kobusine
- CAS NO.:27530-78-5
- Empirical Formula: C20H27NO2
- Molecular Weight: 313.43
- MDL number: MFCD01723543
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
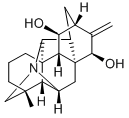
What is kobusine?
Description
Obtained by Suginome and Shimanouti from the precipitation liquors of crude jesaconitine from Aconitum sachalinense, Fr. Schmidt, this alkaloid crystallizes from Me2CO in the rhombic-bisphenoidal system and has (a:b:c = 1.0736: I: 0.9811). It furnishes crystalline salts: the hydrobromide crystallizes as the mono_x0002_hydrate, m.p. 288°C (dec.); [α]22D + 40.68° (H20); hydrochloride (1.5 H20) has m.p. 300°C (dec.);[α]21Dl + 41.4° (H20); perchlorate, m.p. 185-7°C (dec.) although a value of 220°C has also been recorded for this salt; platinichloride, m.p. 262°C (dec.); picrate, m.p. 282-4°C (dec.) and methiodide, m.p. 287°C (dec.). The alkaloid forms a diacetyl derivative, m.p. 139-140°C and catalytic reduction followed by acetylation yields a triacetyltetrahydrokobusine, m.p. 183-4°C (dec.). The alkaloid cannot be hydrolyzed and is non-toxic.
References
Suginome, Shimanouti., Annalen, 545, 220 (1940)
Okamoto., Chern. Pharm. Bull. (Tokyo), 7,44 (1959)
Natsume., ibid, 7,539 (1959)
Properties of kobusine
| Melting point: | 267-267.5°C |
Safety information for kobusine
Computed Descriptors for kobusine
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
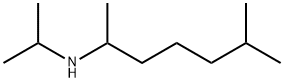
You may like
-
 3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 1-methylindoline-2,3-dione 98%View Details
1-methylindoline-2,3-dione 98%View Details
2058-74-4 -
 614-19-7 98%View Details
614-19-7 98%View Details
614-19-7 -
 3112-85-4 Methyl phenyl sulfone 98%View Details
3112-85-4 Methyl phenyl sulfone 98%View Details
3112-85-4 -
 20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 -
 3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 -
 4,6-dichloropyrimidine-5-carbaldehyde 98%View Details
4,6-dichloropyrimidine-5-carbaldehyde 98%View Details
5305-40-8
