Evogliptin
- CAS NO.:1222102-29-5
- Empirical Formula: C19H26F3N3O3
- Molecular Weight: 401.42
- MDL number: MFCD28502041
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-10-28 23:16:16
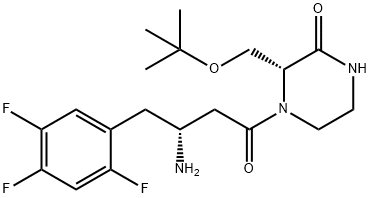
What is Evogliptin?
Description
Developed by Dong-A ST, evogliptin was approved in 2015 in the Republic of Korea for blood glucose control in patients with diabetes mellitus type 2 (type 2 DM). Evogliptin is an orally bioavailable dipeptidyl peptidase IV (DPP-4) inhibitor, which acts to prevent insulin secretion following meals. Dong-A ST arranged licensing agreements with Geropharm and Eurofarma Laboratórios for the sale of evogliptin in various countries in eastern Europe and Brazil, respectively, pending future approvals. While a manufacturing route has not been disclosed to date, the most scalable published route is described below.
The Uses of Evogliptin
ent-Evogliptin L-tartrate Salt is enantiomer of Evogliptin (CAS 1222102-29-5) parent compound, which is a dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitor for the treatment of type 2 diabetes.
Synthesis
The synthesis of piperizone 125 began from commercially
available amino acid derivative 127 . The alcohol
within 125 was then quantitatively converted to tert-butyl ether
128 by treatment with isobutylene gas in the presence of acid.
Subsequent hydrogenation to remove the Cbz protecting group
resulted in amine 129, and this was followed by reductive
amination to provide ethylene diamine intermediate 130.
Hydrogenative carbamate removal facilitated a cyclization
reaction, giving rise to piperizone 131 as the free base. Finally,
treatment with a tartaric acid derivative delivered the stable
piperizone salt 125.
The second key synthon of evogliptin is the |?-amino acid
fragment 136.
Commercially available acid 132 was treated with CDI prior to
subjection to Meldrum?ˉs acid to afford ketodiester 133.
Subjection of 133 to warm EtOH triggered a decarboxylation
event, and this was followed by reductive amination reaction
involving ammonium acetate and the remaining ketone
functionality to afford racemic amine 134 in 91% over the
three steps. Resolution with a tartaric acid derivative followed
by free base formation with sodium carbonate gave the
enantiopure aminoester 135 in good yield. Finally, a two-step
Boc protection followed by ester saponification furnished
aminoester 136 in 89% yield over the final two-step sequence,
setting the stage for the final assembly of evogliptin.
The final API was assembled in a straightforward manner
from intermediates 125 and 136. Acid 136 was
first activated as the mixed anhydride, followed by the addition
of 125 in the presence of Hünig?ˉs base to give penultimate
product 137 in 71% over two steps. Hydrogenolytic removal of the benzyl carbamate afforded evogliptin (XVI), with a longest
linear sequence of eight steps from simple amino acid building
blocks.

Properties of Evogliptin
| Boiling point: | 571.5±50.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.234±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| pka | 14.09±0.40(Predicted) |
Safety information for Evogliptin
Computed Descriptors for Evogliptin
Abamectin manufacturer
New Products
4-AMINO-TETRAHYDRO-PYRAN-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID HCL 4-(Dimethylamino)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-4-carbonitrile 4-Aminotetrahydropyran-4-carbonitrile Hydrochloride (R)-3-Aminobutanenitrile Hydrochloride 3-((Dimethylamino)methyl)-5-methylhexan-2-one oxalate 1,4-Dioxa-8-azaspiro[4.5]decane 5-Bromo-2-nitropyridine Nimesulide BP Aceclofenac IP/BP/EP Diclofenac Sodium IP/BP/EP/USP Mefenamic Acid IP/BP/EP/USP Ornidazole IP Diclofenac Potassium THOMAIND PAPER PH 2.0 TO 4.5 1 BOX BUFFER CAPSULE PH 9.2 - 10 CAP SODIUM CHLORIDE 0.1N CVS ALLOXAN MONOHYDRATE 98% PLATINUM 0.5% ON 3 MM ALUMINA PELLETS (TYPE 73) LITHIUM AAS SOLUTION 2-Bromo-1-(bromomethyl)-3-chloro-5-nitrobenzene 2-Bromo-3-nitroaniline N-(3-Hydroxypropyl)-N-methylacetamide 3-Bromo-6-chloropyridazine 4-ethyl-3-nitrobenzoic acidYou may like
-
 Evogliptin 98%View Details
Evogliptin 98%View Details -
 1-Methyl-6-oxo-1,6-dihydropyridazine-3-carbonitrile 98%View Details
1-Methyl-6-oxo-1,6-dihydropyridazine-3-carbonitrile 98%View Details
99903-60-3 -
 1823368-42-8 98%View Details
1823368-42-8 98%View Details
1823368-42-8 -
 2-(3-(tert-butyl)phenoxy)-2-methylpropanoic acid 1307449-08-6 98%View Details
2-(3-(tert-butyl)phenoxy)-2-methylpropanoic acid 1307449-08-6 98%View Details
1307449-08-6 -
 Ethyl 3-(furan-2-yl)-3-hydroxypropanoate 25408-95-1 98%View Details
Ethyl 3-(furan-2-yl)-3-hydroxypropanoate 25408-95-1 98%View Details
25408-95-1 -
 2-Chloro-5-fluoro-1-methoxy-3-methylbenzene 98%View Details
2-Chloro-5-fluoro-1-methoxy-3-methylbenzene 98%View Details
1805639-70-6 -
 1784294-80-9 98%View Details
1784294-80-9 98%View Details
1784294-80-9 -
 Lithium ClavulanateView Details
Lithium ClavulanateView Details
61177-44-4