GLUCOSE-6-PHOSPHATE DEHYDROGENASE
Synonym(s):G-6-P-DH;G6P-DH;Glucose-6-Phosephate Dehydrogenase;Glucose-6-phosphate Dehydrogenase, Leuconostoc mesenteroides;Zwischenferment
- CAS NO.:9001-40-5
- Empirical Formula: n.a.
- Molecular Weight: 0
- MDL number: MFCD00081656
- EINECS: 232-602-6
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 14:08:57
What is GLUCOSE-6-PHOSPHATE DEHYDROGENASE?
Chemical properties
White to yellow powder
The Uses of GLUCOSE-6-PHOSPHATE DEHYDROGENASE
Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase, Leuconostoc mesenteroides is used to convert p-glucose-6-phosphate to p-glucono-d-lactone-6-phosphate in presence of NADP+ or NAD+. It is used as an intermediate, chemical and research purpose and also used fo analysis.
The Uses of GLUCOSE-6-PHOSPHATE DEHYDROGENASE
Glucose-6-phosphate Dehydrogenase from Leuconostoc mesenteroides has been used along with hexokinase in the determination of glucose from mice liver samples.
The Uses of GLUCOSE-6-PHOSPHATE DEHYDROGENASE
Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase has been used in a study to investigate the effect of dehydroepiandrosterone on cell growth and mitochondrial function in TM-3 cells. Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase has also been used in a study to investigate the incidence of apoptosis and transcript abundance in bovine follicular cells. Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase is used to test ketose reductase activity in developing maize endosperm.
General Description
Glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G-6-P-DH) is a key regulatory enzyme in the first step of the pentose phosphate pathway. G-6-P-DH is a glycoprotein with a molecular mass of 128 kDa (gel filtration).
Biochem/physiol Actions
Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase catalyzes the conversion of glucose-6-phosphate to 6-phosphogluconolacetone as the first step in the pentose phosphate pathway<<<17>>>.
Purification Methods
The enzyme is useful for measuring pyridine nucleotides in enzyme recycling. The enzyme from Baker's yeast has been purified by (NH4)2SO4 fractionation, Me2CO precipitation, a second (NH4)2SO4 fractionation, concentration by DEAE-SF chromatography, a third (NH4)2SO4 fractionation and recrystallisation. Crystallisation is induced by addition of its coenzyme NADP, which in its presence causes rapid separation of crystals at (NH4)2SO4 concentration much below that required to precipitate the amorphous enzyme. To recrystallise, the crystals are dissolved in 0.01M NADP (pH 7.3) with (NH4)2SO4 at 0.55 saturation, and the crystals appear within 10 to 60minutes. After standing for 2-3days (at 4o) the (NH4)2SO4 is increased to 0.60 of saturation, and more than 80% of the activity in the original crystals is recovered in the fresh crystals. [Noltmann et al. J Biol Chem 236 1255 1961]. Large amounts can be obtained from rat livers. The livers are extracted with 0.025M phosphate buffer (pH 7.5) and precipitated with 3M (NH4)2SO4 (70% of activity). The precipitate is dissolved in 3volumes of 0.025M phosphate (pH 7.5), dialysed against this buffer + 0.2mM EDTA at 4o for 5hours, then diluted to 1% protein and the nucleic acids are precipitated by addition of 0.4volumes of 1% protamine sulfate. (NH4)2SO4 is added to a concentration of 2M (pH adjusted to 7.0 with NH3), the precipitate is discarded and the supernatant is adjusted to 2.8M (NH4)2SO4, dialysed, and the protein is adjusted to 1% and treated with Ca3(PO4)2 gel. The gel is added in three steps (1.5mL of 0.4% gel/mL per step), and the gel is removed by centrifugation after each addition. The third gel adsorbed 50% of the activity. The gel is eluted with 0.2M phosphate buffer (pH 7.4, 40mL/g of gel; 60% recovery). The extract is precipitated in 3volumes of (NH4)2SO4 (adjusted to 4M) to give enzyme with an activity of 30Wmoles/mg of protein per hour. [Lowry et al. J Biol Chem 236 2746 1961.] The Km values for the yeast enzyme are 20WM for G-6P and 2WM for NADP (Tris pH 8.0, 10-2 M MgCl2, 38o) [Noltmann & Kuby The Enzymes VII 223 1963].
Properties of GLUCOSE-6-PHOSPHATE DEHYDROGENASE
| Melting point: | ~120℃ |
| storage temp. | -20°C |
| form | suspension |
| color | white |
| Water Solubility | Soluble in water and dilute buffer. |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Dehydrogenase, glucose 6-phosphate (9001-40-5) |
Safety information for GLUCOSE-6-PHOSPHATE DEHYDROGENASE
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Health Hazard GHS08 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H334:Sensitisation, respiratory |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P284:Wear respiratory protection. P501:Dispose of contents/container to..… |
Computed Descriptors for GLUCOSE-6-PHOSPHATE DEHYDROGENASE
New Products
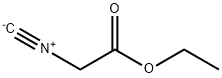
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid 1-Bromo-3,5-Di-Tert-Butylbenzene S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran



You may like
-
 Glucose-6-Phosphate Dehydrogenase ex. Leuconostoc Mesenteroides CAS 9001-40-5View Details
Glucose-6-Phosphate Dehydrogenase ex. Leuconostoc Mesenteroides CAS 9001-40-5View Details
9001-40-5 -
 Glucose-6-Phosphate Dehydrogenase (G6P-DH) CASView Details
Glucose-6-Phosphate Dehydrogenase (G6P-DH) CASView Details -
 Glucose-6-Phosphate Dehydrogenase ex.Leuconostoc Mesenteroides CAS 9001-40-5View Details
Glucose-6-Phosphate Dehydrogenase ex.Leuconostoc Mesenteroides CAS 9001-40-5View Details
9001-40-5 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1