ISOBUTANE
Synonym(s):Isobutane
- CAS NO.:75-28-5
- Empirical Formula: C4H10
- Molecular Weight: 58.12
- MDL number: MFCD00008926
- EINECS: 200-857-2
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-17 09:49:46
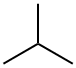
What is ISOBUTANE?
Chemical properties
colourless odourless gas (or colourless cryogenic liquid)
Chemical properties
2-Methylpropane (isobutane), C4H10, a flammable gas, occurs in small quantities in natural gas and crude oil. It has been detected in urban atmospheres at concentrations of 44–74 ppb. It also evolves from natural sources and has been measured in diesel exhaust at 1.4–11 ppm and in cigarette smoke at 10 ppm. The partition coefficient of propane between olive oil and air at 37℃ is 12 using the method described by Sato and Nakajima and Perbellini et al.. The lower explosive limit is 18,000 ppm in air.
The Uses of ISOBUTANE
Isobutane occurs in petroleum, natural gas,and petroleum cracking products. It is usedas a fuel gas or a liquefied petroleum gas. Itis also used in organic synthesis.
The Uses of ISOBUTANE
Organic synthesis, refrigerant, motor fuels, aerosol propellant, synthetic rubber, instrument calibration fluid.
The Uses of ISOBUTANE
In the production of propylene glycols and oxides and polyurethane foams and resins; as component of motor fuels and aerosol propellants; as an industrial gas carrier and general fuel source
Definition
ChEBI: An alkane that is propane substituted by a methyl group at position 2.
General Description
ISOBUTANE is a colorless gas with a faint petroleum-like odor. ISOBUTANE is shipped as a liquefied gas under its vapor pressure. Contact with the liquid can cause frostbite. ISOBUTANE is easily ignited. The vapors are heavier than air. Any leak can either be liquid or vapor. ISOBUTANE can asphyxiate by the displacement of air. Under prolonged exposure to fire or intense heat the containers may rupture violently and rocket.
Air & Water Reactions
Highly flammable.
Reactivity Profile
ISOBUTANE is incompatible with the following: Strong oxidizers (e.g., nitrates & perchlorates), chlorine, fluorine, (nickel carbonyl + oxygen) .
Hazard
Highly flammable, dangerous fire and explosive risk; explosive limits in air 1.9–8.5%.
Health Hazard
Central nervous system depression ranging from dizziness and incoordination to anesthesia and respiratory arrest, depending on concentration and extent of inhalation. Irregular heartbeat is rare but is a dangerous complication at anesthetic levels.
Health Hazard
Isobutane, like other saturated aliphatic alkanes,is nontoxic. It is an asphyxiate. Exposureto high concentrations of 1% in air maycause narcosis and drowsiness. Other thanthis, there is no report of any adverse healtheffect from exposure to this gas.
Fire Hazard
EXTREMELY FLAMMABLE. Will be easily ignited by heat, sparks or flames. Will form explosive mixtures with air. Vapors from liquefied gas are initially heavier than air and spread along ground. CAUTION: Hydrogen (UN1049), Deuterium (UN1957), Hydrogen, refrigerated liquid (UN1966) and Methane (UN1971) are lighter than air and will rise. Hydrogen and Deuterium fires are difficult to detect since they burn with an invisible flame. Use an alternate method of detection (thermal camera, broom handle, etc.) Vapors may travel to source of ignition and flash back. Cylinders exposed to fire may vent and release flammable gas through pressure relief devices. Containers may explode when heated. Ruptured cylinders may rocket.
Safety Profile
An asphyxiant. A common air contaminant. A very dangerous fire and explosion hazard when exposed to heat, flame, or oxidizers. To fight fire, stop flow of gas. When heated to decomposition it emits acrid smoke and irritating fumes.
Source
California Phase II reformulated gasoline contained 2-methylpropane at a concentration of 1.04 g/kg. Gas-phase tailpipe emission rate from gasoline-powered automobiles equipped with a catalytic converter was 130 μg/km (Schauer et al., 2002).
Environmental Fate
Photolytic. Based upon a photooxidation rate constant of 2.34 x 10-12 cm3/molecule?sec with OH
radicals in summer daylight, the atmospheric lifetime is 59 h (Altshuller, 1991). At atmospheric
pressure and 300 K, Darnall et al. (1978) reported a rate constant of 2.52 x 10-12 cm3/molecule?sec
for the same reaction. Rate constants of 1.28 x 10-9 and 6.03 x 10-12 L/molecule?sec were reported
for the reaction of 2-methylpropane with OH radicals in air at 300 and 296 K, respectively
(Greiner, 1967, 1970). Rate constants of 7.38 x 10-13 and 6.50 x 10-17 cm3/molecule?sec were
reported for the reaction of 2-methylpropane with OH and NO3, respectively (Sablji? and Güsten,
1990).
Chemical/Physical. Complete combustion in air produces carbon dioxide and water vapor. 2-
Methylpropane will not hydrolyze because it does not contain a hydrolyzable functional group.
Solubility in organics
(mole fraction):
In 1-butanol: 0.0897, 0.0491, and 0.0308 at 25, 30, and 70 °C, respectively; chlorobenzene: 0.157,
0.0837, and 0.0542 at 25, 30, and 70 °C, respectively; and octane: 0.301, 0.161, and 0.101 at 25,
30, and 70 °C, respectively (Hayduk et al., 1988).
In 1-butanol: 0.0889 and 0.0486 at 25 and 70 °C, respectively; in chlorobenzene: 0.162 and 0.0853
at 25 and 70 °C, respectively; and in carbon tetrachloride: 0.238 and 0.132 at 25 and 70 °C,
respectively (Blais and Hayduk, 1983).
Purification Methods
Olefins and moisture can be removed by passage at 65o through a bed of silica-alumina catalyst which has previously been evacuated at about 400o. Alternatively, water and CO2 can be removed by passage through P2O5, then asbestos impregnated with NaOH. Treatment with anhydrous AlBr3 at 0o then removes traces of olefins. Inert gases can be separated by freezing the isobutane at -195o and evacuating out the system. [Beilstein 1 IV 282.]
Properties of ISOBUTANE
| Melting point: | −160 °C(lit.) |
| Boiling point: | −12 °C(lit.) |
| Density | 2.064 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) |
| vapor density | 2.01 (21 °C, vs air) |
| vapor pressure | 72.2 psi ( 37.7 °C) |
| refractive index | 1.3518 |
| Flash point: | -83 °C |
| form | Colorless gas |
| color | Colorless, very flammable gas with a faint odor |
| explosive limit | 8.3% |
| Water Solubility | 48.9 mg/kg at 25 °C (shake flask-GC, McAuliffe, 1963, 1966) |
| BRN | 1730720 |
| Henry's Law Constant | 1.171 atm?m3/mol at 25 °C (Hine and Mookerjee, 1975) |
| Exposure limits | NIOSH REL: TWA 800 ppm (1,900 mg/m3). |
| Stability: | Stable. Extremely flammable. May form explosive mixtures with air. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 75-28-5(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Isobutane (75-28-5) |
Safety information for ISOBUTANE
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Flame Flammables GHS02  Gas Cylinder Compressed Gases GHS04 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H220:Flammable gases H280:Gases under pressure |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P410+P403:Protect from sunlight. Store in a well-ventilated place. |
Computed Descriptors for ISOBUTANE
| InChIKey | NNPPMTNAJDCUHE-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
ISOBUTANE manufacturer
J B Air Products
New Products
Indole Methyl Resin tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Boc-His(Boc)-OH 2-CTC Resin 4-Chloro-7-tosy1-7Hpyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine 5,7-Dibromo-1H-indole 2,5-dichloro-N-hydroxy-4,6-dimethylpyridine-3-carboximidamide 2,2-Dimethoxy-7-azaspiro[3.5]nonane hydrochloride 4-chloromethyl-5-methyl-1,3-dioxol-2-one (DMDO-Cl) R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID 4-((2-hydroxyethyl)thio)benzoic acid 1-(TERT-BUTOXYCARBONYL)-2-PYRROLIDINONE Methyl 6-methylnicotinate 3-Pyridineacrylic acid tert-Butyl carbazate TETRAHYDRO-2H-PYRAN-3-OL 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 1,3-Diethyl-1,3-Diphenylurea Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran




You may like
-
 75-28-5 Isobutane 98%View Details
75-28-5 Isobutane 98%View Details
75-28-5 -
 75-28-5 98%View Details
75-28-5 98%View Details
75-28-5 -
 Isobutane 99%View Details
Isobutane 99%View Details
75-28-5 -
 2-Methylpropane CAS 75-28-5View Details
2-Methylpropane CAS 75-28-5View Details
75-28-5 -
 2-Methylpropane CAS 75-28-5View Details
2-Methylpropane CAS 75-28-5View Details
75-28-5 -
 Hydrocarbon Solvents Isobutane Pure Gases, Grade Standard: Industrial GradeView Details
Hydrocarbon Solvents Isobutane Pure Gases, Grade Standard: Industrial GradeView Details
75-28-5 -
 Pyridine 99.5% HPLC /UV SpectroscopyView Details
Pyridine 99.5% HPLC /UV SpectroscopyView Details
110-86-1 -
 Thiourea 99% ARView Details
Thiourea 99% ARView Details
62-56-6
