Isoleucine
Synonym(s):(2S,3S)-2-Amino-3-methylpentanoic acid;L -Isoleucine
- CAS NO.:7004-09-3
- Empirical Formula: C6H13NO2
- Molecular Weight: 131.17
- Update Date: 2023-04-23 13:52:06
What is Isoleucine?
Description
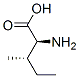
Isoleucine ( abbreviated as Ile or I ) is an α - amino acid with the chemical formula HO2CCH(NH2)CH(CH3)CH2CH3. It is an essential amino acid, which means that humans cannot synthesize it, so it must be ingested. Its codons are AUU, AUC and AUA.
With a hydrocarbon side chain, isoleucine is classified as a hydrophobic amino acid. Together with threonine, isoleucine is one of two common amino acids that have a chiral side chain. Four stereoisomers of isoleucine are possible, including two possible diastereomers of L-isoleucine. However, isoleucine present in nature exists in one enantiomeric form, (2S,3S)-2-amino-3-methylpentanoic acid.
Chemical properties
Crystals. Slightly soluble in water; nearly insoluble in alcohol; insoluble in ether.
Occurrence
Even though this amino acid is not produced in animals, it is stored in high quantities. Foods that have high amounts of isoleucine include eggs, soy protein, seaweed, turkey, chicken, lamb, cheese, and fish.
The Uses of Isoleucine
Amino acid.
Definition
An essential amino acid, found naturally in the L(+) form.
Biosynthesis
As an essential nutrient, it is not synthesized in the body, hence it must be ingested, usually as a component of proteins. In plants and microorganisms, it is synthesized via several steps, starting from pyruvic acid and alpha - keto glutarate. Enzymes involved in this biosynthesis include :
Aceto lactate synthase (also known as aceto hydroxy acid synthase)
Aceto hydroxy acid iso meroreductase
Dihydroxy acid dehydratase
Valine amino transferase.
Synthesis
Isoleucine can be synthesized in a multistep procedure starting from 2-bromobutane and diethylmalonate.Synthetic isoleucine was originally reported in 1905.
German chemist Felix Ehrlich discovered isoleucine in hemoglobin in 1903.
Metabolism
Isoleucine is both a glucogenic and a ketogenic amino acid. After transamination with alpha-ketoglutarate the carbon skeleton can be converted into either Succinyl CoA, and fed into the TCA cycle for oxidation or converted into oxaloacetate for gluconeogenesis (hence glucogenic). It can also be converted into Acetyl CoA and fed into the TCA cycle by condensing with oxaloacetate to form citrate. In mammals Acetyl CoA cannot be converted back to carbohydrate but can be used in the synthesis of ketone bodies or fatty acids, hence ketogenic.
Properties of Isoleucine
| Melting point: | >166°C (dec.) |
| storage temp. | Refrigerator |
| solubility | Aqueous Acid (Slightly), DMSO (Slightly, Sonicated) |
| form | Solid |
| pka | 2.32(at 25℃) |
| color | White to Off-White |
Safety information for Isoleucine
Computed Descriptors for Isoleucine
New Products
Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate (S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL N-octanoyl benzotriazole 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid Fmoc-Val-Cit-PAB DIETHYL AMINOMALONATE HYDROCHLORIDE 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5-BROMO-2CYANO PYRIDINE 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonateYou may like
-
 2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 -
 733039-20-8 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 98+View Details
733039-20-8 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 98+View Details
733039-20-8