GLIADIN
- CAS NO.:9007-90-3
- Empirical Formula: C29H41N7O9
- Molecular Weight: 631.67734
- MDL number: MFCD00131160
- EINECS: 232-707-7
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2023-05-25 18:01:06
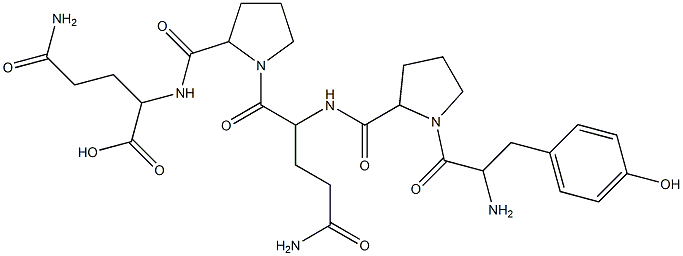
What is GLIADIN?
The Uses of GLIADIN
Gliadin from wheat has been used in
- peptic tryptic digestion to study the effect of?in vitro?gliadin challenge on biopsies from celiac disease (CD) patients on gluten-free diet (GFD)
- to prepare gliadin for antigliadin antibody assay
- as a standard for the quantification of gliadin levels to the picogram level by flow cytometry
The Uses of GLIADIN
Chemical synthesis of spinal anesthetics, pharmaceutical preparations.
Definition
A prolamin occurring in gluten, the protein of wheat, rye, and other grains. Wheat gliadin has the following composition: 52.7% carbon, 17.7% nitrogen, 21.7% oxygen, 6.9% hydrogen, 1.0% sulfur. It is composed of 18 amino acids, 40% being glutamic acid. In
General Description
Gluten consists of two families of prolamins, known as gliadin and glutenin. Gliadin is a strongly hydrophobic glycoprotein, with a very poor solubility. The gliadins can be further subdivided into α-gliadins, γ-gliadins and ω-gliadins (based on their order of mobility on electrophoresis at low pH).
Biochem/physiol Actions
The gliadins comprise a family of glutamine- and proline-rich monomeric proteins that account for 40-50% of the total protein content of wheat kernels. The alcohol-soluble gliadins aggregate with the alcohol-insoluble glutenins to form gluten, which is responsible for the structure and properties of wheat dough. The gliadins are also involved in the pathogenesis of celiac disease. an autoimmune disease in which human leukocyte antigens DQ2 and DQ8 present gliaden peptides to a subset of T cells inducing the release of proinflammatory cytokines that, in turn, induce degradation of the intestinal mucosal matrix and cell death. B cells are also stimulated to produce gluten-specific and transglutaminase 2 (TG2)-specific antibodies, the latter may result from the presentation of gliadin peptides covalently bound to TG2.
Properties of GLIADIN
| form | powder |
| Merck | 4437 |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Gliadins (9007-90-3) |
Safety information for GLIADIN
Computed Descriptors for GLIADIN
New Products
4-AMINO-TETRAHYDRO-PYRAN-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID HCL 4-(Dimethylamino)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-4-carbonitrile 4-Aminotetrahydropyran-4-carbonitrile Hydrochloride (R)-3-Aminobutanenitrile Hydrochloride 3-((Dimethylamino)methyl)-5-methylhexan-2-one oxalate 1,4-Dioxa-8-azaspiro[4.5]decane 5-Bromo-2-nitropyridine Nimesulide BP Aceclofenac IP/BP/EP Diclofenac Sodium IP/BP/EP/USP Mefenamic Acid IP/BP/EP/USP Ornidazole IP Diclofenac Potassium THOMAIND PAPER PH 2.0 TO 4.5 1 BOX BUFFER CAPSULE PH 9.2 - 10 CAP SODIUM CHLORIDE 0.1N CVS ALLOXAN MONOHYDRATE 98% PLATINUM 0.5% ON 3 MM ALUMINA PELLETS (TYPE 73) LITHIUM AAS SOLUTION 2-Bromo-1-(bromomethyl)-3-chloro-5-nitrobenzene 2-Bromo-3-nitroaniline N-(3-Hydroxypropyl)-N-methylacetamide 3-Bromo-6-chloropyridazine 4-ethyl-3-nitrobenzoic acidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


You may like
-
 Gliadin from wheat CAS 9007-90-3View Details
Gliadin from wheat CAS 9007-90-3View Details
9007-90-3 -
 1-Methyl-6-oxo-1,6-dihydropyridazine-3-carbonitrile 98%View Details
1-Methyl-6-oxo-1,6-dihydropyridazine-3-carbonitrile 98%View Details
99903-60-3 -
 1823368-42-8 98%View Details
1823368-42-8 98%View Details
1823368-42-8 -
 2-(3-(tert-butyl)phenoxy)-2-methylpropanoic acid 1307449-08-6 98%View Details
2-(3-(tert-butyl)phenoxy)-2-methylpropanoic acid 1307449-08-6 98%View Details
1307449-08-6 -
 Ethyl 3-(furan-2-yl)-3-hydroxypropanoate 25408-95-1 98%View Details
Ethyl 3-(furan-2-yl)-3-hydroxypropanoate 25408-95-1 98%View Details
25408-95-1 -
 2-Chloro-5-fluoro-1-methoxy-3-methylbenzene 98%View Details
2-Chloro-5-fluoro-1-methoxy-3-methylbenzene 98%View Details
1805639-70-6 -
 1784294-80-9 98%View Details
1784294-80-9 98%View Details
1784294-80-9 -
 Lithium ClavulanateView Details
Lithium ClavulanateView Details
61177-44-4