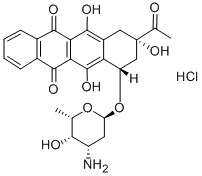
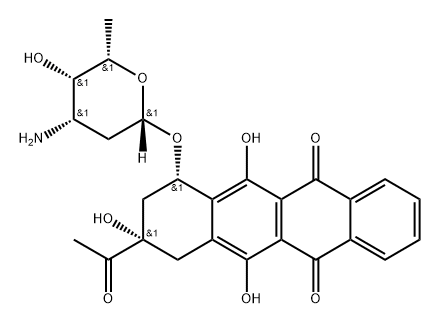
Idarubicin hydrochloride
Synonym(s):(7S-cis)-9-Acetyl-7-[(3-amino-2,3,6-trideoxy-α-L -lyxo-hexopyranosyl)oxy]-7,8,9,10-tetrahydro-6,9,11-trihydroxy-5,12-naphthacenedione;4-Demethoxydaunorubicin hydrochloride;DMDR;Idamycin;IMI-30
- CAS NO.:57852-57-0
- Empirical Formula: C26H28ClNO9
- Molecular Weight: 533.95
- MDL number: MFCD00897212
- EINECS: 260-990-7
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-11-19 23:02:33
What is Idarubicin hydrochloride?
Description
Idarubicin hydrochloride is a derivative of daunorubicin indicated for acute nonlymphocytic leukemia, acute lymphocytic leukemia, and acute myeloid leukemia. Compared with daunorubicin, idarubicin hydrochloride is less cardiotoxic, has milder side effects, is orally active and more potent in experimental leukemias. Idarubicin hydrochloride is also reportedly active in daunorubicin-resistant patients, breast cancer,Hodgkin's and non-Hodgkin's lymphoma.
Chemical properties
Orange Solid
Originator
Erbamont (Italy)
The Uses of Idarubicin hydrochloride
Idarubicin hydrochloride (Idamycin) is used to traet acute myeloid leukemia in adults.
The Uses of Idarubicin hydrochloride
Orally active anthracycline; analog of Daunorubicin. Antineoplastic
The Uses of Idarubicin hydrochloride
Idarubicin HCl is a hydrochloride salt form of Idarubicin which is an anthracycline antibiotic and a DNA topoisomerase II (topo II) inhibitor for MCF-7 cells with IC50 of 3.3 ng/mL
What are the applications of Application
Idarubicin Hydrochloride is an apoptosis inducer
Definition
ChEBI: Idarubicin hydrochloride is an anthracycline.
brand name
Zavedos
General Description
Idarubicin is available in 5-, 10-, and 20-mL vials for IV administrationin the treatment of acute myeloid leukemia andacute nonlymphocytic leukemia. The compound lacks the4-methoxy group and terminal side-chain alcohol of doxorubicinmaking it the most lipophilic of the four major anthracyclines(doxorubicin, daunorubicin, epirubicin, idarubicin),and it is considered less cardiotoxic than doxorubicin. Theremoval of the 4-methoxy group also increases inhibition oftopoisomerase II. The drug has a fast distributive phase anda high volume of distribution reflecting binding to tissue.Concentrations in blood and bone marrow cells are 100 timeshigher than those found in plasma, reflecting its use in treatingleukemias. Metabolism of the agent primarily occurs byconversion to idarubicinol via reduction of the side chain ketoneto the alcohol, which retains activity as an antineoplastic.Elimination occurs primarily in the bile. Adverse effectsare similar to those found for doxorubicin; however, there isa lower incidence of cardiotoxicity.
Trade name
Idamycin PFS, Idamycin?
Mechanism of action
Increased rates of remission have been noted with the use of idarubicin compared to other anthracyclines antineoplastic agents. Unlike its congeners, idarubicin shows significant oral bioavailability and is lipophilic enough to penetrate the blood-brain barrier. Currently, however, it is given only by the IV route and is not used in the treatment of brain cancer.
Clinical Use
Its primary indication is in acute myeloid leukemia, and it is administered in combination with other antileukemic drug.
Side Effects
Common adverse reactions to Idarubicin hydrochloride may include nausea and vomiting, mucositis, and some patients may experience serious adverse reactions including transient elevation of hepatic aminotransferases and total bilirubin, alopecia, transient rash, urticaria at the site of injection, and skin toxicity[1].
Safety Profile
A poison by ingestion, subcutaneous, intravenous, and intraperitoneal routes. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic vapors of NOx, HCl, and Cl-.
Drug interactions
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs
Other myelosuppressant medication and
radiotherapy: increased risk of myelosuppression.
Antipsychotics: avoid concomitant use with
clozapine, increased risk of agranulocytosis.
Ciclosporin: concentration increased by ciclosporin.
Cytotoxics: possible increased cardiotoxicity with
trastuzumab.
Live vaccines: risk of generalised infections - avoid.
Metabolism
Idarubicin is reduced by aldoketoreductases to idarubicinol, which is as active as the parent drug. Because there is no aromatic methoxy group, there is no O-dealkylation to the C4-phenol. The major metabolite is free, unconjugated idarubicinol. The half-lives of both idarubicin and idarubicinol are 22 and 45 hours, respectively. Idarubicin is administered IV at a dose of 10 to 12 mg/m2 /day for 3 to 4 days, and the idarubicinol metabolite can still be found in therapeutic concentrations in the blood 8 days after administration. Like other anthracyclines, excretion primarily is fecal, with a lesser dependence on renal elimination.
References
[1] h. dorota halicka, m. fevzi ozkaynak, oya levendoglu-tugal, claudio sandoval , karen seiter, malgorzata kajstura, frank traganos, somasunadaram jayabose, and zbigniew darzynkiewicz. dna damage response as a biomarker in treatment of leukemias. cell cycle. 2009, 8(11): 1720–1724.
[2] haydar çelik and emel arinç. evaluation of the protective effects of quercetin, rutin, resveratrol, naringenin and trolox against idarubicin-induced dna damage. j pharm pharmaceut sci. 2010, 13(2): 231 – 241.
[3] ching-hon pui, siebold s. n. de graaf, lois w. dow, john h. rodman, william e. evans, bruce s. alpert and sharon b. murphy. phase i clinical trial of orally administered 4-demethoxydaunorubicin (idarubicin) with pharmacokinetic and in vitro drug sensitivity testing in children with refractory leukemia. cancer research. 1988, 48: 5348-5352.
References
[1] S M FIELDS J M K. Idarubicin: a second-generation anthracycline.[J]. DICP?: the annals of pharmacotherapy, 1991, 25 5: 505-517. DOI:10.1177/106002809102500511.
Properties of Idarubicin hydrochloride
| Melting point: | 183-185 C |
| alpha | D20 +205° (c = 0.1 in methanol) (Arcamone); D20 +188° (c = 0.10 in methanol) (Kimura) |
| storage temp. | Inert atmosphere,2-8°C |
| solubility | ≥26.7 mg/mL in DMSO; insoluble in EtOH; ≥2.39 mg/mL in H2O with ultrasonic |
| form | solid |
| color | Orange to red |
| Stability: | Hygroscopic, Light Sensitive |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 57852-57-0 |
Safety information for Idarubicin hydrochloride
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06  Health Hazard GHS08 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H300:Acute toxicity,oral H351:Carcinogenicity H360:Reproductive toxicity |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P201:Obtain special instructions before use. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P308+P313:IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/attention. |
Computed Descriptors for Idarubicin hydrochloride
| InChIKey | JVHPTYWUBOQMBP-RVFAQHLVSA-N |
| SMILES | C12=C(O)C3=C(C(=O)C4C=CC=CC=4C3=O)C(O)=C1C[C@@](O)(C(=O)C)C[C@]2([H])O[C@@H]1O[C@H]([C@@H](O)[C@@H](N)C1)C.Cl |&1:19,25,28,30,31,33,r| |
New Products
Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate (S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL 3-(2,4-Dimethoxybenzyl)dihydropyrimidine-2,4(1H,3H)-dione 7-Bromo-1H-indazole N-octanoyl benzotriazole 3,4-Dibenzyloxybenzaldehyde 4-Hydrazinobenzoic acid Electrolytic Iron Powder Fmoc-Val-Cit-PAB 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 4-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5-BROMO-2CYANO PYRIDINE 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 1-(4-Methylphenylsulfonyl)-1H-1,2,3-benzotriazole 1-(2-Chlorobenzyl)-4-nitro-1H-pyrazole 1-(2-Nitrophenyl)-4-phenylpiperazineRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
![(1S)-4,5-Dimethoxy-1-[(methylamino)methyl]benzocyclobutane hydrochloride](https://img.chemicalbook.in/CAS/GIF/866783-13-3.gif)
You may like
-
 Idarubicin CAS 57852-57-0View Details
Idarubicin CAS 57852-57-0View Details
57852-57-0 -
 55441-95-7 2 2-BIS(2-HYDROXYETHOXY)-1 1-BINAPHTHYL 99%View Details
55441-95-7 2 2-BIS(2-HYDROXYETHOXY)-1 1-BINAPHTHYL 99%View Details
55441-95-7 -
 Ste-Glu-AEEA-AEEA-OSUView Details
Ste-Glu-AEEA-AEEA-OSUView Details
1169630-40-3 -
 1446013-08-6 Fmoc-His-Aib-OH TFA 98%View Details
1446013-08-6 Fmoc-His-Aib-OH TFA 98%View Details
1446013-08-6 -
 127464-43-1 99%View Details
127464-43-1 99%View Details
127464-43-1 -
 Chloro Uracil 99%View Details
Chloro Uracil 99%View Details
1820-81-1 -
 2-ETHYLPYRIDINE 100-71-0 99%View Details
2-ETHYLPYRIDINE 100-71-0 99%View Details
100-71-0 -
 13162-05-5 99%View Details
13162-05-5 99%View Details
13162-05-5