ketazolam
- CAS NO.:27223-35-4
- Empirical Formula: C20H17ClN2O3
- Molecular Weight: 368.81
- EINECS: 248-346-3
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2023-05-15 10:43:34
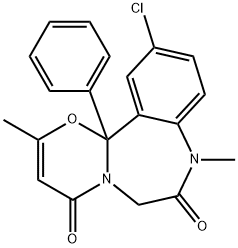
What is ketazolam?
Toxicity
Symptoms of overdose include somnolence, confusion, coma, and diminished reflexes. Respiration, pulse and blood pressure should be monitored.
Description
Benzodiazepines are psychoactive compounds that act as sedatives, hypnotics, anxiolytics, anticonvulsants, and muscle relaxants. Ketazolam is a benzodiazepine derivative that was used as an anxiolytic in the 1980s. Tolerance within fifteen days, physical dependence, and benzodiazepine withdrawal syndrome are associated with ketazolam use. This product is intended for forensic purposes.
Originator
Anxon,Beecham,UK,1980
The Uses of ketazolam
A psychotropic benzodiazepine derivative with hypnotic and anxiolytic properties. Controlled Substance.
Indications
Ketazolam could be used for the treatment of anxiety. In approved countries, it is indicated for the treatment of anxiety, tension, irritability and similar stress related symptoms.
Background
Ketazolam is a benzodiazepine derivative with anxiolytic, anticonvulsant, sedative and skeletal muscle relaxant activity. Ketazolam is not approved in Canada or America.
Definition
ChEBI: Ketazolam is a benzodiazepine.
Manufacturing Process
A solution of 0.7 g of 2-(2-amino-N-methylacetamido)-5-chlorobenzophenone in 10 ml of a 50% solution (by weight) of diketene in acetone is refluxed for 3 hours and then evaporated to give a brown oil. The oil is chromatographed on 200 g of silica gel using a 1:1 (by volume) mixture of ethyl acetate cyclohexane; 25 ml fractions are collected. Fractions 11-14 are combined, mixed with chloroform, evaporated and triturated with ether to give 0.337 g of 11-chloro-8,12b-dihydro-2,8-dimethyl-12b-phenyl-4H-[1,3]oxazino[3,2-d] [1.4] benzodiazepine-4,7(6H)-dione as a pale yellow solid, MP 174°C to 176°C.
Therapeutic Function
Antianxiety
Pharmacokinetics
Benzodiazepines enhance the effect of the neurotransmitter gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), which results in sedative, hypnotic, anxiolytic, anticonvulsant, muscle relaxant and amnesic action. Benzodiazepines bind nonspecifically to benzodiazepine receptors which mediate sleep, affects muscle relaxation, anticonvulsant activity, motor coordination, and memory. As benzodiazepine receptors are thought to be coupled to gamma-aminobutyric acid-A (GABAA) receptors, this enhances the effects of GABA by increasing GABA affinity for the GABA receptor. Binding of GABA to the site opens the chloride channel, resulting in a hyperpolarized cell membrane that prevents further excitation of the cell.
Metabolism
Ketazolam is metabolized to diazepam, followed by demoxepam, and finally desmethyldiazepam.
Properties of ketazolam
| Melting point: | 182-183.5° (sinters at 170°) |
| Boiling point: | 645.0±55.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.41±0.1 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| solubility | DMF: 5 mg/ml; DMSO: 5 mg/ml; DMSO:PBS(pH7.2) (1:1): 0.5 mg/ml; Methanol: 1 mg/ml |
| form | A crystalline solid |
| pka | -0.84±0.60(Predicted) |
| Stability: | Unstable in Solution |
Safety information for ketazolam
Computed Descriptors for ketazolam
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid 1-Bromo-3,5-Di-Tert-Butylbenzene S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
![7-CHLORO-2,3,4,5-TETRAHYDRO-1H-BENZO[E][1,4]DIAZEPINE](https://img.chemicalbook.in/CAS/GIF/107479-55-0.gif)
![2,3,4,5-TETRAHYDRO-1H-BENZO[E][1,4]DIAZEPINE](https://img.chemicalbook.in/CAS/GIF/1904-65-0.gif)
![4,5-DIHYDRO-1H-BENZO[E][1,4]DIAZEPIN-2(3H)-ONE](https://img.chemicalbook.in/CAS/GIF/1824-72-2.gif)
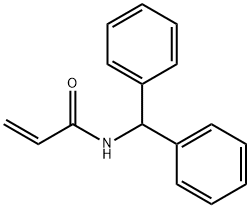
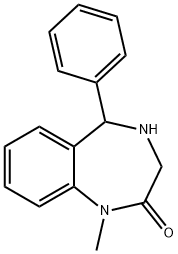
You may like
-
 2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 -
 42831-50-5 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID 98%View Details
42831-50-5 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID 98%View Details
42831-50-5 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1