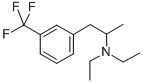
FENFLURAMINE
- CAS NO.:458-24-2
- Empirical Formula: C12H16F3N
- Molecular Weight: 231.26
- MDL number: MFCD00864474
- EINECS: 207-276-3
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-03-19 15:37:51
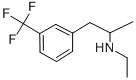
What is FENFLURAMINE?
Absorption
Fenfluramine has a steady-state Tmax of between four and five hours and an absolute bioavailability of approximately 68-74%. Fenfluramine administered to pediatric patients at 0.7 mg/kg/day up to 26 mg resulted in a mean Cmax of 68.0 ng/mL with a coefficient of variation of 41%; similarly the AUC0-24 was 1390 (44%) ng*h/mL.
Toxicity
Overdosage of fenfluramine has been reported; in overdose cases, symptoms include agitation, anxiety, restlessness, twitching, tremors/muscle spasms, flushing, tachycardia, mydriasis, increased muscle tone, respiratory distress/failure, seizure, and coma. Some overdosage cases proved fatal, and in most fatal cases, patients experienced seizures, coma, and cardiorespiratory arrest.
There is currently no standard practice for managing fenfluramine overdose. Symptomatic management, including ensuring proper ventilation and monitoring of both cardiac and respiratory functions is recommended.
Description
Fenfluramine is the only marketed anorectic agent that exerts its appetite depressant effect via a serotoninrgic mechanism. Its major metabolite, norfenfluramine, is believed to be the main active form in humans .
Originator
Obenon,Neofarma
The Uses of FENFLURAMINE
Anorexic.
Background
Dravet syndrome is a pediatric encephalopathy that typically manifests within the first year of life following exposure to elevated temperatures. It is characterized by recurrent pharmacoresistant seizures, which increase in frequency and severity with disease progression. Concomitantly with these seizures, patients typically display delayed development and neurocognitive impairment. Fenfluramine is a serotonergic phenethylamine originally used as an appetite suppressant until concerns regarding cardiotoxicity in obese patients lead to its withdrawal from the market in 1997. Through its ability to modulate neurotransmission, fenfluramine has reemerged as an effective therapy against pharmacoresistant seizures, such as those involved in Dravet syndrome.
Fenfluramine was granted initial FDA approval in 1973 prior to its withdrawal; it was granted a new FDA approval on June 25, 2020, for treatment of patients with Dravet syndrome and Lennox-Gastaut syndrome through the restricted FINTEPLA REMS program. It is currently sold under the name FINTEPLA? by Zogenix INC.
Indications
Fenfluramine is indicated for the treatment of seizures associated with Dravet syndrome and Lennox-Gastaut syndrome in patients aged two years and older.
Definition
ChEBI: A secondary amino compound that is 1-phenyl-propan-2-amine in which one of the meta-hydrogens is substituted by trifluoromethyl, and one of the hydrogens attached to the nitrogen is substituted by an ethyl group. It binds to the serotonin reu take pump, causing inhbition of serotonin uptake and release of serotonin. The resulting increased levels of serotonin lead to greater serotonin receptor activation which in turn lead to enhancement of serotoninergic transmission in the centres of feeding ehavior located in the hypothalamus. This suppresses the appetite for carbohydrates. Fenfluramine was used as the hydrochloride for treatment of diabetes and obesity. It was withdrawn worldwide after reports of heart valve disease and pulmonary hypertensio .
Manufacturing Process
38.5 parts of (trifluoromethyl-3'-phenyl)-1-oximino-2-propane in 550 parts of ethanol (with ammonia) was hydrogenated under pressure of hydrogen 90 kg with a catalyst nickel Reney (20 parts). After a completion of reaction to the reaction mixture was added 1000 parts of water and 300 parts of hydrochloric acid. The mixture was concentrated in vacuo and extracted with 450 parts of ether. To an aqueous phase was added the sodium carbonate and the mixture was extracted with 500 parts of ether. Organic phase was concentrated in vacuo to obtain 29 g of 1-(meta-trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-2-ethylaminopropane. B.P. 96°C at 17 mm.
brand name
Pondimin (Robins).
Therapeutic Function
Anorexic
World Health Organization (WHO)
Fenfluramine, dexfenfluramine and phentermine were approved individually more than 20 years ago in the USA for single-drug, short-term treatment of obesity. The manufacturers of fenfluramine and dexfenfluramine have since voluntarily withdrawn both products from the market worldwide. Phentermine remains available.
Pharmacokinetics
Fenfluramine increases extracellular serotonin levels, and also acts as both a serotonergic 5-HT2 receptor agonist and σ1 receptor antagonist. These activities, through an incompletely understood mechanism, lead to anti-epileptiform activity and therapeutic benefit. This modulation has other effects such as decreased appetite, weight loss, sedation, lethargy, increased blood pressure, and mood alteration including possible suicidal ideation. There is a risk of glaucoma and potentially fatal serotonin syndrome. Fenfluramine should be gradually withdrawn following treatment alteration or cessation.
Synthesis
Fenfluramine is prepared by reductive alkylation
of norfenfluramine with acetaldehyde .
The nor compound is obtained by catalytic
hydrogenation of the oxime made from 3-trifluoromethlyphenyl
acetone (Eq. 2).
Metabolism
Fenfluramine is metabolized primarily in the liver by CYP1A2, CYP2B6, CYP2D6, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, and CYP3A4/5 to yield the major active metabolite norfenfluramine and several other minor inactive metabolites.
Properties of FENFLURAMINE
| Melting point: | 170°C |
| Boiling point: | bp12 108-112° |
| Density | 1.0950 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | -20°C |
| solubility | Chloroform (Slightly), Methanol (Slightly) |
| pka | pKa 9.10 (Uncertain) |
| form | Oil |
| color | Colourless to Pale Yellow |
| Stability: | Hygroscopic |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 458-24-2 |
Safety information for FENFLURAMINE
Computed Descriptors for FENFLURAMINE
Related products of tetrahydrofuran




You may like
-
 37951-47-6 3'-Benzyloxy propiophenone, 98% 99%View Details
37951-47-6 3'-Benzyloxy propiophenone, 98% 99%View Details
37951-47-6 -
 99-30-9 99%View Details
99-30-9 99%View Details
99-30-9 -
 104944-18-5 99%View Details
104944-18-5 99%View Details
104944-18-5 -
 3'-Methoxypropiophenone, 99% 37951-49-8 99%View Details
3'-Methoxypropiophenone, 99% 37951-49-8 99%View Details
37951-49-8 -
 98-56-6 99%View Details
98-56-6 99%View Details
98-56-6 -
 694-48-4 99%View Details
694-48-4 99%View Details
694-48-4 -
 51364-51-3 99%View Details
51364-51-3 99%View Details
51364-51-3 -
 Methyl chloroacetate, 98% 96-34-4 99%View Details
Methyl chloroacetate, 98% 96-34-4 99%View Details
96-34-4