INULIN
- CAS NO.:9005-80-5
- Empirical Formula: C18H32O16
- Molecular Weight: 504.43708
- MDL number: MFCD00131407
- EINECS: 232-684-3
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-26 08:49:36
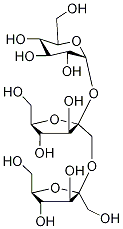
What is INULIN?
Description
Inulin is a type of plant polysaccharide—a fructan—that partially or completely replaces starch as a reserve energy source. In 1946, E. J. McDonald isolated it from dahlia tubers. It has ≈10% the sweetness of sucrose and is an ingredient in commercial stevia natural sweeteners.
Chemical properties
white crystalline solid
Chemical properties
Inulin occurs as an odorless white powder with a neutral to slightly sweet taste.
The Uses of INULIN
Inulin is a nondigestible oligosaccharide containing fructose which provides texture, rheology, dietary fiber properties, and selective fer- mentation by colon bacteria. commercially obtained from chicory root; common sources include onion, garlic, leek, asparagus, and jerusalem artichoke. it is a hygroscopic powder with solubility in water dependent on water temperature. with increasing concentra- tion, viscosity gradually increases, and at about 30% concentration, it can form discrete particle gels which are characterized as creamy and fat-like. it is not hydrolyzed by the digestive system. it func- tions as a prebiotic, passing into the colon where it is preferentially fermented by healthy bacteria such as bifidobacteria and lactobacilli to increase their proliferation and inhibit unwanted bacteria. it is used in ice cream products to replace fat and sugar, and in baked goods.
The Uses of INULIN
Is a safe plant polysaccharide with a variety of uses in the food and chemical medical industry. It is a functional food, providing functional groups for beneficial bacteria, as well as improving prop erties of food such as texture, hydration and shelf-life. They are also used for vaccine and drug delivery via soluble storage.
The Uses of INULIN
Mixture of fructose polymers that serves as carbohydrate storage in plantsInulin is used in the treatment of high blood fats, cholesterol and triglycerides. It is also used for weight loss, constipation and also serves as a food additive to improve taste and as a vaccine adjuvant. Further, it is utilized to replace sugar, fat and flour. It is also used to measure kidney function by determining the glomerular filtration rate (GFR). In addition to this, it is used to replace some of the flour in baked goods.
What are the applications of Application
Inulin from dahlia tubers is a fructosan starch from dahlia tubers
Production Methods
Inulin is extracted from the tubers of Dahlia variabilis, Helianthus, in a procedure similar to the extraction of sugar from sugar beet.
Pharmaceutical Applications
Inulin has many potential uses in pharmaceutical applications, as a
filler–binder in tablet formulations; to stabilize therapeutic
proteins; or to enhance the dissolution of lipophilic drugs.
Methacrylated inulin hydrogels have been investigated for the
development of colon-specific drug delivery systems.
Inulin is used as a diagnostic agent to measure the glomerular
filtration rate. It is used in the food industry as a sweetener and
stabilizer; and also as a prebiotic, where it has been shown to
provide protection against inflammatory and malignant colonic
diseases in animals. It is also used as a noncaloric dietary fiber
supplement.
Biochem/physiol Actions
A heterogeneous blend of fructose polymers that function as plant storage carbohydrates.
Safety
Inulin is a naturally occurring plant polysaccharide and is one of the major constituents of the Compositae family. Inulin is recommended to diabetics, as it has a mild sweet taste, but is not absorbed and does not affect blood sugar levels. It is used widely in the food industry as a sweetener and stabilizer.
Storage
Inulin is slightly hygroscopic and should be stored at cool to normal temperatures, in air-tight and water-tight containers.
Incompatibilities
Inulin is incompatible with strong oxidizing agents.
Regulatory Status
GRAS listed.
Properties of INULIN
| Melting point: | 176-181 °C |
| alpha | D20 -40° (c = 2) for the anhydr |
| Density | 1,35 g/cm3 |
| storage temp. | Store at RT. |
| solubility | Soluble in hot water and solutions of dilute acids and
alkalis; slightly soluble in cold water and organic solvents. |
| form | Solid |
| color | White to Off-White |
| Odor | odorless |
| Water Solubility | Soluble in water. |
| Sensitive | Hygroscopic |
| Merck | 14,5004 |
| Stability: | Stable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Inulin (9005-80-5) |
Safety information for INULIN
Computed Descriptors for INULIN
| InChIKey | YKHPIEZXTCQOCC-YWMIBZCHSA-N |
INULIN manufacturer
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran






You may like
-
 Inulin extrapure CAS 9005-80-5View Details
Inulin extrapure CAS 9005-80-5View Details
9005-80-5 -
 Inulin (by Enzymatic synthesis) CAS 9005-80-5View Details
Inulin (by Enzymatic synthesis) CAS 9005-80-5View Details
9005-80-5 -
 Inulin, for biochemistry CAS 9005-80-5View Details
Inulin, for biochemistry CAS 9005-80-5View Details
9005-80-5 -
 INULIN For Biochemistry CAS 9005-80-5View Details
INULIN For Biochemistry CAS 9005-80-5View Details
9005-80-5 -
 Inulin from chicory CAS 9005-80-5View Details
Inulin from chicory CAS 9005-80-5View Details
9005-80-5 -
 Inulin from dahlia tubers CAS 9005-80-5View Details
Inulin from dahlia tubers CAS 9005-80-5View Details
9005-80-5 -
 Powder Inulin, Packaging Type: Bag, Packaging Size: 25View Details
Powder Inulin, Packaging Type: Bag, Packaging Size: 25View Details
9005-80-5 -
 20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0
