Guanine
Synonym(s):2-Amino-1,7-dihydro-6H-purin-6-one;2-Amino-6-hydroxypurine;2-Aminohypoxanthine
- CAS NO.:73-40-5
- Empirical Formula: C5H5N5O
- Molecular Weight: 151.13
- MDL number: MFCD00071533
- EINECS: 200-799-8
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-17 09:49:38
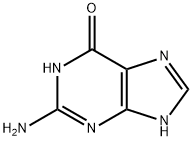
What is Guanine?
Chemical properties
white to light yellow crystal powder
History
Guanine is one of the two purines comprising the five nucleic acid bases. Much of the information regarding the general role of nucleic acid bases is covered in Adenine and Cytosine. Guanine gets its name from guano, from which it was first isolated in the 1840s. Albrecht Kossel (1853 1927) determined that guanine (as well as adenine, cytosine, thymine and uracil) was a component of nucleic acid in the last two decades of the 19th century. Similar to adenine, guanine combines with ribose to form a nucleoside. The nucleoside produced is guanosine, which in turn combines with one to three phosphoryls to yield the nucleotides guanosine monophosphate (GMP), guanosine diphosphate (GDP), and guanosine triphosphate (GTP), respectively. Guanine nucleotides play an important role in metabolism including the conversion of adenosine diphosphate (ADP) to adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and carbohydrate metabolism.
The Uses of Guanine
Guanine is on one of the five nucleobases incorporated into biological nucleic acids. Guanine, along with adenine and cytosine, is present in both DNA and RNA, whereas thymine is usually seen only in DNA, and uracil only in RNA.
The Uses of Guanine
guanine is mixed in water and used primarily in nail polish to achieve a pearlized effect. It has been greatly replaced by either synthetic pearl or aluminum and bronze particles. guanine is obtained from plant or animal sources.
The Uses of Guanine
Guanine is a crystalline amorphous substance that is found in guano, fish scales, and theliver of certain mammals. Guanine is responsible for the silvery iridescence of certain fishscales. Before its discovery, guanine was scraped from fish scales and used to coat beads to produceimitation pearls. Thus it was called pearl essence or pearly white in the 1700s. Guanineobtained from fish scales is used in cosmetics, especially for eye cosmetics and nail polishes.
Definition
ChEBI: A 2-aminopurine carrying a 6-oxo substituent.
Definition
A nitrogenous base found in DNA and RNA. Guanine has a purine ring structure.
Definition
guanine: A purine derivative. It isone of the major component bases ofnucleotides and the nucleic acidsDNA and RNA.
Occurence
Guanine exists in diverse sources such as guano (collected excrement and dead bodies of bats, birds and seals) , yeast, fish scales and sugar beets.
General Description
Pharmaceutical secondary standards for application in quality control, provide pharma laboratories and manufacturers with a convenient and cost-effective alternative to the preparation of in-house working standards.
Guanine is one of the building blocks of both RNA and DNA that plays a significant role in protein biosynthesis as well as the storage of genetic information.
Biological Activity
guanine is one of the four main nucleobases found in the nucleic acids dna and rna.guanine is a purine derivative, consisting of a fused pyrimidine-imidazole ring system with conjugated double bonds.
Properties of Guanine
| Melting point: | >300 °C (lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 273.11°C (rough estimate) |
| Density | 1.4456 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 2.0000 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | 1 M NaOH: 0.1 M at 20 °C, clear, colorless |
| pka | 9.92(at 40℃) |
| form | Powder |
| color | White to cream |
| Odor | Odorless |
| Water Solubility | practically insoluble |
| Decomposition | 360°C |
| Merck | 14,4564 |
| BRN | 9680 |
| Stability: | Stable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 73-40-5(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | 6H-Purin-6-one, 2-amino-1,7-dihydro-(73-40-5) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Guanine (73-40-5) |
Safety information for Guanine
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P271:Use only outdoors or in a well-ventilated area. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P302+P352:IF ON SKIN: wash with plenty of soap and water. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Guanine
| InChIKey | UYTPUPDQBNUYGX-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
Guanine manufacturer
Clickchem Research LLP
Dr .Silviu Pharmachem Pvt. Ltd.
Innovative
New Products
Indole Methyl Resin tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Boc-His(Boc)-OH 2-CTC Resin 4-Chloro-7-tosy1-7Hpyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine 5,7-Dibromo-1H-indole 2,5-dichloro-N-hydroxy-4,6-dimethylpyridine-3-carboximidamide 2,2-Dimethoxy-7-azaspiro[3.5]nonane hydrochloride 4-chloromethyl-5-methyl-1,3-dioxol-2-one (DMDO-Cl) R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID 4-((2-hydroxyethyl)thio)benzoic acid 1-(TERT-BUTOXYCARBONYL)-2-PYRROLIDINONE Methyl 6-methylnicotinate 3-Pyridineacrylic acid tert-Butyl carbazate TETRAHYDRO-2H-PYRAN-3-OL 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 1,3-Diethyl-1,3-Diphenylurea Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
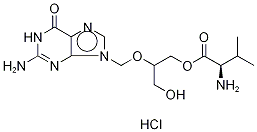

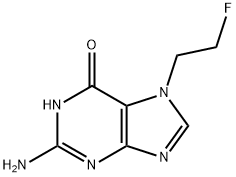
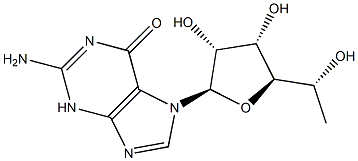

You may like
-
 Guanine CAS 73-40-5View Details
Guanine CAS 73-40-5View Details
73-40-5 -
 Guanine extrapure CAS 73-40-5View Details
Guanine extrapure CAS 73-40-5View Details
73-40-5 -
 Guanine CASView Details
Guanine CASView Details -
 Powder White Guanine (CAS Number: 73-40-5), Packaging Size: 1 kg / 5 kg / 10 kg / 25 kgView Details
Powder White Guanine (CAS Number: 73-40-5), Packaging Size: 1 kg / 5 kg / 10 kg / 25 kgView Details
73-40-5 -
 GuanineView Details
GuanineView Details
73-40-5 -
 GuanineView Details
GuanineView Details
73-40-5 -
 Aciclovir EP Impurity B, OR 2-Amino-Hypoxanthine CAS: 73-40-5, 25mg, Analytical GradeView Details
Aciclovir EP Impurity B, OR 2-Amino-Hypoxanthine CAS: 73-40-5, 25mg, Analytical GradeView Details
73-40-5 -
 99% Valaciclovir EP Impurity AView Details
99% Valaciclovir EP Impurity AView Details
73-40-5
