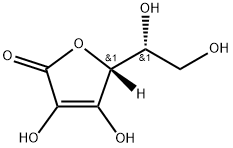
Erythorbic Acid
Synonym(s):Erythorbic acid;Glucosaccharonic acid;D- (?)-Isoascorbic acid;D -(?)-Isoascorbic acid;D -erythro-Hex-2-enoic acid γ-lactone
- CAS NO.:89-65-6
- Empirical Formula: C6H8O6
- Molecular Weight: 176.12
- MDL number: MFCD00005378
- EINECS: 201-928-0
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-17 09:49:40
What is Erythorbic Acid?
Chemical properties
Erythorbic acid occurs as a white or slightly yellow-colored crystals or powder. It gradually darkens in color upon exposure to light.
The Uses of Erythorbic Acid
Erythorbic Acid is a food preservative that is a strong reducing agent (oxygen accepting) which functions similarly to antioxidants. In the dry crystalline state it is nonreactive, but in water solutions it reacts readily with atmospheric oxygen and other oxidizing agents, making it valuable as an antioxidant. During preparation, dissolving and mixing should incorporate a minimum amount of air, and storage should be at cool temperatures. It has a solubility of 43 g/100 ml of water at 25°c. One part is equivalent to one part ascorbic acid and equivalent to one part sodium erythorbate. It is used to control oxidative color and flavor deterioration in fruits at 150–200 ppm. It is used in meat curing to speed and control the nitrite curing reaction and prolong the color of cured meat at levels of 0.05%.
The Uses of Erythorbic Acid
Antioxidant (industrial and food), especially in brewing industry, reducing agent in photography.
The Uses of Erythorbic Acid
Erythorbic Acid is used as a food additive as an antimicrobial and antioxidative agent.
Production Methods
Erythorbic acid is synthesized by the reaction between methyl 2- keto-D-gluconate and sodium methoxide. It can also be synthesized from sucrose, and produced from Penicillium spp.
Definition
ChEBI: D-isoascorbic acid is an ascorbic acid.
Biotechnological Production
Yeasts and other fungi synthesize the C5 sugar acid D-erythroascorbic acid which shares structural and physicochemical properties with Asc. D-erythroascorbic acid serves similar protective functions in these microorganisms as Asc does in plants and animals, including the scavenging of reactive oxygen species. The biosynthesis of D-erythroascorbic acid starts from D-arabinose obtained by the microorganism from decaying plant material. D-arabinose, presumably in its 1,4-furanosidic isomeric form, is oxidized by NAD(P)+ specific dehydrogenases to D-arabinono-1,4-lactone, which is further oxidized to D-erythroascorbic acid by D-arabinono-1,4-lactone oxidase. Resting cells of Saccharomyces cerevisiae can synthesize Asc from L-galactose, L-galactono-1,4-lactone, or L-gulono- 1,4-lactone via the pathway naturally used for D-erythroascorbic acid.
Flammability and Explosibility
Non flammable
Pharmaceutical Applications
Erythorbic acid is a stereoisomer of L-ascorbic acid, and is used as an antioxidant in foods and oral pharmaceutical formulations. It has approximately 5% of the vitamin C activity of L-ascorbic acid.
Safety
Erythorbic acid is widely used in food applications as an
antioxidant. It is also used in oral pharmaceutical applications as
an antioxidant. Erythorbic acid is generally regarded as nontoxic
and nonirritant when used as an excipient. Erythorbic acid is readily
metabolized and does not affect the urinary excretion of ascorbic
acid.
The WHO has set an acceptable daily intake of erythorbic acid
and its sodium salt in foods at up to 5 mg/kg body-weight.
Solubility in organics
40% soluble in water. Soluble in alcohol, slightly soluble in Glycerin and Propylene glycol.
Storage
Erythorbic acid should be stored in an airtight container, protected from light, in a cool, dry place.
Purification Methods
Crystallise D(-)-isoascorbic acid from H2O, EtOH or dioxane. is at 245nm with 7,500 (EtOH). [Reichstein et al. Helv max Chim Acta 17 510, 516 1934, Heslop et al. J Chem Soc 225 1944, Beilstein 18 III/IV 3037, 18/5 V 26.]
Incompatibilities
Erythorbic acid is incompatible with chemically active metals such as aluminum, copper, magnesium, and zinc. It is also incompatible with strong bases and strong oxidizing agents.
Regulatory Status
GRAS listed. Accepted for use as a food additive in Europe. Included in the FDA Inactive Ingredients Database (oral concentrate and tablets).
Properties of Erythorbic Acid
| Melting point: | 169-172 °C (dec.) (lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 227.71°C (rough estimate) |
| alpha | -17.25 º (c=10, H2O 25 ºC) |
| Density | 1.3744 (rough estimate) |
| vapor pressure | 0Pa at 25℃ |
| refractive index | -17.5 ° (C=10, H2O) |
| FEMA | 2410 | ERYTHROBIC ACID |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | H2O: 0.1 g/mL, clear, colorless to very faintly yellow |
| form | Crystals or Crystalline Powder |
| pka | 4.09±0.10(Predicted) |
| color | White to slightly yellow |
| Odor | odorless |
| optical activity | [α]25/D 16.8°, c = 2 in H2O |
| Water Solubility | 1g/10mL |
| Merck | 14,5126 |
| BRN | 84271 |
| Stability: | Stable. Combustible. Incompatible with chemically active metals, aluminium, zinc, copper, magnesium, strong bases, strong oxidizing agents. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 89-65-6(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Isoascorbic acid (89-65-6) |
Safety information for Erythorbic Acid
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Erythorbic Acid
| InChIKey | CIWBSHSKHKDKBQ-JLAZNSOCSA-N |
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran



You may like
-
 89-65-6 99%View Details
89-65-6 99%View Details
89-65-6 -
 D-(-)-Isoascorbic acid CAS 89-65-6View Details
D-(-)-Isoascorbic acid CAS 89-65-6View Details
89-65-6 -
 D-(-)-Isoascorbic acid CAS 89-65-6View Details
D-(-)-Isoascorbic acid CAS 89-65-6View Details
89-65-6 -
 D-Araboascorbic acid, 98% CAS 89-65-6View Details
D-Araboascorbic acid, 98% CAS 89-65-6View Details
89-65-6 -
 D-Isoascorbic acid 97 - 102% CAS 89-65-6View Details
D-Isoascorbic acid 97 - 102% CAS 89-65-6View Details
89-65-6 -
 D-Araboascorbic Acid CAS 89-65-6View Details
D-Araboascorbic Acid CAS 89-65-6View Details
89-65-6 -
 D-Araboascorbic acid 95% CAS 89-65-6View Details
D-Araboascorbic acid 95% CAS 89-65-6View Details
89-65-6 -
 Erythorbic acid CAS 89-65-6View Details
Erythorbic acid CAS 89-65-6View Details
89-65-6
