Hyperoside
Synonym(s):3,3′,4′,5,7-Pentahydroxyflavone 3-D -galactoside;Hyperin;Hyperoside;Quercetin 3-D -galactoside
- CAS NO.:482-36-0
- Empirical Formula: C21H20O12
- Molecular Weight: 464.38
- MDL number: MFCD00016933
- EINECS: 207-580-6
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-11-29 14:36:51
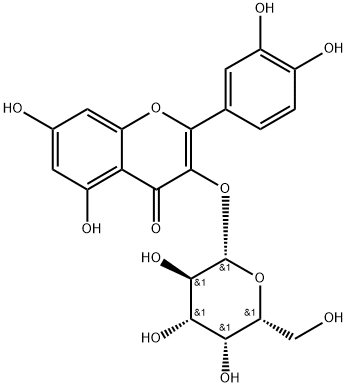
What is Hyperoside?
Description
Hypericin, which is widely found in various plants, such as Hypericum, Rosaceae, Campanulaceae, Labiatae, Rhododendron, Asteraceae Kwai, Garciniaceae, Leguminosae, Euonymus, and other fruits and whole grass, is a flavonoid compound.
Chemical properties
Yellow Solid
Physical properties
Appearance: yellowish needlelike crystals. Melting point: 227–229 °C. Specific optical rotation: ?83° (c = 0.2, pyridine). Solubility: soluble in ethanol, methanol, acetone, and pyridine. Hydrochloric acid–magnesium powder reaction yielded formation of cherry red; ferric chloride reaction was green; α-naphthol reaction was positive.
History
In 1960, Nair et al. isolated hyperin from redosier dogwood, in which its content is 0.075%. Flavonoids in the treatment of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases play a pivotal role, among which rutin is a typical representative. Isoquetin mainly presents in the leaves of kumquat flowers and the oleander plant kenaf, and it can also be obtained by chemical synthesis. It shows an anti-inflammatory effect through the capillary permeability test and other animal experiments. It also has a toxic effect on the larvae of Chilohabala larvae. It is one of the active ingredients of Hypericum japonicum, which is used in the treatment of hepatitis because of its inhibition of the activities of hepatic enzyme.
The Uses of Hyperoside
Hyperoside is used as a primary reference standard in the analysis of herbal medicinal products. It may be used as a calibration standard in method validation of polyphenols from leaf extracts using HPLC method.
The Uses of Hyperoside
A major flavonoid in apple peels; a bioactive constituent of apple peels
The Uses of Hyperoside
It may be used as calibration standard solutions in method validation of polyphenols from leaf extracts using HPLC method.
What are the applications of Application
Quercetin 3-D-galactoside is a flavonol glycoside with potent antioxidant properties
Definition
ChEBI: A quercetin O-glycoside that is quercetin with a beta-D-galactosyl residue attached at position 3. Isolated from Artemisia capillaris, it exhibits hepatoprotective activity.
Indications
This product is available in the British Pharmacopoeia (2017) and the European
Pharmacopoeia (9.0th ed.).
Monomeric compounds are currently used clinically. In clinical practice, hypericin
is the main active ingredient of proprietary Chinese medicines, such as
Acanthopanax capsules, of which Acanthopanax stem and leaf extract are the raw
materials for the preparation. Xin’an capsules, prepared with hawthorn leaf extract,
are rich in flavonoids, in which hyperoside, a kind of flavonoid, is one of the main
components. Qi yue lipid-lowering tablets are prepared from the effective parts of
Chinese medicinal herbs such as hawthorn (Nucleation) and Astragalus membranaceus.
Flavonoid is one of the main active ingredients in hawthorn, in which hyperoside
content is higher. Xinxuening tablets, containing ursolic acid, vitexin
rhamnoside, hyperoside, citric acid, and others, is a preparation made from hawthorn
and pueraria and other traditional Chinese medicines, in which hawthorn
enhances the actions of the medicine. Clinical indications of Xinxuening tablets are
coronary heart disease, angina pectoris, chest tightness, palpitations, high blood
pressure, arrhythmia, hyperlipidemia, and mental depression.
General Description
Produced and qualified by HWI pharma services GmbH.
Exact content by quantitative NMR can be found on the certificate.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Protects against peroxide-induced oxidative damage to cells by scavenging reactive oxygen species and enhancing activity of anti-oxidant enzymes, in particular, catalase and glutathione peroxidase.
Pharmacology
Hyperoside has a protective effect against myocardial ischemia. It achieves its protective effect on the myocardium by reducing the apoptosis rate of myocardial cells,
inhibiting myocardial cell lactate dehydrogenase release, enhancing anti-freeradical
effect , and inhibiting calcium influx so as to .
Hyperoside has a protective effect against cerebral ischemia. Hyperoside can
significantly lower oxygen-free radicals, reduce the content of malondialdehyde
and NO in brain tissue, inhibit the decrease of the activity of LDH, SOD and glutathione
peroxidase, and hence result in reduced brain energy, and improve the antianoxic
ability . At the same time, hyperoside can reduce the degree of cerebral edema in ischemia-reperfusion rats .
Hypericin has a significant local analgesic effect that is weaker than that of morphine
and stronger than that of aspirin and does not create dependency; it is a new
type of local analgesic. Studies have shown that the analgesic effect of hyperoside
occurs by reducing the Ca2 + of the pain nerve, thereby inhibiting high potassium-induced
Ca2 + influx, which distinguishes it from morphine and aspirin .
Hyperoside has a significant anti-inflammatory effect and a strong cough effect and inhibits the role of eye aldose reductase, which may be beneficial for the prevention
of diabetic cataracts. Hypericin has an obvious protective effect on liver tissue and gastric mucosa , and its mechanism is related to antioxidant activity and the promotion of a normal return of NO level and improvement of SOD activity.
Hyperoside significantly enhances immune function. In vivo, hyperoside has a significant inhibitory effect on spleen B, T lymphocyte proliferation and peritoneal macrophage phagocytosis, and mouse thymus index; in vitro hyperoside, at a concentration
of 6.25–100 μg/mL, significantly enhanced B, T lymphocyte proliferation and promoted the production of interleukin 2 in T lymphocytes .
In addition, hypericin still has hypolipidemic and antidepressant pharmacological
effects. Its derivative rutin has anti-inflammatory and antiviral effects. Another
derivative, quercetin, is effective at inhibiting expectorant, cough, and asthma for
use in the treatment of chronic bronchitis, coronary heart disease, and hypertension.
Properties of Hyperoside
| Melting point: | 225-226°C |
| Boiling point: | 872.6±65.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.87±0.1 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | -20°C |
| solubility | DMSO (Slightly), Methanol (Slightly, Heated) |
| form | Solid |
| pka | 6.17±0.40(Predicted) |
| color | Light Yellow to Yellow |
| BRN | 5784795 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 482-36-0(CAS DataBase Reference) |
Safety information for Hyperoside
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P270:Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product. P301+P312:IF SWALLOWED: call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician IF you feel unwell. P501:Dispose of contents/container to..… |
Computed Descriptors for Hyperoside
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid 1-Bromo-3,5-Di-Tert-Butylbenzene S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 Hyperoside 98% (HPLC) CAS 482-36-0View Details
Hyperoside 98% (HPLC) CAS 482-36-0View Details
482-36-0 -
 Hyperoside, ≥97% (HPLC) CAS 482-36-0View Details
Hyperoside, ≥97% (HPLC) CAS 482-36-0View Details
482-36-0 -
 Hyperoside CAS 482-36-0View Details
Hyperoside CAS 482-36-0View Details
482-36-0 -
 Hyperoside CAS 482-36-0View Details
Hyperoside CAS 482-36-0View Details
482-36-0 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1