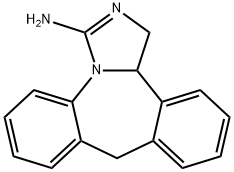
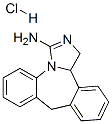
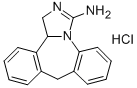
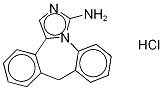
Epinastine
- CAS NO.:80012-43-7
- Empirical Formula: C16H15N3
- Molecular Weight: 249.31
- MDL number: MFCD00865648
- EINECS: 616-785-3
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-10-23 15:23:57
What is Epinastine?
Absorption
The absolute bioavailability of epinastine is about 40%.
Description
Epinastine hydrochloride, an orally active antihistaminic agent, was marketed in Japan for the treatment of bronchial asthma, allergic rhinitis, urticaria, eczema, dermatitis, and psoriasis vulgaris.Epinastine is one of the most effective peripherally acting histamine H1-receptor antagonists without sedative effects.In addition, it exhibits potent anti-PAF and anti-LT activity which may also contribute significantly to its antiallergic activity. Chronic epinastine has been reported to effectively inhibit airway hyper-responsiveness in rats. Potent inhibitory effects of epinastine on bronchoconstriction induced by histamine and bradykinin, but not by other chemical mediators, has also been reported. Studies have indicated that there are no significant differences in pharmacological properties among D-, L-, and racemic epinastine.
Originator
Boehringer lngelheim (Germany)
The Uses of Epinastine
Epinastine is antihistamine and mast cell stabilize that is used in eye drops for the treatment of allergic conjunctivitis.
Indications
For the prevention of itching associated with allergic conjunctivitis.
Background
Epinastine is used for the prevention of itching associated with allergic conjunctivitis. It has a multi-action effect that inhibits the allergic response in 3 ways: 1. stabilizes mast cells by preventing mast cell degranulation to control the allergic response, 2. prevents histamine binding to both the H1- and H2-receptors to stop itching and provide lasting protection, and 3. prevents the release of proinflammatory chemical mediators from the blood vessel to halt progression of the allergic response.
What are the applications of Application
Epinastine is an antihistamine and mast cell stabilizer
Definition
ChEBI: A benzazepine that is 6,11-dihydro-5H-dibenzo[b,e]azepine in which the azepine ring is fused to the e side of 4,5-dihydro-1H-imidazol-2-amine.
brand name
Aleslon
Pharmacokinetics
Epinastine is an antihistamine and an inhibitor of histamine release from the mast cell for topical administration to the eyes. Epinastine is indicated for the prevention of itching associated with allergic conjunctivitis. Epinastine is a topically active, direct H1-receptor antagonist and an inhibitor of the release of histamine from the mast cell. Epinastine is selective for the histamine H1-receptor and has affinity for the histamine H2 receptor. Epinastine also possesses affinity for the a1-, a2-, and 5-HT2 -receptors. Epinastine does not penetrate the blood/brain barrier and, therefore, is not expected to induce side effects of the central nervous system.
Clinical Use
Epinastine is a potent, long-acting H1 antihistamine and an inhibitor of the release of histamine and other transmitters from mast cells. It has some affinity for H2 receptors as well. It is used as an eye drop for allergic conjunctivitis. It does not penetrate into the CNS and is classified as a nonsedating antihistamine.
Synthesis
Several patents on the synthesis of
epinastin (VIII) have appeared in Europe and Japan.
The synthesis described below is taken partly from the US
patent and a Japanese patent. All the syntheses
utilized 6-aminomethyl-6,11-dihydro-5H-dibenzo[b.e]azepine
(80) as the key intermediate which was converted to the final
guanidine epinastine by reacting with cyanogen bromide.
The solution of 80 in ethanol was treated with a solution of
cyanogen bromide in THF at room temperature and stirred
overnight. The hydrobromide salt was collected in 79%
yield after adding ether to the reaction mixture. The salt was
free based with a solution of sodium hydroxide and then
treated with an ethereal solution of HCl to obtain the
epinastine hydrochloride salt VIII. For the preparation of the
key intermediate, chloroimine 78, presumably obtained from
ketone 77 via Beckmann rearrangement, was reacted
with sodium cyanide in DMSO to give the nitrile 79 in 70%
yield. Reduction of the imino nitrile was carried out in THF
in the presence of an acid with LAH to give the key
intermediate 80 in 67% yield.
An alternate approach to preparation of 80 is shown in
Scheme 8 as well. Reaction of the commercially available
chloride 81 with phthalimide in the presence of a
base gave the phthalimide 82. Reduction of the imine with
sodium borohydride gave 83, which was then reacted with
hydrazine hydrate to free up the amine in 90% yield. The
amine intermediate was isolated as the fumarate salt.

Metabolism
Mainly excreted unchanged, less than 10% metabolized.
Properties of Epinastine
| Melting point: | 205-208° |
| Boiling point: | 428.0±55.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.32±0.1 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | Keep in dark place,Inert atmosphere,Room temperature |
| solubility | DMSO : ≥ 50 mg/mL (200.55 mM);Water : < 0.1 mg/mL (insoluble) |
| pka | 11.2(at 25℃) |
| form | Solid |
| color | White to off-white |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 80012-43-7(CAS DataBase Reference) |
Safety information for Epinastine
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07  Health Hazard GHS08  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral H372:Specific target organ toxicity, repeated exposure H411:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P273:Avoid release to the environment. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. |
Computed Descriptors for Epinastine
Epinastine manufacturer
New Products
Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate (S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL N-octanoyl benzotriazole 3,4-Dibenzyloxybenzaldehyde 4-Hydrazinobenzoic acid 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 4-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 4-(3-chloropropyl)morpholine phenylhydrazine hydrochloride (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5-BROMO-2CYANO PYRIDINE 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 80012-43-7 Epinastine 98%View Details
80012-43-7 Epinastine 98%View Details
80012-43-7 -
 Epinastine 95.00% CAS 80012-43-7View Details
Epinastine 95.00% CAS 80012-43-7View Details
80012-43-7 -
 (9H-fluoren-9-yl)methyl (2,5-dioxopyrrolidin-1-yl) carbonate 82911-69-1 98.0%View Details
(9H-fluoren-9-yl)methyl (2,5-dioxopyrrolidin-1-yl) carbonate 82911-69-1 98.0%View Details
82911-69-1 -
 13057-17-5 95.0%View Details
13057-17-5 95.0%View Details
13057-17-5 -
 4-bromoaniline 106-40-1 99.0%View Details
4-bromoaniline 106-40-1 99.0%View Details
106-40-1 -
 1421517-99-8 99.0%View Details
1421517-99-8 99.0%View Details
1421517-99-8 -
 5-bromo-2-chlorobenzoic acid 99.0%View Details
5-bromo-2-chlorobenzoic acid 99.0%View Details
21739-92-4 -
 15761-38-3 97.0%View Details
15761-38-3 97.0%View Details
15761-38-3