Fullerene C60
Synonym(s):Buckminsterfullerene;Buckminsterfullerene C70;Fullerene-C70
- CAS NO.:131159-39-2
- Empirical Formula: C60
- Molecular Weight: 720.64
- MDL number: MFCD00151408
- EINECS: 000-000-0
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-06-21 13:10:12
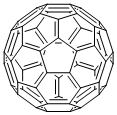
What is Fullerene C60?
Chemical properties
black fine powder
Fullerene C60 is molecular carbon in the form of C60 and other members of the fullerene family were first synthesized in 1985. Solid C6o exhibits a large number of interesting physical and chemical properties. One of the theoretical predictions was that the C60 molecule itself would have a bulk modulus larger than that of diamond and the soft material under high pressure would become harder than diamond.

Fullerene-C60 (C60) is approximately 0.7 nm in diameter. It is a hollow, icosahedrally-shaped, closed-cage structure consisting of 60 sp2 hybridized carbon atoms which can be utilized for the preparation of novel carbon nanomaterials.
History
Fullerenes were first observed in 1985 in the sooty residue left after vaporizing carbon in a helium atmosphere. The discoverers thought the icosahedral structures with exactly 60 unsaturated carbon atoms resembled geodesic domes popularized by famous architect Buckminster Fuller and named them "buckminsterfullerenes" in his honor. The name has since been shortened to "fullerene," but they are sometimes also called "buckyballs."
The Uses of Fullerene C60
Fullerene C60 (CAS# 99685-96-8) is a carbon-based nanoparticle used in a variety of studies, typically after further functionalization, such as its interaction with proteins and its aggregation and deposition kinetics.
The Uses of Fullerene C60
fullerenes is also known as fullerines; buckyball. Fullerenes are soluble carbon molecules that are studied and incorporated into cosmetics for their anti-oxidant and free-radical scavenging properties. Some manufacturers cite significantly greater anti-oxidant potential than vitamins C and e and an ability to retain their antifree radical activity under a variety of external conditions such as heat, strong ultraviolet radiation. They are most commonly used to minimize potential reactions through an interaction with the immune system. Fullerenes are generally incorporated into antiaging and skin rejuvenation formations. The most common form of fullerenes is C60; other forms include C70, C76, and C84. They are the result of nanotechnology and its application in skin care.
Definition
An allotrope of carbon containing clusters of 60 carbon atoms bound in a highly symmetric polyhedral structure. The C60 polyhedron has a combination of pentagonal and hexagonal faces similar to the panels on a soccer ball. The molecule was named for the American architect Richard Buckminster Fuller (1895–1983) because its structure resembles a geodesic dome (invented by Fuller). The C60 polyhedra are informally called bucky balls. The original method of making the allotrope was to fire a high-power laser at a graphite target. This also produces less stable carbon clusters, such as C70. It can be produced more conveniently using an electric arc between graphite electrodes in an inert gas. The allotrope is soluble in benzene, from which it can be crystallized to give yellow crystals. This form of carbon is also known as fullerite.
The discovery of buckminsterfullerene led to a considerable amount of research into its properties and compounds. Particular interest has been shown in trapping metal ions inside the carbon cage to form enclosure compounds. Buckminsterfullerene itself is often simply called fullerene. The term also applies to derivatives of buckminsterfullerene and to similar cluster (e.g. C70). Carbon structures similar to that in C60 can also form small tubes, known as bucky tubes.
Definition
A form ofcarbon composed of clusters of 60carbon atoms bonded together in apolyhedral structure composed ofpentagons and hexagons.Originally it was identified in1985 in products obtained by firing ahigh-power laser at a graphite target.It can be made by an electric arcstruck between graphite electrodesin an inert atmosphere. The molecule,C60, was named after the USarchitect Richard Buckminster Fuller(1895–1983) because of the resemblanceof the structure to the geodesicdome, which Fuller invented.The molecules are informally calledbuckyballs; more formally, the substanceitself is also called fullerene.The substance is a yellow crystallinesolid (fullerite), soluble in benzene.
Various fullerene derivatives areknown in which organic groups areattached to carbon atoms on thesphere. In addition, it is possible toproduce novel enclosure compoundsby trapping metal ions within the C60cage. Some of these have semiconductingproperties. The electric-arcmethod of producing C60 also leadsto a smaller number of fullerenessuch as C70, which have less symmetricalmolecular structures. It is alsopossible to produce forms of carbonin which the atoms are linked in acylindrical, rather than spherical,framework with a diameter of a fewnanometres. They are known asbuckytubes (or nanotubes).
General Description
Fullerite is a mixture of C60 and C70 fullerenes. It is a crystalline material with high light absorption and an energy band gap of 1.6 eV. It can be used as an acceptor molecule for the fabrication of bulk heterojunction polymeric solar cells.
Industrial uses
Buckyballs, the soccer-shaped molecules discoveredover a decade ago, are made entirelyof carbon atoms linked with unusual chemicalbonds.
Buckybowls, large fragments of buckyballs,have been synthesized. The moleculeshave the ability to take up electrons and givethem back later, under the right conditions, inhigher concentrations than buckyballs.The only practical application thus far hasbeen the computer industry’s use of anotherrelative, the buckytube, as an atomic-scaleprobe. Some researchers believe that the buckybowlsmay facilitate the development of plasticbatteries that would be lighter, smaller, andmore environmentally friendly than therechargeable batteries now used to power cellularphones and laptop computers.
The shape of the molecule may also allowit to bond with other molecules. It fits over thebuckyball much like a contact lens, and may beable to serve as a medium that links other substancesto the balls.
Industrial uses
Fullerenes are a family of molecules that containan even number of carbon atoms in a closedcage.The molecule is a hollow, pure carbonmolecule in which the atoms lie at the verticesof a polyhedron with 12 pentagonal faces andany number (other than one) of hexagonalfaces.The fullerenes were discovered as a consequenceof astrophysically motivated chemicalphysics experiments that were interpreted byusing geodesic architectural concepts.Fullerene chemistry,a field that appears to holdmuch promise for materials development andother applied areas,was born from pure fundamentalscience.
Buckminster fullerene (C60 or fullerene-60),is the archetypal member of the fullerenes.Otherstable members of the fullerene family have similarstructures.The fullerenes can beconsidered,after graphite and diamond,to be thethird well-defined allotrope of carbon.
The fullerenes promise to have synthetic,pharmaceutical, and industrial applications.Derivatives have been found to exhibit fascinatingelectrical and magnetic behavior, in particularsuperconductivity and ferromagnetism.
The properties of fullerene materials that have been determined suggest that there is likely to be a wide range of areas in which the fullerenes or their derivatives will have uses. The facility for acceptance and release of electrons suggests a possible role as a charge carrier in batteries.
Fullerene nanotubes, tiny, tubular carbon fibers, were recently cut into open-ended pipes for the first time. This allows them to be chemically manipulated for use in nanotechnologies and materials. The attachment of molecules to the ends of the pipes lets them serve as means of binding to other chemical groups or surfaces.
The properties of graphite suggest that lubricative as well as tensile and other mechanical properties of the fullerenes are worthy of investigation. Liquid solutions exhibit excellent properties of optical harmonic generation. The high temperature at which superconducting behavior is observed suggests possible applications in microelectronics devices, as does the detection of ferromagnetism in other fullerene derivatives.
Properties of Fullerene C60
| Melting point: | >280 °C(lit.) |
| Density | 1,6 g/cm3 |
| Flash point: | >94 °C |
| storage temp. | Sealed in dry,Room Temperature |
| solubility | organic solvents: soluble |
| form | Powder |
| Specific Gravity | 1.6 |
| color | black |
Safety information for Fullerene C60
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P271:Use only outdoors or in a well-ventilated area. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Fullerene C60
| InChIKey | XMWRBQBLMFGWIX-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid 1-Bromo-3,5-Di-Tert-Butylbenzene S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
![BENZO[G]CHRYSENE](https://img.chemicalbook.in/CAS/GIF/196-78-1.gif)
You may like
-
 Fullerene C70 CASView Details
Fullerene C70 CASView Details -
 2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1