Hippuric acid
Synonym(s):N-Benzoylglycine;Benzamidoacetic acid, Benzoylglycine, Benzoylaminoacetic acid;Benzoylaminoacetic acid;Hippuric acid
- CAS NO.:495-69-2
- Empirical Formula: C9H9NO3
- Molecular Weight: 179.17
- MDL number: MFCD00002692
- EINECS: 207-806-3
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-19 17:28:17
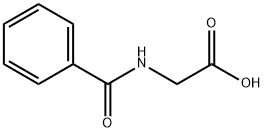
What is Hippuric acid?
Description
Hippuric acid, or N-benzoylglycine, is an amino acid derivative found in the urine of herbivorous animals. The name is derived from Greek hippos (horse) and ouron (urine). In 1829, the pioneering German chemist Justus von Liebig so named it because his research on the compound concentrated on horse urine.
Hippuric acid also occurs in avocadoes (Persea americana) and common beans (Phaseolus vulgaris). As its chemical name suggests, the compound is formed by the reaction of benzoic acid and glycine in the urine.
Later in the 19th century, von Liebig’s last student, Oscar Loew, also studied hippuric acid. In 1879, Loew wrote about the source of the acid in herbivores’ urine. According to an account of the article in the first volume of the Journal of the American Chemical Society (1879), quinic acid1 in hay turns into hippuric acid during digestion. This finding had previously been observed in 1863 by Eduard Lautemann, a student of another important German chemist, Hermann Kolbe.
Synthetic hippuric acid is produced similarly to the biochemical reaction: Glycine is acylated with benzoyl chloride in the presence of base, followed by acidification to form the acid. Hydrolysis in strong base restores it to glycine and benzoic acid.
Extensive information about the biochemistry of hippuric acid and its implications for human health can be found in the ScienceDirect entry on the compound.
1. CAS Reg. No. 77-95-2.
Chemical properties
White crystalline powder
The Uses of Hippuric acid
N-Benzoylglycine also known as Hippuric Acid is the glycine conjugate of benzoic acid commonly found in ruminant urine. It is synthesized in the liver and its production is greatly increased following consuption of benzoic acid. In itself it does not have a direct biological function, however p-hydroxy-hippurica acid can be used as an inhibitor of Ca2+ ATPase.
The Uses of Hippuric acid
Hippuric acid is used as a intermediate for the manufacturing medicine and other organic compounds. Hippuric acid can be used to study cell biology, chemical biology, bioactive small molecules, amino acid derivatives, peptide synthesis, chemical synthesis and nutrition. Hippuric acid has been used to inform the metabolism and urinary excretion of procyanidins.
Definition
ChEBI: An N-acylglycine in which the acyl group is specified as benzoyl.
Preparation
Preparation of Hippuric acid from Glycine.
Principle: The hydroxy and amino functions can be easily benzoylated using Benzoyl chloride in aqueous alkaline conditions. This reaction is known as Schotten-Baumann reaction.
Reaction:

Procedure: Dissolve 0.5 g of glycine in 5 ml of 10% NaOH solution in a 25 ml conical flask. Add 0.9 ml of benzoyl chloride in five portions to the solution. Stopper the flask and shake vigorously after each addition until all the benzoyl chloride is reacted. Transfer the solution to a beaker and add few grams of ice and add conc. HCl slowly with stirring until the solution is acidic to litmus paper. Filter the crystalline precipitate of the product on a Buchner funnel, wash with cold water and drain well. Place the solid in a conical flask with 10 ml CCl4 and boil gently for 10 min. Allow the mixture to cool slightly, filter under gentle suction and wash with 10-20 ml CCl4. Record the practical yield and re-crystallize it.
Re-crystallization: Dissolve the crude product from boiling water (5 ml), with addition of decolorizing charcoal if necessary, filter the hot solution and cool the filtrate. The crystals of the product separate out. Filter, dry and record the melting point and TLC [using Butanal : acetic acid: water (4 : 1 : 1) as solvent or CHCl3:methanol (9 : 1) or toluene].
Purification Methods
Crystallise the acid from boiling H2O. Dry it over P2O5. Also purify it by dissolving 135-140g in 2L of boiling H2O, filtering through a steam-heated funnel and allowing to crystallise at ~20o (yield 115-122g first crop, m 186-187o). [Ingersoll & Babcock Org Synth Coll Vol II 328 1943, Beilstein 9 225, I 100.]
Properties of Hippuric acid
| Melting point: | 187-191 °C (lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 311.69°C (rough estimate) |
| Density | 1,371 g/cm3 |
| refractive index | 1.5600 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | Store below +30°C. |
| solubility | 3.26g/l |
| pka | 3.62(at 25℃) |
| appearance | white crystals or powder |
| form | Crystalline Powder |
| color | White to almost white |
| PH | 2.5-3.5 (10g/l, H2O, 20℃)(slurry) |
| Water Solubility | Soluble in water. |
| Merck | 14,4716 |
| BRN | 1073987 |
| Stability: | Stable. Incompatible with oxidizing agents. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 495-69-2(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Glycine, N-benzoyl- (495-69-2) |
Safety information for Hippuric acid
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Corrosion Corrosives GHS05  Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H318:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P304+P340:IF INHALED: Remove victim to fresh air and Keep at rest in a position comfortable for breathing. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. P405:Store locked up. |
Computed Descriptors for Hippuric acid
| InChIKey | QIAFMBKCNZACKA-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
Hippuric acid manufacturer
NSR Amino Organics
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


You may like
-
 Hippuric Acid Reference Standard CAS 495-69-2View Details
Hippuric Acid Reference Standard CAS 495-69-2View Details
495-69-2 -
 Hippuric acid, 99% CAS 495-69-2View Details
Hippuric acid, 99% CAS 495-69-2View Details
495-69-2 -
 Hippuric Acid CAS 495-69-2View Details
Hippuric Acid CAS 495-69-2View Details
495-69-2 -
 HIPPURIC ACID For Synthesis CAS 495-69-2View Details
HIPPURIC ACID For Synthesis CAS 495-69-2View Details
495-69-2 -
 Hippuric AcidView Details
Hippuric AcidView Details
495-69-2 -
 Hippuric Acid (495-69-2 ), 99%, Grade: IndustrialView Details
Hippuric Acid (495-69-2 ), 99%, Grade: IndustrialView Details
495-69-2 -
 Hippuric AcidView Details
Hippuric AcidView Details
495-69-2 -
 Hippuric AcidView Details
Hippuric AcidView Details
495-69-2
