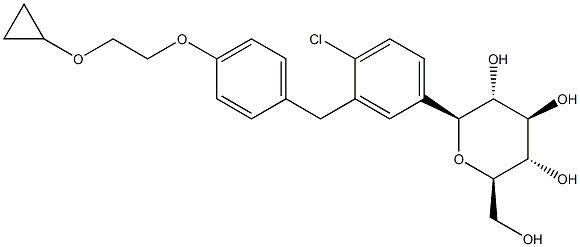
Bexagliflozin
- CAS NO.:1118567-05-7
- Empirical Formula: C24H29ClO7
- Molecular Weight: 464.94
- MDL number: MFCD28100944
- EINECS: 257-874-6
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-18 14:26:18
What is Bexagliflozin?
Absorption
Healthy subjects and adult patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus given bexagliflozin have similar pharmacokinetic profiles. In a fasted state, the mean Cmax and AUC0-∞ of bexagliflozin were 134 ng/mL and 1,162 ng·h/mL, respectively. Bexagliflozin does not follow a time-dependent pharmacokinetic profile, and after multiple doses, approximately up to 20% is accumulated in plasma. The peak plasma concentration of bexagliflozin is reached between 2 and 4 hours after oral administration. This timing can be delayed if bexagliflozin is taken after a meal or with medications that slow gastric emptying. Between single doses of 3 mg and 90 mg (0.15 to 4.5 times the recommended dose), the plasma Cmax and AUC of bexagliflozin increase in a dose-proportional manner.
Compared to dosing in the fasted state, consuming a standard high-fat, high-caloric meal leads to a 31% and 10% higher Cmax and AUC, respectively. Under these conditions, the median Tmax was increased to 5 hours. The effects of food on bexagliflozin pharmacokinetics are not considered clinically relevant.
Toxicity
In case of a bexagliflozin overdose, the FDA product label recommends contacting the Poison Help line or a medical toxicologist for additional overdosage management recommendations. Usual supportive measures based on the patient’s clinical status should be employed. The removal of bexagliflozin by hemodialysis has not been evaluated. Carcinogenicity was evaluated in mice and rats, and no drug-related neoplastic findings were reported at up to the highest doses, which corresponded to 156 times (mice) and 68 times (rats) the clinical dose of bexagliflozin (20 mg) based on AUC. In vitro and in vivo studies found that bexagliflozin was not mutagenic or clastogenic. Fertility studies done in male and female rats showed that bexagliflozin had no effects on mating, fertility or early embryonic development at up to 200 mg/kg/day, which corresponded to 280 and 439 times the clinical dose of bexagliflozin in males and females, respectively.
Description
EGT-1442 is a potent, selective sodium glucose co-transporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitor with IC50 values of 5.6 μM and 2 nM for human SGLT1 and SGLT2, respectively. It produces a stable urinary excretion of glucose in rats and dogs with ED50 values of 0.38 and 0.09 mg/kg, respectively, and reduces HbA(1c) and blood glucose in db/db mice in a concentration dependent manner.
The Uses of Bexagliflozin
Bexagliflozin, also known as EGT1442, is a potent and selective SGLT2 inhibitor, attenuates blood glucose and HbA(1c) levels in db/db mice and prolongs the survival of stroke-prone rats. EGT1442 showed favorable properties both in vitro and in vivo and could be beneficial to the management of type 2 diabetic patients.
Background
Bexagliflozin is a highly specific and potent sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitor. Similar to other SGLT2 inhibitors, bexagliflozin contains three basic moieties: glucose, two benzene rings and a methylene bridge. SGLT2 is responsible for 60% to 90% of renal glucose re-uptake, and unlike other isoforms such as SGLT1, SGLT2 is mainly expressed in the kidney. By inhibiting SGLT2, bexagliflozin reduces renal reabsorption of filtered glucose and increases urinary glucose excretion, which reduces blood glucose levels independently of insulin sensitivity. In January 2023, bexagliflozin was approved by the FDA for the treatment of adults with type 2 diabetes. Its use is not recommended in patients with type 1 diabetes since it may increase their risk of diabetic ketoacidosis.
Indications
Bexagliflozin is indicated as an adjunct to diet and exercise to improve glycemic control in adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Definition
ChEBI: Bexagliflozin is a C-glycosyl comprising of beta-D-glucose in which the anomeric hydroxy group is replaced by a 4-chloro-3-({4-[2-(cyclopropyloxy)ethoxy]phenyl}methyl)phenyl group. It is a sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitor indicated as an adjunct to diet and exercise to improve glycemic control in adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus. It has a role as a sodium-glucose transport protein subtype 2 inhibitor, a hypoglycemic agent and an antihypertensive agent. It is a C-glycosyl compound, an aromatic ether, a member of monochlorobenzenes, a diether and a member of cyclopropanes.
Mechanism of action
Bexagliflozin is a highly selective inhibitor of sodium-glucose cotransporter protein 2 (SGLT2), which cotransports sodium and glucose from the filtrate to the epithelium of the proximal renal tubule, thereby lowering the tubular glucose reabsorption threshold, reducing renal glucose reabsorption, and increasing urinary glucose excretion without affecting insulin levels.
Pharmacokinetics
Healthy subjects and adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus given single or multiple doses of bexagliflozin had dose-dependent increases in urinary glucose excretion (UGE) accompanied by increases in urine volume. A 20 mg bexagliflozin dose can provide near-maximal UGE, and elevated UGE values are maintained with multiple-dose administration. Bexagliflozin does not cause clinically significant QTc interval prolongation at 5 times the recommended dose.
The use of bexagliflozin may cause ketoacidosis, volume depletion, urosepsis, pyelonephritis, necrotizing fasciitis of the perineum and genital mycotic infections. There is also an increased incidence of lower limb amputation in patients treated with bexagliflozin compared to those receiving a placebo. In addition, the use of bexagliflozin in patients treated with insulin and insulin secretagogues may increase the risk of hypoglycemia.
Metabolism
Bexagliflozin is metabolized in the liver mainly by UGT1A9 and, to a lesser extent, CYP3A. In healthy volunteers given an oral [14C]-bexagliflozin solution, the 3'-O-glucuronide, a pharmacologically inactive metabolite, constituted 32.2% of the parent compound AUC. The rest of the bexagliflozin metabolites contributed less than 10% of the parent AUC. None of the metabolites are expected to have clinically relevant pharmacological effects.
Properties of Bexagliflozin
| Boiling point: | 671.0±55.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.41 |
| storage temp. | Store at -20°C |
| solubility | DMSO:100.0(Max Conc. mg/mL);215.08(Max Conc. mM) |
| form | A crystalline solid |
| pka | 13.23±0.70(Predicted) |
Safety information for Bexagliflozin
Computed Descriptors for Bexagliflozin
| InChIKey | BTCRKOKVYTVOLU-IZSIRFNDNA-N |
| SMILES | [C@H]1(C2C=C(CC3C=CC(OCCOC4CC4)=CC=3)C(Cl)=CC=2)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](CO)O1 |&1:0,22,24,26,28,r| |
Bexagliflozin manufacturer
SRINI PHARMACEUTICALS PVT LTD
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidYou may like
-
 Bexagliflozin 98%View Details
Bexagliflozin 98%View Details -
 1118567-05-7 98%View Details
1118567-05-7 98%View Details
1118567-05-7 -
 3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 614-19-7 98%View Details
614-19-7 98%View Details
614-19-7 -
 20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 -
 3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 -
 4,6-dichloropyrimidine-5-carbaldehyde 98%View Details
4,6-dichloropyrimidine-5-carbaldehyde 98%View Details
5305-40-8
