
1-Boc-4-cyanopiperidine tert-Butyl carbazate 1-(TERT-BUTOXYCARBONYL)-2-PYRROLIDINONE TETRABUTYLAMMONIUM CYANIDE TETRAHYDRO-2H-PYRAN-3-OL 3-Pyridineacrylic acid Nickel(II) perchlorate hexahydrate, 98% 4-Bromophenylacetonitrile, 95% 3-Bromo-4-fluoroaniline, 97% Sodium tetraborate decahydrate, 98% Palladium(II) acetate, trimer, Pd 99% 4-Bromo-2-chlorotoluene, 97% Tadalafil Clopidogrel bisulfate Sitagliptin Phosphate Monohydrate Cabergoline Fexofinadine HCl Etoricoxib 4-Amino Acetophenone 2-Chloro Acetophenone Amlodipine Base 2,3,5-Triiodobenzoic Acid Pyrrolidine Diiodo PentoxideRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 1113-41-3 L(+) PENICILLAMINE 99%View Details
1113-41-3 L(+) PENICILLAMINE 99%View Details
1113-41-3 -
 4-Amino benzonitrile 1113-41-3 98%+View Details
4-Amino benzonitrile 1113-41-3 98%+View Details
1113-41-3 -
 L-Penicillamine 95% CAS 1113-41-3View Details
L-Penicillamine 95% CAS 1113-41-3View Details
1113-41-3 -
 L-Penicillamine CAS 1113-41-3View Details
L-Penicillamine CAS 1113-41-3View Details
1113-41-3 -
 366789-02-8 Riveroxaban 98%View Details
366789-02-8 Riveroxaban 98%View Details
366789-02-8 -
 Carvedilol 98%View Details
Carvedilol 98%View Details
72956-09-3 -
 73590-58-6 Omeprazole 98%View Details
73590-58-6 Omeprazole 98%View Details
73590-58-6 -
 Sertraline HCl 98%View Details
Sertraline HCl 98%View Details
79559-97-0
