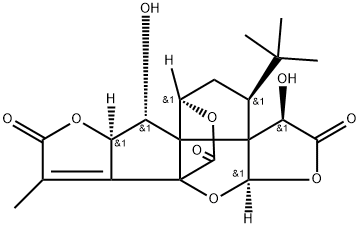
Ginkgolide B
Synonym(s):BN-52021
- CAS NO.:15291-77-7
- Empirical Formula: C20H24O10
- Molecular Weight: 424.4
- MDL number: MFCD05662347
- EINECS: 604-876-0
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-11-19 23:02:33
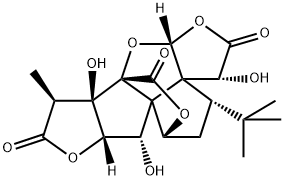
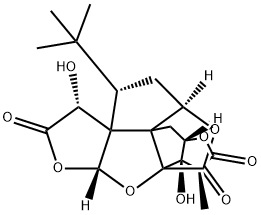
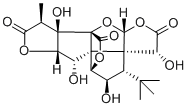
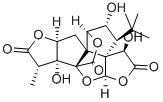
What is Ginkgolide B?
Description
Ginkgo biloba is a perennial tree belonging to Ginkgoaceae (Ginkgo biloba L., Yin
Xing). Its seeds, also known as ginkgo, have a long history of application in traditional medicine for its medicinal value. With promoting blood circulation by removing blood stasis, Ginkgo biloba has a long history of its application in traditional
Chinese medicine
In recent years, it has been widely used in the treatment of cerebral ischemic
diseases. After further study, it was found that the effective component is ginkgolide
compound, which laid the foundation for the development of small molecule drugs.
Chemical properties
White Crystalline Solid
Physical properties
Appearance: ginkgolide B is a white powder. Solubility: weighed 0.98?g and dissolves in 1L water (calculation). Melting point: the compound melts at 280? °C (calculation)
History
The leaf of Ginkgo biloba is sweet, bitter, astringent, and mild. With activating
blood circulation to remove blood stasis, dredging collaterals, relieving pain, and
asthma, it is applied for treating blood stasis, chest pain, stroke, lung deficiency
cough, and hyperlipidemia.
As early as in the 1930s, scientists began to study ginkgo and harvest a variety of
ginkgolide . Ginkgolide B was isolated and its structure illustrated by Wan Shan
et?al. in 1967. Subsequently, it was synthesized by Corey et?al. in 1988. The
preparation of effective components of Ginkgo biloba has been listed at home and
abroad with development.
The Ginkgo biloba extract consisting of ticlopidine is widely used in overseas
market for the treatment of cerebral infarction. Intravenous injection of ginkgolide
B is applied for the treatment of inflammation, but the project has been in the state,
and there is no progress in it for many years. In addition, whether other extract of
Ginkgo biloba can be used for the treatment of stable angina, cognitive impairment
is still in preclinical research status.
The Uses of Ginkgolide B
Ginkgolide B is used as a potent PAF-R antagonist. Ginkgolide B speeds up PAF hydrolysis by promoting PAF-AH I α2 homodimer activity. Additionally, this compound has been reported to inhibit neutrophil degranulation in vitro. Inhibits superoxide production in vitro and inhibits bronchoconstriction and is neuroprotective following oral administration in vivo.
The Uses of Ginkgolide B
Family of bioactive terpenes treating cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases. Specific platelet activating factor (PAF) antagonists
The Uses of Ginkgolide B
Ginkgo (Ginkgo biloba) Plant Profile: bioactives, mechanism of action, references
What are the applications of Application
Ginkgolide B is a potent PAF-R antagonist
Indications
The injection consists of multiple components, and there are three kinds of substance mainly in diterpene ginkgolides meglumine injection. It promotes blood circulation by removing blood stasis and activates the channels and collaterals for cerebral ischemia treatment.
Biological Activity
Platelet-activating factor (PAF) receptor antagonist (K i = 1.3 μ M). Inhibits neutrophil degranulation and superoxide production in vitro and inhibits bronchoconstriction and is neuroprotective following oral administration in vivo .
Pharmacology
Ginkgolide B has a variety of pharmacological effects, mainly in cardiovascular and cerebrovascular protection and neuroprotection. On the one hand, with the strongest activity in nature, the platelet-activating factor (PAF) receptor antagonist is recognized by the public . PAF can inhibit the downstream inflammatory cascade for anti-inflammatory. It also can alleviate cerebral infraction volume and cerebral edema induced by cerebral ischemia among the animal model of cerebral ischemia reperfusion through unknown mechanism. By inhibiting NF-κB and TNF-α, the apoptosis of nerve cell can be alleviated. The compound protects the abdominal cavity and intestinal tract by inhibiting release of neutrophil chemotactic protein by macrophage.
Clinical Use
Oral and injection preparations are applied widely in clinical therapy. Made in oral preparation, flavonoids are the main component of raw material. There are little chemical compounds in injection, and ginkgolides are the main component whose content is different from each other. Listed ginkgolide injection is applied for ischemia stroke formed by blood stasis with promoting blood circulation by removing blood stasis and clearing and activating the channels and collaterals. Compared with Shuxuening injection in clinical trials, ginkgolides injection is consistent in improving indicators effect, such as protection in nerve injury and others.
References
1) Foldes-Filep et al. (1987), Inhibition by BN 52021 (ginkgolide B) of the binding of [3H]-platelet-activating factor to human neutrophil granulocytes; Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 148 1412 2) Desquand et al. (1986), Interference of BN 52021 (ginkgolide B) with the bronchopulmonary effects of PAF-acether in the guinea-pig; Eur. J. Pharmacol., 127 83 3) Maclennan et al. (2002), The CNS effects of Ginko biloba extracts and ginkgolide B; Prog. Neurobiol., 67 235 4) Li et al. (2013), Neuroprotective effect of ginkogolide B on bupivacaine-induced apoptosis in SH-SY5Y cells; Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev., 2013 159864 5) Wang et al. (2014), Neuroprotection against permanent focal cerebral ischemia by ginkgolides A and B is associated with obstruction of the mitochondrial apoptotic pathway via inhibition of c-Jun N-terminal kinase in rats; J. Neurosci. Res., 92 232
Properties of Ginkgolide B
| Melting point: | 280°C (dec.) |
| Boiling point: | 762.4±60.0 °C(Predicted) |
| alpha | D24 -52.6° (c = 1 in ethanol) |
| Density | 1?+-.0.1 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | Sealed in dry,Store in freezer, under -20°C |
| solubility | Soluble in DMSO (up to 40 mg/ml) or in Ethanol (up to 10 mg/ml). |
| form | neat |
| pka | pKa1 7.14; pKa2 8.60; pKa3 11.89(at 25℃) |
| form | Solid |
| color | White |
| Water Solubility | Soluble in DMSO. Slightly soluble in water and ethanol |
| BRN | 4727611 |
| Stability: | Stable for 2 years from date of purchase as supplied. Solutions in DMSO or ethanol may be stored at -20°C for up to 3 months |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 15291-77-7(CAS DataBase Reference) |
Safety information for Ginkgolide B
Computed Descriptors for Ginkgolide B
| InChIKey | SQOJOAFXDQDRGF-MMQTXUMRSA-N |
| SMILES | [C@@]12(O)[C@]34C(=O)O[C@@H]5C[C@@H](C(C)(C)C)C6([C@@H](O)C(=O)O[C@@]6([H])O3)C45[C@H](O)[C@]1([H])OC(=O)[C@H]2C |
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid 1-Bromo-3,5-Di-Tert-Butylbenzene S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
![Ethyl 4-[2-(5-Chloro-2-methoxybenzamido)ethyl]benzene Sulfonamide Carbamate](https://img.chemicalbook.in/CAS/GIF/14511-59-2.gif)
You may like
-
 Ginkgolide B CAS 15291-77-7View Details
Ginkgolide B CAS 15291-77-7View Details
15291-77-7 -
 Ginkgolide b 95% CAS 15291-77-7View Details
Ginkgolide b 95% CAS 15291-77-7View Details
15291-77-7 -
 Ginkgolide B from Ginkgo biloba leaves CAS 15291-77-7View Details
Ginkgolide B from Ginkgo biloba leaves CAS 15291-77-7View Details
15291-77-7 -
 Ginkgolide B CAS 15291-77-7View Details
Ginkgolide B CAS 15291-77-7View Details
15291-77-7 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1