Imipenem
- CAS NO.:64221-86-9
- Empirical Formula: C12H17N3O4S
- Molecular Weight: 299.35
- MDL number: MFCD00864955
- EINECS: 264-734-5
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-16 16:15:04
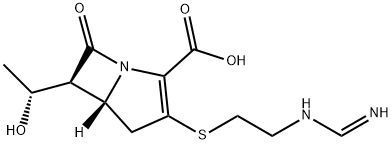
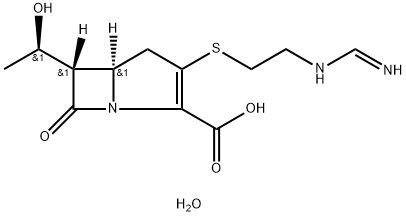
What is Imipenem?
Absorption
Imipenem is not effectively absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract and therefore must be administered parenterally. The bioavailability of the IM injection is 89%.
Toxicity
In case of overdose with the combination product, including relebactam and cilastatin, it is recommended to provide supportive care. Imipenem, cilastatin, and relebactam may be removed via hemodialysis.
Description
Imipenem is a chemically stable thienamycin derivative with an antibacterial activity that is broader in spectrum and of greater potency than most of the third generation cephalosporins. Combination with cilastatin, an inhibitor of renal brush-border dehydropeptidase-I, increases both urinary and plasma levels of imipenem.
Chemical properties
White Crystals
Originator
Merck (USA)
The Uses of Imipenem
Carbapenem antibacterial.
Indications
Imipenem is indicated, in combination with cilastatin with or without relebactam, for the treatment of bacterial infections including respiratory, skin, bone, gynecologic, urinary tract, and intra-abdominal as well as septicemia and endocarditis.
What are the applications of Application
Imipenem Monohydrate is a third generation cephalosporin and β-lactam carbapenem antibiotic that exhibits broad-spectrum antibacterial activity.
Background
Imipenem is a semisynthetic thienamycin that has a wide spectrum of antibacterial activity against gram-negative and gram-positive aerobic and anaerobic bacteria, including many multiresistant strains. It is stable to many beta-lactamases. Similar compounds include meropenem, known for having greater activity against Gram negative bacteria, and the newer ertapenem which exhibits a longer half-life due to increased binding to plasma proteins. Imipenem is commonly used in combination with cilastatin and is now available in a triple-drug product with cilastatin and relebactam which was recently approved by the FDA. Imipenem was first approved by the FDA in November 1985 as the combination product Primaxin marketed by Merck & Co.
Definition
ChEBI: Imipenem is a broad-spectrum, intravenous beta-lactam antibiotic of the carbapenem subgroup. It has a role as an antibacterial drug. It is a beta-lactam antibiotic allergen and a member of carbapenems. It is a tautomer of an imipenem zwitterion.
Manufacturing Process
Preparation of N-formimidoyl thienamycin:
Thienamycin (517 mg) is dissolved in pH 7 0.1 N phosphate buffer (25 ml)
and cooled in an ice bath with magnetic stirring. The solution is adjusted to
pH 8.5 using 2.5 N sodium hydroxide solution dispensed from an automatic
burette. While maintaining a pH of 8.5, methyl formimidate hydrochloride
(711 mg) is added portionwise over 2-3 minutes. After an additional 10 min,
the pH of the solution is brought to 7.0 using 2.5 N hydrochloric acid. The
solution is chromatographed on a column of XAD-2 resin (150 ml) which is
eluted with water. The N-formimidoyl thienamycin derivative (imipenem)
elutes in 1.5-2.0 column volumes (200-300 ml) and is lyophilized to a white
solid (217 mg). UV (pH 7 0.1 N phosphate buffer); λmax297 nm (8,590); ir
(Nujol mull) 1767 Cm-1(β-lactam).
Another method preparation of imipenem:
6-(1)-Hydroxyethyl-1-azabicyclo(3.2.0)heptane-3,7-dione-2-carboxylate is
converted to the diphenoxyphosphate enol ester and this in turn reacted with
N,S-bistrimethylsilyl-N-formimidoylcysteamine (use of the bistrimethylsilylated
reagent is necessary in order to avoid side reactions caused by cyclization
reactions). As a result the (PhO)2OPO-groups are converted to Me3SiN =
CHNH-groups. Removal of the protecting groups complete the synthesis of 1-
azabicyclo[3.2.0]hept-2-ene-2-carboxylic acid, 6-(1-hydroxyethyl)-3-((2-
((iminomethyl)amino)ethyl)thio)-7-oxo-, (5R-(5-alpha,6-alpha(R*)))-.
brand name
ZIENAM
Therapeutic Function
Antibiotic
Antimicrobial activity
Imipenem shows potent activity against a wide range of Grampositive
and Gram-negative aerobes and anaerobes, including
many resistant to other agents.Concentrations
(mg/L) inhibiting 50% of strains of other organisms are:
Listeria monocytogenes, 0.03; Legionella pneumophila, 0.03;
Enterococcus faecium, 4; Yersinia spp., 0.06. Mycobacterium fortuitum
is inhibited by 6.25 mg/L. Imipenem is active against
many Pseudomonas species, but not Sten. maltophilia. It is
active against most anaerobes, with the exception of Cl. perfringens,
which is only moderately susceptible. It is bactericidal
at 2–4 times the MIC for most species, but some strains
of Staph. aureus exhibit ‘tolerance’ . Bactericidal
synergy with aminoglycosides, glycopeptides, fosfomycin and
rifampicin (rifampin) has been observed against many strains
of Staph. aureus and enterococci.
Antibacterial activity is unaffected by the presence of cilastatin,
which is itself devoid of antimicrobial activity.
Imipenem is stable to hydrolysis by most serine β-lactamases,
with the exception of the group 2f carbapenem-hydrolyzingenzymes hydrolyzingenzymes
. Strains of B. fragilis, Aeromonas spp.
and Sten. maltophilia can produce metallo-β-lactamases that
hydrolyze the drug rapidly. These strains, in addition to occasional
strains of enterobacteria, Acinetobacter baumannii and
Ps. aeruginosa, show variable resistance to imipenem depending
upon the level of carbapenem-hydrolyzing enzymes and
the presence or absence of imipenem-specific porins. Efflux
pumps also exist that may extrude imipenem from Gramnegative
bacteria.
Acquired resistance
Some strains of Citrobacter, Enterobacter, Proteus vulgaris,
Providencia, Ps. aeruginosa and Serratia spp. may be resistant
to imipenem and other β-lactam agents, often because
of the selection of stably derepressed mutants expressing
high levels of group 1 β-lactamases coupled with decreased
intracellular drug levels due to porin mutations or increased
efflux.
Induction of class 1 β-lactamases by imipenem in strains
of Aeromonas, Pseudomonas and Serratia spp. is responsible
for antagonism of β-lactamase-labile β-lactam agents in vitro.
Imipenem resistance in Ps. aeruginosa can occur following
selection of mutants that hyperproduce the group 1 cephalosporinase
and which are also deficient in an outer membrane
protein (OprD or D2) which specifically transports
imipenem, but not cephalosporins or monobactams.
General Description
Thienamycin was found in the culture broth of Streptomyces cattleya by Merck Sharp & Dohme in 1976, as a very unstable substance. It has a unique carbapenem structure, like that of the olivanic acids found in S. olivaceus by Beecham Research Laboratories in 1979. Thienamycin shows excellent activity against a variety of pathogenic bacteria, including Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Its chemical stability has been improved by derivatization with the formimidoyl group, and its biological stability has been improved by combining it with cilastatin, an inhibitor of kidney dihydropeptidase. The combination drug imipenem – cilastatin is now under study to evaluate its clinical efficacy and safety.
Pharmacokinetics
Imipenem is a beta-lactam antibiotic belongings to the subgroup of carbapenems. Imipenem is active against aerobic and anaerobic Gram positive as well as Gram negative bacteria including Pseudomonas aeruginosa and the Enterococcus. It exerts a bactericidal effects by disrupting cell wall synthesis.
Clinical Use
Lower respiratory tract infections
Urinary tract infections (complicated and uncomplicated)
Intra-abdominal infections
Gynecological infections
Bacterial septicemia
Bone and joint infections
Skin and skin structure infections
Endocarditis
Polymicrobial infections
Side Effects
CNS effects such as confusional states and seizures have been
reported, especially when recommended doses were exceeded,
and in patients with renal failure or creatinine clearances of
≤20 mL/min/1.73 m2.
Other reactions include phlebitis/thrombophlebitis (3.1%),
nausea (2.0%), diarrhea (1.8%) and vomiting (1.5%).
Increased hepatic enzymes may be seen in adults and children.
Superinfection with Aspergillus, Candida and resistant
Pseudomonas spp. have been described and pseudomembranous
colitis has been reported.
Patients with a history of hypersensitivity reactions to penicillins,
cephalosporins or other β-lactam antibiotics should be
treated cautiously with carbapenems.
Metabolism
Imipenem is metabolized by renal dehydropeptidase.
Properties of Imipenem
| Melting point: | 106-111 C |
| Boiling point: | 530.2±60.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.62±0.1 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | Keep in dark place,Sealed in dry,Store in freezer, under -20°C |
| solubility | Sparingly soluble in water, slightly soluble in methanol. |
| pka | 4.29±0.40(Predicted) |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 64221-86-9(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Imipenem (64221-86-9) |
Safety information for Imipenem
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. |
Computed Descriptors for Imipenem
Imipenem manufacturer
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran





You may like
-
 64221-86-9 Imipenem 98%View Details
64221-86-9 Imipenem 98%View Details
64221-86-9 -
 64221-86-9 98%View Details
64221-86-9 98%View Details
64221-86-9 -
 Imipenem 98%View Details
Imipenem 98%View Details
64221-86-9 -
 64221-86-9 Imipenem 99%View Details
64221-86-9 Imipenem 99%View Details
64221-86-9 -
 Imipenem CASView Details
Imipenem CASView Details -
 20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 -
 3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4
