GLIOTOXIN
Synonym(s):(3R,5aS,6S,10aR)-2,3,5a,6-Tetrahydro-6-hydroxy-3-(hydroxymethyl)-2-methyl-10H-3,10a-epidithiopyrazino[1,2-a]indole-1,4-dione;2,3,5a,6-Tetrahydro-6-hydroxy-3(hyroxymethyl)-2-methyl-10H-3a,10a-epidithio-pyrazinol[1,2α]indole-1,4-dione;Aspergillin;Aspergillin solution;Gliotoxin, Gladiocladium fimbriatum - CAS 67-99-2 - Calbiochem
- CAS NO.:67-99-2
- Empirical Formula: C13H14N2O4S2
- Molecular Weight: 326.39
- MDL number: MFCD00058534
- EINECS: 636-170-3
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-08-06 15:14:14
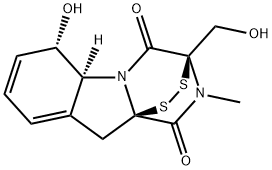
What is GLIOTOXIN?
Description
Gliotoxin is an immunosuppressive mycotoxin produced by pathogenic strains of Aspergillus and other fungi with diverse biological activities. It inhibits 20S proteasomal chymotrypsin activity (IC50 = 10 μM), blocking the degradation of IκBα and preventing the activation of NF-κB. Gliotoxin induces apoptosis in monocytes and dendritic cells and reduces phagocytosis by neutrophils. It suppresses viral infection by Nipah and Hendra virus in HEK293T cells (IC50s = 149 and 579 nM, respectively). Under reducing conditions, gliotoxin inhibits leukotriene A4 hydrolase (LTA4H; ) epoxide hydrolase activity, but not aminopeptidase activity, and leukotriene B4 (LTB4; ) synthesis in neutrophils and monocytes. In vivo, gliotoxin (5 mg/kg) reduces LTB4 plasma levels and blocks peritoneal neutrophil infiltration in a mouse model of peritonitis induced by zymosan A . It also inhibits geranylgeranyltransferase I and farnesyltransferase (IC50s = 17 and 80 μM, respectively).
Chemical properties
White powder
The Uses of GLIOTOXIN
Gliotoxin is a sulfur-containing mycotoxin produced by species of fungi and pathogens of humans. Gliotoxin exhibits inhibitory activities against histone H3K9 methyltransferase, a key enzyme in the re gulation of transcriptional activity by writing epigenetic marks. Gliotoxin also exhibits immunosuppressive properties by causing apoptosis of cells of the immune system. In addition, various studies suggests Gliotoxin may also be a potential anti-inflammatory, antibiotic, antifungal and antiviral agent.
The Uses of GLIOTOXIN
Gliotoxin is a potent epithiodioxopiperazine mycotoxin produced by species of Gliocladium, Aspergillus and Penicillium. At the cellular level gliotoxin inhibits a broad range of unrelated mechanisms, including inhibition of chymotrypsin-like activity of the 20S proteasome and Ca2+ release from mitochondria, activation of transcription factor NF-κB in response to a variety of stimuli in T and B cells, anti-inflammatory activity, and inhibition of farnesyltransferase and geranylgeranyltransferase. The mode of action appears to be via covalent interaction with proteins through mixed disulphide formation. Gliotoxin inhibits a number of thiol-requiring enzymes and also displays antioxidant and immunomodulatory activity.
What are the applications of Application
Gliotoxin is a toxic epipolythiodioxopiperazine metabolite that induces apoptosis and inhibits NF-κB
Definition
ChEBI: A pyrazinoindole with a disulfide bridge spanning a dioxo-substituted pyrazine ring; mycotoxin produced by several species of fungi.
Hazard
Poison.
Biological Activity
Immunosuppressive agent; blocks phagocytosis, cytokine production and proliferation of T and B cells. Non-competitively inhibits chymotrypsin-like activity of 20S proteasome; prevents degradation of I κ B α , an endogenous blocker of NF- κ B. Also inhibits farnesyltransferase and geranylgeranyltransferase I (IC 50 values are 80 and 17 μ M respectively) and displays antitumor activity against breast cancer in vivo .
Safety Profile
Poison by intraperitoneal andintravenous routes. When heated to decomposition itemits very toxic fumes such as SOx and NOx.
Storage
-20°C (desiccate)
Purification Methods
Purify gliotoxin by recrystallisation from MeOH. Its solubility in CHCl3 is 1%. The dibenzoyl derivative has m 202o (from CHCl3/MeOH). [Glister & Williams Nature 153 651 1944, Elvidge & Spring J Chem Soc Suppl 135 1949, Johnson et al. J Am Chem Soc 65 2005 1943, Bracken & Raistrick Biochem J 41 569 1947.]
References
Waring & Beaver (1996), Gliotoxin and related epipolythiodioxopiperazines; Gen. Pharmacol., 27 1311 Kroll et al. (1999), The secondary fungal metabolite gliotoxin targets proteolytic activities of the proteasome; Chem. Biol., 6 689 Fitzpatrick et al. (2000), In vitro and in vivo effects of gliotoxin, a fungal metabolite: efficacy against dextran sodium sulfate-induced colitis in rats; Dig. Dis. Sci., 45 2327 Konig et al. (2019), Gliotoxin from Aspergillus fumigatus Abrogates Leukotriene B4 Formation through Inhibition of Leukotriene A4 Hydrolase ; Cell Chem. Biol., 26 524 Hubmann et al. (2020), Targeting Nuclear NOTCH2 by Gliotoxin Recovers a Tumor-Suppressor NOTCH3 Activity in CLL; Cells, 9 1484
Properties of GLIOTOXIN
| Melting point: | 221°C (rough estimate) |
| Boiling point: | 699.7±55.0 °C(Predicted) |
| alpha | D25 -290° (c = 0.08 in ethanol) |
| Density | 1.4069 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.6510 (estimate) |
| Flash point: | 2℃ |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | chloroform: 10 mg/mL, clear, colorless |
| form | White solid |
| pka | 12.90±0.40(Predicted) |
| color | Monoclinic crystals from MeOH |
| Merck | 13,4454 |
| BRN | 50675 |
| Stability: | Stable for 2 yeara as supplied. Solutions in DMSO may be stored at -20°C for up to 1 month. |
Safety information for GLIOTOXIN
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H301:Acute toxicity,oral |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P301+P310:IF SWALLOWED: Immediately call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician. |
Computed Descriptors for GLIOTOXIN
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 Gliotoxin from Gliocladium fimbriatum CAS 67-99-2View Details
Gliotoxin from Gliocladium fimbriatum CAS 67-99-2View Details
67-99-2 -
 3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 614-19-7 98%View Details
614-19-7 98%View Details
614-19-7 -
 3112-85-4 Methyl phenyl sulfone 98%View Details
3112-85-4 Methyl phenyl sulfone 98%View Details
3112-85-4 -
 20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 -
 3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 -
 4,6-dichloropyrimidine-5-carbaldehyde 98%View Details
4,6-dichloropyrimidine-5-carbaldehyde 98%View Details
5305-40-8
