Finerenone
- CAS NO.:1050477-31-0
- Empirical Formula: C21H22N4O3
- Molecular Weight: 378.42
- MDL number: MFCD29047135
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-19 17:28:17
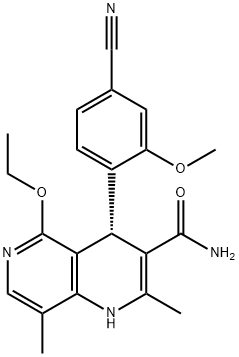
What is Finerenone?
Absorption
A 10 mg oral dose of finerenone reaches a Cmax of 351 μg/L, with a Tmax of 1.5 hours, and an AUC of 2820 μg*h/L in plasma. The same dose of finerenone reaches a Cmax of 226 μg/L, with a Tmax of 1.5 hours, and an AUC of 1840 μg*h/L in whole blood.
Regular doses of 20 mg of finerenone reach a geometric mean steady state Cmax of 160 μg/L with an AUC of 686 μg*h/L.
Toxicity
Patients experiencing an overdose of finerenone may experience hyperkalemia. In the even of an overdose, immediately stop taking finerenone. Treat patients with symptomatic and supportive treatment, including treatment for hyperkalemia if it develops. Hemodialysis is not expected to remove finerenone from the blood due to its high plasma protein binding.
Description
Finerenone is a novel mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist that has the effect of delaying the progression of chronic kidney disease. Some people may be aware of two other mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists: the diuretic antihypertensive drug spironolactone, and eplerenone.Finerenone is their cognate derivative and is a third-generation mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist. So far, finerenone is the only nonsteroidal mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist to be FDA approved. Finerenone was granted FDA approval on 9 July 2021, followed by the EMA approval on 11 March 2022.
The Uses of Finerenone
Finerenone is the first non-steroidal selective mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist, which can be used for the treatment of diabetic nephropathy, chronic kidney disease and end-stage renal disease. It can reduce the proteinuria of patients and improve the glomerular filtration rate.
Background
Finerenone, or BAY 94-8862, is a mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist indicated to reduce the risk of sustained decline in glomerular filtration rate, end stage kidney disease, cardiovascular death, heart attacks, and hospitalization due to heart failure in adults with chronic kidney disease associated with type II diabetes mellitus. Patients with kidney disease, would originally be given spironolactone or eplerenone to antagonize the mineraclocorticoid receptor. Spironolactone has low selectivity and affinity for the receptor; it dissociates quickly and can also have effects at the androgen, progesterone, and glucocorticoid receptors. Eplerenone is more selective and has longer lasting effects. More selective nonsteroidal mineralocorticoid antagonists such as apararenone, esaxerenone, and finerenone were later developed. So far, finerenone is the only nonsteroidal mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist to be FDA approved.
Finerenone was granted FDA approval on 9 July 2021, followed by the EMA approval on 11 March 2022.
Indications
In the US, finerenone is indicated to reduce the risk of sustained decline in glomerular filtration rate, end stage kidney disease, cardiovascular death, heart attacks, and hospitalization due to heart failure in adults with chronic kidney disease associated with type II diabetes mellitus.
In Europe, finerenone is indicated for the treatment of chronic kidney disease (stage 3 and 4 with albuminuria) associated with type 2 diabetes in adults.
brand name
Finerenone is sold under the brand name Kerendia and Firialta.
Biological Activity
Finerenone (FIN, BAY 94-8862) is a highly selective, orally active, nonsteroidal antagonist of mineralocorticoid receptor (MR) with IC50 of 18 nM. Finerenone has the potential to study cardio-renal diseases such as type 2 diabetes and chronic kidney disease.
Pharmacokinetics
Finerenone is a non-steroidal mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist indicated to reduce the risk of sustained decline in glomerular filtration rate, end stage kidney disease, cardiovascular death, heart attacks, and hospitalization due to heart failure in adults with chronic kidney disease associated with type II diabetes mellitus. It has a moderate duration of action as it is taken once daily, and a wide therapeutic window as patients were given doses from 1.25 mg to 80 mg in clinical trials. Patients should be counselled regarding the risk of hyperkalemia.
in vivo
Finerenone (BAY 94-8862) lowers albuminuria by >40% and significantly reduces systolic blood pressure (SBP) in Munich Wistar Fr?mter (MWF) rat.
Metabolism
Finerenone is approximately 90% metabolized by CYP3A4, and 10% metabolized by CYP2C8. There is a minor contribution to metabolism by CYP1A1. Finerenone has no active metabolites.
Finerenone is aromatized to the M1 metabolite by CYP3A4 and CYP2C8, which is further hydroxylated by CYP3A4 to the M2 metabolite, and finally oxidized bye CYP3A4 to the M3 metabolite. Alternatively, finerenone can undergo epoxidation and possibly hydrolysis by CYP3A4 and CYP2C8 to form the M4 metabolite, which is hydroxylated again by CYP3A4 to the M5 metabolite, and oxidized to the M8 metabolite. Finerenone can also be hydroxylated by CYP2C8 to the M7 metabolite, and further oxidized to the M9 metabolite.
The M10 metabolite is formed by the demethylation, oxidation, and ring opening of finerenone. The M13 metabolite is formed through de-ethylation of finerenone by CYP1A1, and the M14 metabolite is formed through an undefined multi-step process involving CYP2C8 and CYP3A4.
Mode of action
Finerenone is a Nonsteroidal Mineralocorticoid-Receptor Antagonist. The mechanism of action of finerenone is as a Mineralocorticoid Receptor Antagonist. Finerenone inhibits the effects of mineralocorticoids like aldosterone and cortisol when the MR is overactivated, possibly reducing inflammation and fibrosis in the heart and kidney.
References
Kolkhof, P., Hartmann, E., Freyberger, A., et al.Effects of finerenone combined with empagliflozin in a model of hypertension-induced end-organ damage. Am. J. Nephrol. 52(8), 642-652 (2021).
DOI: 10.1159/000516213
Cardiovascular Events with Finerenone in Kidney Disease and Type 2 Diabetes.
Properties of Finerenone
| Boiling point: | 554.7±50.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.29±0.1 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | -20°C |
| solubility | DMF: 10 mg/ml DMSO: 3 mg/ml Ethanol: insol PBS (pH 7.2): insol |
| form | solid |
| pka | 14.76±0.40(Predicted) |
| color | White to off-white |
| λmax | 255 nm |
| InChI | InChI=1S/C21H22N4O3/c1-5-28-21-18-17(14-7-6-13(9-22)8-15(14)27-4)16(20(23)26)12(3)25-19(18)11(2)10-24-21/h6-8,10,17,25H,5H2,1-4H3,(H2,23,26)/t17-/m1/s1 |
Safety information for Finerenone
Computed Descriptors for Finerenone
| InChIKey | BTBHLEZXCOBLCY-QGZVFWFLSA-N |
| SMILES | N1C2=C(C(OCC)=NC=C2C)[C@H](C2=CC=C(C#N)C=C2OC)C(C(N)=O)=C1C |
Finerenone manufacturer
Aquigen Bio science Pvt Ltd
SRINI PHARMACEUTICALS PVT LTD
New Products
Indole Methyl Resin tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Boc-His(Boc)-OH 2-CTC Resin 4-Chloro-7-tosy1-7Hpyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine 5,7-Dibromo-1H-indole 2,5-dichloro-N-hydroxy-4,6-dimethylpyridine-3-carboximidamide 2,2-Dimethoxy-7-azaspiro[3.5]nonane hydrochloride 4-chloromethyl-5-methyl-1,3-dioxol-2-one (DMDO-Cl) R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID 4-((2-hydroxyethyl)thio)benzoic acid 1-(TERT-BUTOXYCARBONYL)-2-PYRROLIDINONE Methyl 6-methylnicotinate 3-Pyridineacrylic acid tert-Butyl carbazate TETRAHYDRO-2H-PYRAN-3-OL 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 1,3-Diethyl-1,3-Diphenylurea Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylateYou may like
-
 1050477-31-0 Finerenone 98%View Details
1050477-31-0 Finerenone 98%View Details
1050477-31-0 -
 FINERENONE 98%View Details
FINERENONE 98%View Details -
 1050477-31-0 Finerenone 99%View Details
1050477-31-0 Finerenone 99%View Details
1050477-31-0 -
 Finerenone 98%View Details
Finerenone 98%View Details
1050477-31-0 -
 (4S)-4(4-cyano-2-methoxyphenyl)-5-ethoxy-1,4-dihydro-2,8-dimethyl-1,6- naphthyridine-3-caroxamide 1050477-31-0 98%View Details
(4S)-4(4-cyano-2-methoxyphenyl)-5-ethoxy-1,4-dihydro-2,8-dimethyl-1,6- naphthyridine-3-caroxamide 1050477-31-0 98%View Details
1050477-31-0 -
 Finerenone 98%View Details
Finerenone 98%View Details -
 Finerenone 97 %View Details
Finerenone 97 %View Details
1050477-31-0 -
 FinerenoneView Details
FinerenoneView Details
1050477-31-0
