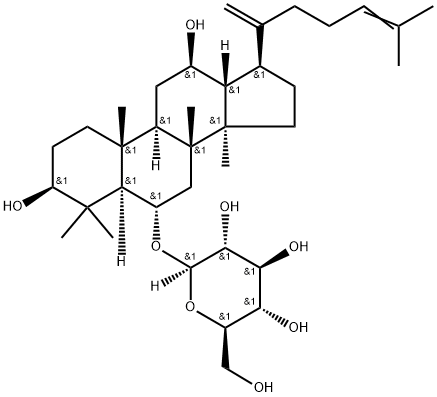
Ginsenoside CK
- CAS NO.:39262-14-1
- Empirical Formula: C36H62O8
- Molecular Weight: 622.88
- MDL number: MFCD07772261
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-26 12:07:08
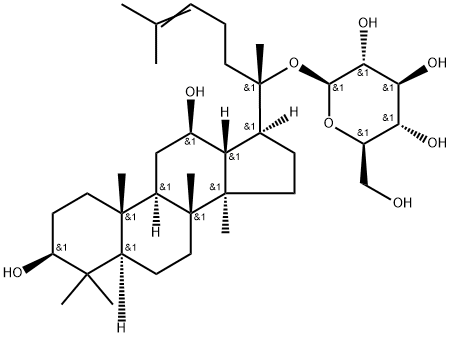
What is Ginsenoside CK?
Description
Ginsenoside compound K (C-K) is a metabolite of the protopanaxadiol-type saponins of Panax ginseng C.A. Meyer, has long been used to treat against the development of cancer, inflammation, allergies, and diabetes; C-K acts as a unique HUVEC migration inhibitor by regulating MMP expression, as well as the activity of SPHK1 and its related sphingolipid metabolites. C-K exhibits anti-inflammatory effects by reducing iNOS and COX-2, C-K exhibits an inhibition against the activity of CYP2C9 and CYP2A6 in human liver microsomes with IC50s of 32.0±3.6 μM and 63.6±4.2 μM, respectively. C-K promotes Aβ clearance by enhancing autophagy via the mTOR signaling pathway in primary astrocytes.
The Uses of Ginsenoside CK
Ginsenoside C-K is reported to exhibit anti-wrinkle effects. Also, it potentiates tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-related apotosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL)-induced apotosis in HCT116 colon cancer.
Definition
ChEBI: Ginsenoside C-K is a ginsenoside found in Panax species that is dammarane which is substituted by hydroxy groups at the 3beta, 12beta and 20 pro-S positions, in which the hydroxy group at position 20 has been converted to the corresponding beta-D-glucopyranoside, and in which a double bond has been introduced at the 24-25 position. It has a role as a plant metabolite, an antineoplastic agent, a hepatoprotective agent, an anti-allergic agent and an anti-inflammatory agent. It is a beta-D-glucoside, a 12beta-hydroxy steroid, a ginsenoside, a tetracyclic triterpenoid, a 3beta-hydroxy steroid and a 3beta-hydroxy-4,4-dimethylsteroid. It derives from a hydride of a dammarane.
General Description
This substance is a primary reference substance with assigned absolute purity (considering chromatographic purity, water, residual solvents, inorganic impurities). The exact value can be found on the certificate.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Ginsenoside compound K (GCK, 20-O-beta-D-glucopyranosyl-20(S)-protopanaxadiol, C36H62O8, also known as M1, IH-901, Ginsenoside CK), belonging to tetracyclic dammarane-type triterpenoid saponins. Ginsenosides are poorly absorbed from the gut by oral administration. Still, their major intestinal bacterial metabolite GCK is absorbed, indicating that the in vivo action of ginsenosides oral administration is mediated by their intestinal bacterial metabolic component GCK. The various processes used for GCK synthesis include enzymatic use, microbial conversion, heating, mycelial fermentation, and metabolic engineering[1-3].
Mechanism of action
Mechanistically, Ginsenoside CK (CK) was found to inhibit hormone-independent breast cancer growth by decreasing cyclin D1 expression to induce G1 cycle arrest and induce apoptosis in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells by activating adenosine 5′-monophosphate (AMP)-activated protein kinase (AMPK) through the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS). High glutamine-addicted TNBC cells were particularly sensitive to CK treatment. Ginsenoside CK exerted antitumor activity against TNBC by suppressing glutamine consumption and glutamate production via downregulation of glutaminase 1 (GLS1) expression. CK treatment further decreased cellular ATP production, reduced the utilisation of amino acids associated with glutamine metabolism, and induced glutathione (GSH) depletion and reactive oxygen species (ROS) accumulation, consequently triggering apoptosis in TNBC. Furthermore, CK decreased GLS1 expression in SUM159 xenograft mouse mammary tumors and significantly inhibited tumor growth with few side effects[2].
References
[1] Anshul Sharma, Hae-Jeung Lee. “Ginsenoside Compound K: Insights into Recent Studies on Pharmacokinetics and Health-Promoting Activities.” Biomolecules (2020).
[2] Bo Zhang. “Ginsenoside CK induces apoptosis in triple-negative breast cancer cells by targeting glutamine metabolism.” Biochemical pharmacology 1 1 (2022): 115101.
[3] Mengshi Tang . “Ginsenoside compound K- a potential drug for rheumatoid arthritis.” Pharmacological research 166 (2021): Article 105498.
Properties of Ginsenoside CK
| Melting point: | 181~183℃ |
| Boiling point: | 723.1±60.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.19 |
| solubility | DMF: 10 mg/ml; DMSO: 10 mg/ml; DMSO:PBS (pH 7.2) (1:1): 0.5 mg/ml |
| pka | 12.94±0.70(Predicted) |
| form | powder |
| color | White |
| Stability: | Hygroscopic |
Safety information for Ginsenoside CK
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P270:Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product. P501:Dispose of contents/container to..… |
Computed Descriptors for Ginsenoside CK
| InChIKey | FVIZARNDLVOMSU-SFEJUJENNA-N |
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 Ginsenoside C-K CAS 39262-14-1View Details
Ginsenoside C-K CAS 39262-14-1View Details
39262-14-1 -
 3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 614-19-7 98%View Details
614-19-7 98%View Details
614-19-7 -
 3112-85-4 Methyl phenyl sulfone 98%View Details
3112-85-4 Methyl phenyl sulfone 98%View Details
3112-85-4 -
 20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 -
 3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 -
 4,6-dichloropyrimidine-5-carbaldehyde 98%View Details
4,6-dichloropyrimidine-5-carbaldehyde 98%View Details
5305-40-8
