Flumequine
- CAS NO.:42835-25-6
- Empirical Formula: C14H12FNO3
- Molecular Weight: 261.25
- MDL number: MFCD00079298
- EINECS: 255-962-6
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 14:07:02
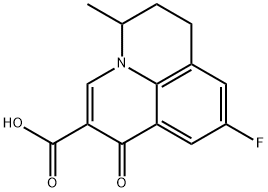
What is Flumequine?
Description
Flumequine is a synthetic antibiotic belonging to the second-generation quinolone group and is mainly active against Gram negative bacteria. It is currently the only non-humans shared broad-spectrum antimicrobial veterinary drug. It is taken as the substitute product of norfloxacin. It has a strong bactericidal activity with excellent efficacy in the treatment of animal bacterial diseases. Its main effect is to inhibit bacterial deoxy nucleic acid (DNA) gyrase, interfering with the deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) synthesis, thereby causing failure of cell for further division, and thus playing the role of killing bacteria. It is used in bovine, ovine, chicken, rabbits, goats, horses and salmonidae, however the establishment of MRLs was only requested for non-lactating cattle, pigs, sheep, chicken and salmonidae.
Chemical properties
White Crystalline Solid
Originator
Apurone,Riker,France,1977
The Uses of Flumequine
Flumequine is a fluoroquinolone compound with antimicrobial activity against Gram-negative organisms. It is used in the treatment of enteric infections in food animals and in the treatment of bacterial infections in farmed fish. Flumequine is replacing oxolinic acid in aquaculture because of its more appropriate pharmacokinetic profile and lower effective doses (Treves-Brown 2000). Flumequine also has limited use in humans for the treatment of urinary tract infections.
Definition
ChEBI: Flumequine is a member of the class of pyridoquinolines that is 1-oxo-6,7-dihydro-1H,5H-pyrido[3,2,1-ij]quinoline carrying additional carboxy, methyl and fluoro substituents at positions 2, 5 and 9 respectively. It is a pyridoquinoline, a 3-oxo monocarboxylic acid, an organofluorine compound and a quinolone antibiotic.
Preparation
Synthesis: Condensation of 5-fluoro-2-methyltetrahydroquinoline with diethyl ethoxy-methylenemalonate followed by thermal cycli- zation gives ethyl 6,7-dihydro-9-fluoro-5-meth-yl-1-oxo-1H,5H-benzo[i,j]quinolizine-2-car-boxylate,which is saponified with sodium hydroxide to give flumequine.
Manufacturing Process
6-Fluoro-2-methyltetrahydroquinoline (32.2 g, 0.2 mol) is mixed with diethyl ethoxymethylenemalonate, and the mixture is heated at 125°C to 130°C for 3 hours. Polyphosphoric acid (200 g) is added, and the solution is gradually heated to 115°C to 120°C in an oil bath with occasional stirring. The temperature is maintained for 1 hour, then the mixture is poured into 600 ml of water and neutralized with 40% sodium hydroxide solution. The product ester which precipitates is separated by filtration, washed with water and suspended in 2 liters of 10% sodium hydroxide solution. The mixture is heated on the steam bath for 1 hour, treated with decolorizing charcoal, filtered, then neutralized with concentrated hydrochloric acid. The solid product is isolated by filtration of the hot solution, washed with water and recrystallized from dimethylformamide.
Therapeutic Function
Antibacterial
Pharmaceutical Applications
A tricyclic fluorinated 4-quinolone, with activity similar to that of nalidixic acid in vitro, although it is somewhat more active against some Enterobacteriaceae.
Following escalating oral doses of 400, 800 or 1200 mg, mean peak plasma levels reached at 2 h are 13.5, 23.8 and 31.9 mg/L, respectively. The apparent elimination half-life is about 7 h. The main metabolite, hydroxyflumequine, is much more rapidly eliminated. About 60% of a dose appears in the urine, mostly in the form of conjugates. Urinary concentrations following an 800 mg dose are 10–35 mg/L, with a peak of 105 mg/L. It has no effect on the pharmacokinetics of theophylline.
Flumequine is generally well tolerated, side effects being mainly mild gastrointestinal tract disturbances, rashes, dizziness and confusion.
It is principally used in uncomplicated urinary tract infections.
Properties of Flumequine
| Melting point: | 253-255°C |
| Boiling point: | 439.7±45.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.45±0.1 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| RTECS | DK1672000 |
| Flash point: | >110°(230°F) |
| storage temp. | Sealed in dry,Store in freezer, under -20°C |
| solubility | 1 M NH4OH: soluble50mg/mL |
| form | powder |
| pka | pKa 6.42(H2O t=25.0 I=0.025)(Approximate) |
| color | white to off-white |
| Water Solubility | Soluble in DMSO and dilute alkali hydroxides. Insoluble in water |
| Merck | 14,4137 |
| BRN | 490724 |
| Stability: | Stable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 42835-25-6(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | 1H,5H-Benzo[ij]quinolizine-2-carboxylic acid, 9-fluoro-6,7-dihydro-5-methyl-1-oxo- (42835-25-6) |
Safety information for Flumequine
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Flumequine
Flumequine manufacturer
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid 1-Bromo-3,5-Di-Tert-Butylbenzene S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


![Benzo[b]thien-2-ylboronic acid](https://img.chemicalbook.in/CAS/GIF/98437-23-1.gif)
You may like
-
 42835-25-6 Flumequine 98%View Details
42835-25-6 Flumequine 98%View Details
42835-25-6 -
 Flumequine CAS 42835-25-6View Details
Flumequine CAS 42835-25-6View Details
42835-25-6 -
 Flumequine CAS 42835-25-6View Details
Flumequine CAS 42835-25-6View Details
42835-25-6 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1