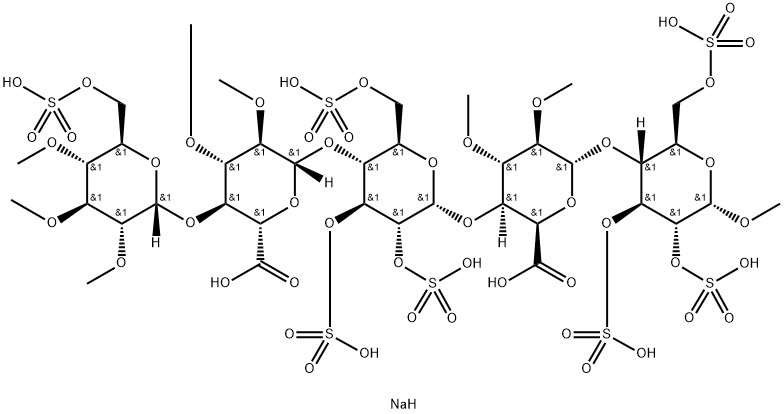
Heparin sodium
Synonym(s):HEP, Na;Heparin sodium;Heparin sodium salt;Heparin, Sodium Salt, Porcine Intestinal Mucosa - CAS 2608411 - Calbiochem
- CAS NO.:9041-08-1
- Empirical Formula: (C12H16NS2Na3)20
- Molecular Weight: 0
- MDL number: MFCD00081689
- EINECS: 232-681-7
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 13:37:16
What is Heparin sodium?
Absorption
Subcutaneous injection - about 90% when measured as anti-Xa activity versus 67% for anti-IIa activity.
Toxicity
Osteoporosis with increasing duration of use, bleeding, alopecia, heparin induced thrombocytopenia (HIT). All of these adverse drug reactions occur less with LMWH compared to unfractionated heparin. Tinzaparin showed no toxic effects at doses up to 5 mg/kg in mice, rats, or dogs in standard acute, subacute, and chronic toxicity studies.
Description
Reviparin sodium, a second-generation low molecular weight heparin produced from porcine mucosal heparin, has been introduced for the prevention of deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism following surgery. It has sustained activity and increased bioavailability over unfractioned heparin. More noticeably, reviparin shows a pronounced inhibitory effect, both in vitro and in vivo , on smooth muscle cell proliferation which plays a predominant role in restenosis following angioplasty. Indeed, a lower incidence of restenosis without major bleeding complications has been reported for reviparin treated patients who successfully underwent percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty.
Chemical properties
off-white powder
Originator
Knoll (Germany)
The Uses of Heparin sodium
Heparin sodium salt is used as a blood anti-coagulant. It is also used as an effective inhibitor of mesenchymal cell proliferation. Further, it binds to antithrombin III, which inhibits coagulation proteases. It is used as a major component of serum free media for preventing cell aggregation. It is also used as an anti-cancer agent in in vitro cancer research.
The Uses of Heparin sodium
for coagulation proteins, nucleic acids
The Uses of Heparin sodium
corrosive moisture sensitive
Background
Reviparin is a low molecular weight heparin which seems to have a better safety profile than unfractionated heparin. It is prepared from porcine intestinal mucosa by nitrous acid depolymerization. Reviparin has a molecular weight of 3.9 kDa. It was developed by Abbott laboratories and in 2009, reviparin presented an orphan drug designation by the FDA.
Indications
By the FDA, reviparin is indicated for the treatment of deep vein which may lead to pulmonary embolism in pediatric patients. It is also indicated for the long-term treatment of acute deep vein thrombosis with or without pulmonary embolism in pregnant patients.
Background
Tinzaparin is a low molecular weight heparin (LMWH), produced by enzymatic depolymerization of unfractionated heparin from porcine intestinal mucosa. It is a heterogeneous mixture of with an average molecular weight between 5500 and 7500 daltons. Tinzaparin is composed of molecules with and without a special site for high affinity binding to antithrombin III (ATIII). This complex greatly accelerates the inhibition of factor Xa. It is an anticoagulant and considered an antithrombotic. Tinzaparin must be given either subcutaneously or parenterally. LMWHs are less effective at inactivating factor IIa due to their shorter length compared to unfractionated heparin.
Indications
Tinzaparin is used for the prevention of postoperative venous thromboembolism in patients undergoing orthopedic surgery and in patients undergoing general surgery who are at high risk of developing postoperative venous thromboembolism. It is also used for the treatment of deep vein thrombosis and/or pulmonary embolism. It is indicated for use in preventing clot formation in indwelling intravenous lines for hemodialysis.
What are the applications of Application
Heparin sodium salt is a heparin polymer that produces its anticoagulant effect by activating ATIII (antithrombin)
Manufacturing Process
Heparinic acid a highly acidic mucopolysaccharide formed of equal parts of
sulfated D-glucosamine and D-glucuronic acid with sulfaminic bridges. The
molecular weight ranges from six to twenty thousand. Heparin occurs in and is
obtained from liver, lung, mast cells, etc., of vertebrates. Its function is
unknown, but it is used to prevent blood clotting in vivo and vitro, in the form
of many different salts.
In a self-regulated process for depolymerizing a heparin in an aqueous
solution by providing about 0.02 to 0.1 M nitrous acid and a pH of about 2 to
3 in said solution, so that process occurs when all the nitrous acid has been
consumed and mucopolysaccharides are produced from the heparin having an
average molecular weight of less than 6,000. Heparin has molecular weight
from 2000 to 50000. The products obtained by a below described method are
constituted by a major part of species of molecular weight of about 2,000 to
8,000, which corresponds to structures having from about 8 to 40 saccharide
entities (the molecular weights are measured by the HPLC method, by means,
for example, of a 0.5 M sodium sulphate buffer).
Self-Regulated Depolymerization of Heparin and Production of MPS of Low
Molecular Weight.
Into 15 liters of distilled water at +20°C, 1,500 grams of commercial heparin
having a YW/USP ratio in the vicinity of 1 and a USP titer of 160 iu, are
dissolved. 51.8 g of sodium nitrate dissolved in 300 ml of distilled water are
added, and immediately the pH is lowered to 2.5 by pure hydrochloric acid.
The reaction then takes place and its progress is checked until the absence of
nitrous ions. After 40 minutes, the presence or absence of nitrous ions is
checked at regular intervals in the reaction medium. Starch-iodine paper, for
example, is used, checking every 5 minutes. After about 60 minutes of
reaction, the nitrous acid had been entirely consumed and no more NO2
- ions
remained in the reaction medium. The pH was then adjusted to 7 with pure
caustic soda, and the products of the reaction were recovered by the addition
of 31 liters of pure ethanol (2 volumes). The precipitate formed was collected
by centrifugation, washed with ethanol and dried at 60°C under vacuum.
1,200 g of products having the following characteristics were collected: USP
titer: 19 μ/mg; APTT titer: 13 μ/mg; Yin and Wessler titer: 202 μ/mg.
In 10 liters of distilled water, at room temperature (15°-20°C) 1,000 grams of
commercial injectable heparin having a USP titer of 170 μ/mg and a YW titer
of 160 μ/mg, are dissolved. 38 g of sodium nitrite (final molarity 0.055 M)
dissolved in 200 ml of water, is added. The pH is immediately lowered to 2.5
by pure hydrochloric acid. The reaction is checked as above at regular
intervals of time (5-10 minutes). After 30 minutes, NO2
- ions are no longer
detected in the reaction medium. The pH is then adjusted to 7 with 5 N soda;
the products of the reaction are recovered by the addition of 21 liters of pure
ethanol (2 volumes). The precipitate formed is collected by centrifugation,
washed with ethanol and dried at 60°C under vacuum. Finally there are
obtained 780 grams of white coloured powder having the following
characteristics: USP Titer: 22 μ/mg; Yin and Wessler Titer: 260 μ/mg; APTT
Titer: 10 μ/mg. Content of nitrites-nitrates: 5 ppm: <4 ppm. Average
molecular weight: less than 6,000. Percentage of species whose molecular
weight exceeds 10,000: less than 1%.
brand name
Normiflo (Pharmacia & Upjohn);Clivarin.
Therapeutic Function
Anticoagulant, Antithrombotic
General Description
Heparin is mainly responsible for the delay in the coagulation of blood. It enhances the antithrombin-mediated inactivation of proteases in the coagulation pathway.
Pharmacokinetics
Reviparin is been shown to present significant inhibition of smooth muscle cell migration and proliferation in human cell cultures without affecting endothelial cell growth.
Pharmacokinetics
Tinzaparin, like other LMWHs, have a higher anti-Xa activity than anti-IIa activity. The anti-Xa activity of tinzaparin is 2.0 +/- 0.5 times greater than its to anti-IIa activity. Heparin exhibits approximately equal inhibitory activity against Xa and IIa. Tinzaparin is an anticoagulant that blocks the formation of thrombi. Like all LMWHs, tinzaparin only causes activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT) prolongation at higher doses and routine monitoring is not recommended. However, anti-factor Xa levels may be monitored in some conditions such as pregnancy and renal dysfunction. Its use should be avoided in patients with a creatinine clearance less than 20 mL/min. In these patients, unfractionated heparin should be used. Tinzaparin can be used in patients who have a creatinine clearance between 20-30 mL/min, giving it the highest safety threshold for use in renal failure patients compared to all the LMWHs.
Veterinary Drugs and Treatments
Heparin’s primary uses in small animal medicine has included
treatment of Disseminated
Intravascular Coagulation (DIC) and
prophylaxis of thromboembolic disease. In horses, it has been used
in the treatment of DIC and as prophylactic therapy for laminitis
(unproven efficacy).
Use for treating DIC has become increasingly controversial. The
most recent evidence suggests that heparin not be used during DIC
in patients with concurrent inflammatory processes.
Metabolism
Not Available
Metabolism
Sulfation and polymerization occurs in the liver.
storage
Desiccate at RT
Purification Methods
Dissolve the salt in 0.1M NaCl (1g/100mL) and precipitate it by additing EtOH (150mL). [Wolfrom et al. J Org Chem 29 540 1946, Huggard Adv Carbohydr Chem 10 336-368 1955.]
Properties of Heparin sodium
| Melting point: | >181°C (dec.) |
| alpha | D25 +47° (c = 1.5 in water) |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | H2O: 50 mg/mL, clear, faintly yellow |
| form | crystalline (fine) |
| color | white |
| PH | pH (10g/l, 25℃) : 6.0~8.0 |
| Water Solubility | Soluble in water, dimethyl sulfoxide and ethanol. |
| Merck | 14,4653 |
| Stability: | Stable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents, strong bases. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 9041-08-1 |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Heparin, sodium salt (9041-08-1) |
Safety information for Heparin sodium
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P271:Use only outdoors or in a well-ventilated area. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. |
Computed Descriptors for Heparin sodium
Heparin sodium manufacturer
S D Fine Chem Limited
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran







You may like
-
 Heparin sodium, 20,000 Iu/Vial CAS 9041-08-1View Details
Heparin sodium, 20,000 Iu/Vial CAS 9041-08-1View Details
9041-08-1 -
 Heparin Sodium Salt ex. Bovine Intestinal Mucosa CAS 9041-08-1View Details
Heparin Sodium Salt ex. Bovine Intestinal Mucosa CAS 9041-08-1View Details
9041-08-1 -
 Heparin sodium, 1,00,000 Iu/Vial CAS 9041-08-1View Details
Heparin sodium, 1,00,000 Iu/Vial CAS 9041-08-1View Details
9041-08-1 -
 Heparin Sodium Salt from Hog intestine CAS 9041-08-1View Details
Heparin Sodium Salt from Hog intestine CAS 9041-08-1View Details
9041-08-1 -
 HEPARIN SODIUM PURE 20,000 IU/VIAL CASView Details
HEPARIN SODIUM PURE 20,000 IU/VIAL CASView Details -
 Dalteparin sodium CAS 9041-08-1View Details
Dalteparin sodium CAS 9041-08-1View Details
9041-08-1 -
 Heparin Sodium Salt ex. Bovine Intestinal Mucosa CAS 9041-08-1View Details
Heparin Sodium Salt ex. Bovine Intestinal Mucosa CAS 9041-08-1View Details
9041-08-1 -
 HEPARIN SODIUM PURE 1,00,000 IU/VIAL CASView Details
HEPARIN SODIUM PURE 1,00,000 IU/VIAL CASView Details