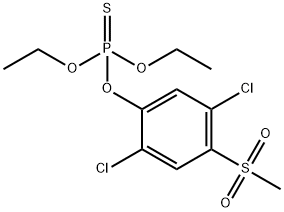
FENSULFOTHION
Synonym(s):Diethyl 4-(methylthio)phenyl phosphate
- CAS NO.:115-90-2
- Empirical Formula: C11H17O4PS2
- Molecular Weight: 308.35
- MDL number: MFCD00055487
- EINECS: 204-114-3
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-03-14 15:18:25
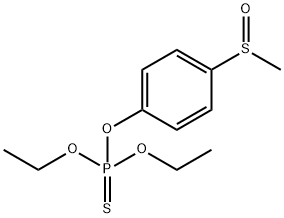
What is FENSULFOTHION?
Description
Fensulfothion is a systemic previously but not currently registered for insecticidal and nematicidal activity in the United States.
Chemical properties
Liquid.
Chemical properties
Fensulfothion is a yellow oil.
The Uses of FENSULFOTHION
Fensulfothion is a highly toxic insecticide used for agriculture purposes.
The Uses of FENSULFOTHION
Nematocide, insecticide.
The Uses of FENSULFOTHION
Nematocide and pesticide used to control free-living, cyst-forming and root-knot nematotodes and soil insects in vegetable and fruit crops.
Definition
ChEBI: Fensulfothion is an organic thiophosphate, a sulfoxide and an organothiophosphate insecticide. It has a role as an EC 3.1.1.7 (acetylcholinesterase) inhibitor, an agrochemical, an avicide and a nematicide. It is functionally related to a 4-(methylsulfinyl)phenol.
General Description
Oily yellow or brown liquid. Used as an insecticide, nematocide and mosquito larvicide.
Air & Water Reactions
Incompatible with alkali chemicals. Hydrolyzes in alkali, isomerize in air [EPA, 1998]. Slightly soluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
Organothiophosphates, such as FENSULFOTHION, are susceptible to formation of highly toxic and flammable phosphine gas in the presence of strong reducing agents such as hydrides. Partial oxidation by oxidizing agents may result in the release of toxic phosphorus oxides.
Hazard
Cholinesterase inhibitor. Questionable carcinogen.
Health Hazard
FENSULFOTHION displays cholinesterase inhibiting properties. Death results primarily from respiratory arrest stemming from failure of the respiratory center, paralysis of respiratory muscles and intense bronchoconstriction.
Fire Hazard
(Non-Specific -- Organophosphorus Pesticide, Liquid, n.o.s.) FENSULFOTHION may burn but may not ignite readily. Containers may explode in heat of fire. When heated highly toxic fumes of phosphorus and sulfur oxides are emitted. Incompatible with alkali chemicals. Hydrolyzes in alkali, isomerizes in air.
Safety Profile
A poison by ingestion, inhalation, and skin contact. Experimental reproductive effects. A pesticide. When heated to decomposition it emits very toxic fumes of SOx and POx.
Potential Exposure
A potential danger to those involved in the manufacture, formulation, or application of this insecticide used to control parasitic, sedentary, and freeliving nematodes.
First aid
If this chemical gets into the eyes, remove anycontact lenses at once and irrigate immediately for at least15 min, occasionally lifting upper and lower lids. Seek medical attention immediately. If this chemical contacts theskin, remove contaminated clothing and wash immediatelywith soap and water. Speed in removing material from skinis of extreme importance. Shampoo hair promptly if contaminated. Seek medical attention immediately. If thischemical has been inhaled, remove from exposure, beginrescue breathing (using universal precautions, includingresuscitation mask) if breathing has stopped and CPR ifheart action has stopped. Transfer promptly to a medicalfacility. When this chemical has been swallowed, get medical attention. Give large quantities of water and inducevomiting. Do not make an unconscious person vomit. Keepvictim quiet and maintain normal body temperature. Effectsmay be delayed; keep victim under observation.
Environmental Fate
Soil. In soils, the bacterium Klebsiella pneumoniae degraded fensulfothion to fensulfothion sul?de (Timms and MacRae, 1982, 1983). The following microorganisms were also capable of degrading the parent compound to the corresponding sul?de: Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas ?uorescens, Nocardia opaca, Lactobacillus plantarum and Leuconostoc mesenteroides (Timms and MacRae, 1983).
Plant. Readily oxidized in plants to the corresponding sulfone (Hartley and Kidd, 1987).
Chemical/Physical. Emits toxic fumes of phosphorus and sulfur oxides when heated to decomposition (Sax and Lewis, 1987; Lewis, 1990).
Isomerizes readily to the O,S-diethyl isomer (Worthing and Hance, 1991). The hydrolysis half-lives of fensulfothion in a sterile 1% ethanol/water solution at 25°C and pH values of 4.5, 6.0, 7.0 and 8.0, were 69, 77, 87 and 58 weeks, respectively (Chapman and Cole, 1982).
storage
Color Code—Blue: Health Hazard/Poison: Storein a secure poison location. Prior to working with thischemical you should be trained on its proper handlingand storage. Store in tightly closed containers in a cool,well-ventilated area away from strong bases; strong oxidizers. Where possible, automatically pump liquid fromdrums or other storage containers to process containers.
Shipping
UN3018 Organophosphorus pesticides, liquid, toxic, Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials. UN2810 Toxic liquids, organic, n.o.s., Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials, Technical Name Required
Incompatibilities
Incompatible with oxidizers (chlorates, nitrates, peroxides, permanganates, perchlorates, chlorine, bromine, fluorine, etc.); contact may cause fires or explosions. Keep away from alkaline materials, strong bases, strong acids, oxoacids, epoxides. Strong oxidizers may cause release of toxic phosphorus oxides. Organophosphates, in the presence of strong reducing agents such as hydrides, may form highly toxic and flammable phosphine gas. Keep away from alkaline materials.
Waste Disposal
Alkaline hydrolysis. In accordance with 40CFR165, follow recommendations for the disposal of pesticides and pesticide containers. Must be disposed properly by following package label directions or by contacting your local or federal environmental control agency, or by contacting your regional EPA office.
Properties of FENSULFOTHION
| Melting point: | 25°C |
| Boiling point: | bp0.01 138-141° |
| Density | 1.2020 |
| storage temp. | 0-6°C |
| solubility | Chloroform (Sparingly), Ethyl Acetate (Slightly), Methanol (Sparingly) |
| form | neat |
| Water Solubility | 1.54g/L(25 ºC) |
| Merck | 13,4028 |
| BRN | 2219515 |
| Exposure limits | ACGIH TLV: TWA 0.1 mg/m3 |
| Stability: | Hygroscopic, Moisture Sensitive |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 115-90-2 |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Fensulfothion (115-90-2) |
Safety information for FENSULFOTHION
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H410:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P262:Do not get in eyes, on skin, or on clothing. P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P273:Avoid release to the environment. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. |
Computed Descriptors for FENSULFOTHION
New Products
4-AMINO-TETRAHYDRO-PYRAN-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID HCL 4-(Dimethylamino)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-4-carbonitrile 4-AMINO-TETRAHYDRO-PYRAN-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID 4-Aminotetrahydropyran-4-carbonitrile Hydrochloride (R)-3-Aminobutanenitrile Hydrochloride 5-Bromo-2-nitropyridine Nimesulide BP Aceclofenac IP/BP/EP Diclofenac Sodium IP/BP/EP/USP Mefenamic Acid IP/BP/EP/USP Ornidazole IP Diclofenac Potassium 3-Bromopyrazole (3aR,4R,5R,6aS)-hexahydro-5-Triethyl silyloxy-4-((E)-3-oxo-5-phenylpent-1- enyl)cyclopenta[b]furan-2-one. 1-Chlorocarbonyl-4-piperidinopiperidine 1-Bromo-4-phenyl-2-Butanone 4-Amino-2-fluoro-N-methylbenzamide 1,1'-Carbonyldiimidazole SODIUM AAS SOLUTION ZINC AAS SOLUTION BUFFER SOLUTION PH 10.0(BORATE) GOOCH CRUCIBLE SINTERED AQUANIL 5 BERYLLIUM AAS SOLUTIONRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 Fensulfothion CAS 115-90-2View Details
Fensulfothion CAS 115-90-2View Details
115-90-2 -
![Dimethyl [2-oxo-3-[3-(trifluoromethyl)phenoxy]propyl]phosphonate 99%](https://img.chemicalbook.in//Content/image/CP5.jpg) Dimethyl [2-oxo-3-[3-(trifluoromethyl)phenoxy]propyl]phosphonate 99%View Details
Dimethyl [2-oxo-3-[3-(trifluoromethyl)phenoxy]propyl]phosphonate 99%View Details
54094-19-8 -
 85-81-4 99%View Details
85-81-4 99%View Details
85-81-4 -
![208111-98-2 (3aR,4R,5R,6aS)-5-(Benzoyloxy)hexahydro-4-[(1E)-3-oxo-4-[3-(trifluoromethyl)phenoxy]-1-buten- 1-yl]-2H-cyclopenta[b]furan-2-one 99%](https://img.chemicalbook.in//Content/image/CP5.jpg) 208111-98-2 (3aR,4R,5R,6aS)-5-(Benzoyloxy)hexahydro-4-[(1E)-3-oxo-4-[3-(trifluoromethyl)phenoxy]-1-buten- 1-yl]-2H-cyclopenta[b]furan-2-one 99%View Details
208111-98-2 (3aR,4R,5R,6aS)-5-(Benzoyloxy)hexahydro-4-[(1E)-3-oxo-4-[3-(trifluoromethyl)phenoxy]-1-buten- 1-yl]-2H-cyclopenta[b]furan-2-one 99%View Details
208111-98-2 -
 2033-24-1 99%View Details
2033-24-1 99%View Details
2033-24-1 -
 Meldrums acid 2033-24-1 99%View Details
Meldrums acid 2033-24-1 99%View Details
2033-24-1 -
 Cyaclopentane carboxylic acid 99%View Details
Cyaclopentane carboxylic acid 99%View Details
3400-45-1 -
 2-Aminopyridine 504-29-0 99%View Details
2-Aminopyridine 504-29-0 99%View Details
504-29-0