Fosravuconazole bis(L-lysine
- CAS NO.:1035654-66-0
- Empirical Formula: C24H29N3O8
- Molecular Weight: 487.5
- MDL number: MFCD22648366
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2023-05-15 10:43:30
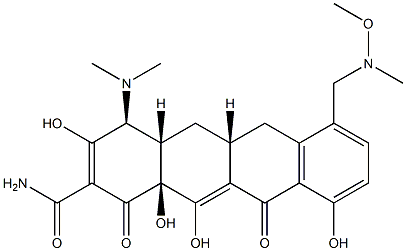
What is Fosravuconazole bis(L-lysine?
Absorption
The median time to peak plasma concentration (Tmax) of sarecycline is 1.5 to 2.0 hours . When the medication is taken with a meal consisting of high fat (about 50% of total caloric content of the meal), high caloric (about 800 to 1000 Kcal), and milk content the Tmax can be delayed by approximately 0.53 hours and the Cmax and AUC can be decreased by 31% and 27%, respectively .
Toxicity
No clinically significant differences in the pharmacokinetics of sarecycline were observed based on age (11 to 73 years), weight (42 to 133 kg), sex, renal impairment, or mild to moderate hepatic impairment (Child Pugh A to B). The effect of end-stage renal disease (ESRD) or severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh C) on sarecycline pharmacokinetics has not been assessed .
In a 2-year oral mouse carcinogenicity study and a 2-year oral rat carcinogenicity study, no drug-related neoplasms were observed in male mice at oral doses of sarecycline up to 100 mg/kg/day (approximately equal to the MRHD based on AUC comparison) or in female mice at doses up to 60 mg/kg/day (approximately equal to the MRHD based on AUC comparison), or in rats at doses up to 200/100 mg/kg/day (dose reduced from 200 to 100 mg/kg/day due to increased mortality; 8 times the MRHD based on AUC comparison) .
Sarecycline was not mutagenic or clastogenic in a series of in vitro and in vivo genotoxicity studies, including a bacteria reverse mutation (Ames) assay, an in vitro chromosomal aberration assay in CHO cells, the L5178Y/TK+/- Mouse Lymphoma Assay, and an in vivo micronucleus assay in rats .
In a fertility and early embryonic development study in rats, sarecycline was administered to both male and female rats at oral doses up to 400 mg/kg/day prior to pairing and through the mating and postmating period . Female fertility was not affected at doses up to 400 mg/kg/day (8 times the MRHD based on AUC comparison) . In sperm evaluation, decreased sperm motility, decreased sperm count and concentration, and an increase in percent abnormal sperm occurred at 400 mg/kg/day (8 times the MRHD based on AUC comparison) . Male fertility was not affected at doses up to 150 mg/kg/day (4 times the MRHD based on AUC comparison) .
Sarecycline, like other tetracycline class drugs, may cause fetal harm, permanent discoloration of teeth, and
reversible inhibition of bone growth when administered during pregnancy . The limited available human data are not sufficient to inform a drug- associated risk for birth defects or miscarriage . Tetracyclines are known to cross the placental barrier; therefore, sarecycline may be transmitted from the mother to the developing fetus . In animal reproduction studies, sarecycline induced skeletal malformations in fetuses when orally administered to pregnant rats during the period of organogenesis at a dose 1.4 times the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) of 150 mg/day (based on AUC comparison) . When dosing with sarecycline continued through the period of lactation, decreases in offspring survival, offspring body weight, and implantation sites and viable embryos in offspring females occurred at a dose 3 times the MRHD (based on AUC comparison) . The potential risk to the fetus outweighs the potential benefit to the mother from sarecycline use during pregnancy; therefore, pregnant patients should discontinue sarecyclin as soon as pregnancy is recognized .
Tetracyclines are excreted in human milk . Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions on bone and tooth development in nursing infants from tetracycline-class antibiotics, advise a woman that breastfeeding is not recommended with sarecycline therapy .
Avoid using sarecycline in males who are attempting to conceive a child . In a fertility study in rats, sarecycline adversely affected spermatogenesis when orally administered to male rats at a dose 8 times the MRHD (based on AUC comparison) .
The safety and effectiveness of sarecycline have been established in pediatric patients 9 years of age and older for the treatment of moderate to severe inflammatory lesions of non-nodular acne vulgaris . The safety and effectiveness of sarecycline in pediatric patients below the age of 9 years has not been established . Use of tetracycline-class antibiotics below the age of 8 is not recommended due to the potential for tooth discoloration .
Clinical studies of sarecycline did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects .
In case of overdosage, discontinue medication, treat symptomatically, and institute supportive measures . Dialysis does not alter serum half-life and thus would not be of benefit in treating cases of overdose .
The Uses of Fosravuconazole bis(L-lysine
Sarecycline-d6 Hydrochloride is a labelled analogue of Sarecycline Hydrochloride(S140525), which is a substituted tetracycline compound used for treatment of bacterial infections and neoplasms.
Background
Sarecycline is a semi-synthetic derivative of tetracycline that was initially discovered by Paratek Pharmaceuticals from Boston, MA but then licensed to Warner Chilcott of Rockaway, NJ in July of 2007 . After completing various phase-II and phase-III trials demonstrating its effectiveness in treating moderate to severe facial acne vulgaris the US Food and Drug Administration approved Barcelona based Almirall, S.A.'s Seysara (sarecylcine) as a new first in class narrow spectrum tetracycline derived oral antibiotic for the treatment of inflammatory lesions of non-nodular moderate to severe acne vulgaris in patients nine years of age and older . Seysara (sarecycline) was originally part of Allergan's US Medical Dermatology portfolio, before Almirall acquired the portfolio in the second half of 2018 as a means of consolidating and reinforcing the dermatology-focused pharmaceutical company's presence in the United States .
Acne vulgaris itself is a common chronic skin condition associated with the blockage and/or inflammation of hair follicles and their accompanying sebaceous glands . The acne often presents physically as a mixture of non-inflammatory and inflammatory lesions mainly on the face but on the back and chest as well . Based upon data from Global Burden of Disease studies, the acne vulgaris condition affects up to 85% of young adults aged 12 to 25 years globally - with the possibility of permanent physical and mental scarring resulting from cases of severe acne .
Subsequently, while a number of first line tetracycline therapies like doxycycline and minocycline do exist for treating acne vulgaris, sarecycline presents a new and innovative therapy choice because it exhibits the necessary antibacterial activity against relevant pathogens that cause acne vulgaris but also possesses a low propensity for resistance development in such pathogens and a narrower, more specific spectrum of antibacterial activity, resulting in fewer off-target antibacterial effects on endogenous intestinal flora and consequently fewer resultant adverse effects associated with diarrhea, fungal overgrowth, etc.
Indications
Sarecycline is a tetracycline-class drug indicated for the treatment of inflammatory lesions of non-nodular moderate to severe acne vulgaris in patients 9 years of age and older .
Pharmacokinetics
Compared to various examples of first-line tetracycline therapies for moderate to severe acne like doxycycline and minocycline, studies have shown that sarecycline can be sixteen to thirty-two fold less active against aerobic Gram-negative bacilli present within the normal human intestinal microbiome . Furthermore, it has also been demonstrated that sarecycline may be four to eight fold less active against various anaerobic bacteria that also comprise the normal human intestinal microbiome . Subsequently, while doxycycline and minocycline typically elicit broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity that can often cause adverse effects like diarrhea, fungal overgrowth, vaginal candidiasis, etc. due to undesirable off-target antibacterial effects on endogenous intestinal flora, sarecycline demonstrates a noticeably more target specific narrow spectrum activity with lower incidence of such side effects .
Moreover, sarecycline also shares a relatively low propensity for resistance development in Cutibacterium acnes - one of the principal anaerobic organisms associated with acne lesions - with doxycycline and minocycline treatments .
Metabolism
Metabolism of sarecycline by enzymes in human liver microsomes is minimal (< 15%) in vitro . Minor metabolites resulting from non-enzymic epimerization, O-/N-demethylation, hydroxylation, and desaturation have been found .
Properties of Fosravuconazole bis(L-lysine
| Boiling point: | 787.0±70.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.53±0.1 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| pka | 4.50±1.00(Predicted) |
Safety information for Fosravuconazole bis(L-lysine
Computed Descriptors for Fosravuconazole bis(L-lysine
Fosravuconazole bis(L-lysine manufacturer
Sumar Biotech LLP
Maithri Drugs Pvt Ltd
New Products
Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate (S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL N-octanoyl benzotriazole 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid Fmoc-Val-Cit-PAB DIETHYL AMINOMALONATE HYDROCHLORIDE 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5-BROMO-2CYANO PYRIDINE 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonateYou may like
-
 1035654-66-0 Sarecycline 98%View Details
1035654-66-0 Sarecycline 98%View Details
1035654-66-0 -
 Sarecycline 1035654-66-0 98%View Details
Sarecycline 1035654-66-0 98%View Details
1035654-66-0 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 -
 733039-20-8 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 98+View Details
733039-20-8 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 98+View Details
733039-20-8